You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: FUN_008351-T1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: FUN_008351-T1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
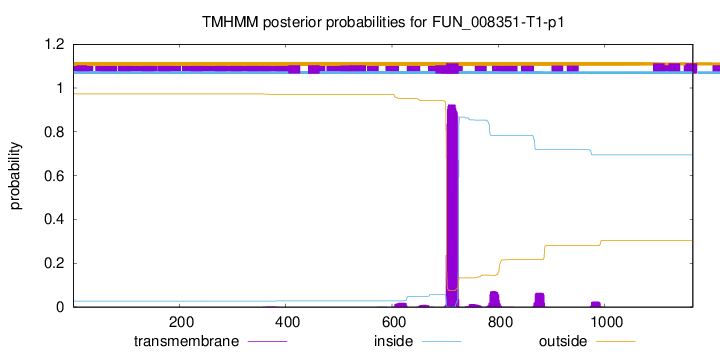
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Rhizophagus irregularis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Mucoromycota; Glomeromycetes; ; Glomeraceae; Rhizophagus; Rhizophagus irregularis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | FUN_008351-T1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH15 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 3466078; End:3470288 Strand: - | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MDPKKSIPNP KRKRNNEELL INKKVKNSNV ENVPSTSINS KNNVTSGIIN KKATTKTRKI | 60 |
| PFNNIVNDTK RFTALPVPKK IIPRPSGKAN VKASGKSVNY GRTVTKSCPI KPLKLVTKSM | 120 |
| TEKNRSRAGI LESKQRLQLV TKSMTERSRS RAGILESKMQ LAKSRREMIE IKKRNEAIRS | 180 |
| RISKIRDDLV RVENEHETLF KSIEQMKKQT ATYNEEMKKL NEHCDVANEE SNKLSEIILE | 240 |
| SRKGLELRNN KIIEKRLLYE YQLKQIQEIY AGLKAEENTR KDLHNQNLDL MGNIRVMCRV | 300 |
| RPYTDKEKEI EQVSLECFDD KHTIQVSTKR LRLWQMQIEK STYEFDHVFN TSADQKEVYL | 360 |
| ELSPLVQSAI DGYNVCIFAY GQTGSGKTYT MEGNVNSPEK KGVIPRSIDE IFDKIEETNK | 420 |
| LGWNFEVYVQ YIEIYNETIQ DLLIDEDKDR KKSCKDRKKS FKEDRKKSFK ESKDLCKIVY | 480 |
| NEDTRMTIIE NAERLKISKK KDMEILIDKA SNHRSKSSTN SNSVSSRSHG VFILHLEGEN | 540 |
| PLEKMSSRGS LSLVDLAGSE NIDKSGSVGD QMTEAQSINK SLFYLRYVIQ QIKDKSNHVN | 600 |
| YRDSVLTSLL KYSLGGTAKV CMLVNVSPST DSTNETKKSL SFGQDARKAH VGTAMRNGPV | 660 |
| IFGNVKKYYF QKVISIMAKY EPLSTSESSS EPQIKRGSQL KALIIILFFV VFISVWNIIP | 720 |
| SYFYLEDTAN NIDQTDQIPI EKTTLAIPTA VQTTSISSTL SPTSTSVTTP VKEPKPPMSE | 780 |
| SGKVIAAYFA SWSIYARAYN VIDIDSDKVT HILYAFANIK PDGEVFLGDS WADTDKHFEG | 840 |
| DSWNDEKKNL YGNFKQLGLL KKKKKHFKVS LSIGGWSWST NFPSVASKSD SRKKFVTSSI | 900 |
| ELLKDLGLDG LDIDWEYPQN EGDAKNYVKL LKELREALDE YSESQNHSHK LLLTAALPCG | 960 |
| EEQYKKMKLK DMNKYLDLFY LMAYDFSGSW SSKASHQSNL YGSDLSTHKA VDYYINKGVD | 1020 |
| EDKIVIGMPM YGRAFQNTNG FGSSYNGVGE GTWEQGVYDY KKLPRQNATE HFDEKAIASY | 1080 |
| SYSASDREFV TYDNPQVIIH KTDYVKHNNL RGVMFWELSG DFPTSHERSL LSAAYHGLGG | 1140 |
| KDAIDQTPNH RSFPDSIYEN VRNGFE | 1166 |
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.14:25 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH18 | 783 | 1126 | 4.3e-84 | 0.9527027027027027 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 276817 | KISc_C_terminal | 1.74e-109 | 291 | 647 | 1 | 325 | Kinesin motor domain, KIFC2/KIFC3/ncd-like carboxy-terminal kinesins. Kinesin motor domain, KIFC2/KIFC3/ncd-like carboxy-terminal kinesins. Ncd is a spindle motor protein necessary for chromosome segregation in meiosis. KIFC2/KIFC3-like kinesins have been implicated in motility of the Golgi apparatus as well as dentritic and axonal transport in neurons. This catalytic (head) domain has ATPase activity and belongs to the larger group of P-loop NTPases. Kinesins are microtubule-dependent molecular motors that play important roles in intracellular transport and in cell division. In this subgroup the motor domain is found at the C-terminus (C-type). C-type kinesins are (-) end-directed motors, i.e. they transport cargo towards the (-) end of the microtubule. Kinesin motor domains hydrolyze ATP at a rate of about 80 per second, and move along the microtubule at a speed of about 6400 Angstroms per second. To achieve that, kinesin head groups work in pairs. Upon replacing ADP with ATP, a kinesin motor domain increases its affinity for microtubule binding and locks in place. Also, the neck linker binds to the motor domain, which repositions the other head domain through the coiled-coil domain close to a second tubulin dimer, about 80 Angstroms along the microtubule. Meanwhile, ATP hydrolysis takes place, and when the second head domain binds to the microtubule, the first domain again replaces ADP with ATP, triggering a conformational change that pulls the first domain forward. |
| 119365 | GH18_chitinase | 5.51e-107 | 785 | 1121 | 1 | 322 | The GH18 (glycosyl hydrolases, family 18) type II chitinases hydrolyze chitin, an abundant polymer of N-acetylglucosamine and have been identified in bacteria, fungi, insects, plants, viruses, and protozoan parasites. The structure of this domain is an eight-stranded alpha/beta barrel with a pronounced active-site cleft at the C-terminal end of the beta-barrel. |
| 214753 | Glyco_18 | 2.31e-106 | 784 | 1121 | 1 | 334 | Glyco_18 domain. |
| 214526 | KISc | 4.34e-101 | 293 | 661 | 1 | 334 | Kinesin motor, catalytic domain. ATPase. Microtubule-dependent molecular motors that play important roles in intracellular transport of organelles and in cell division. |
| 276812 | KISc | 4.37e-93 | 293 | 647 | 1 | 326 | Kinesin motor domain. Kinesin motor domain. This catalytic (head) domain has ATPase activity and belongs to the larger group of P-loop NTPases. Kinesins are microtubule-dependent molecular motors that play important roles in intracellular transport and in cell division. In most kinesins, the motor domain is found at the N-terminus (N-type), in some its is found in the middle (M-type), or C-terminal (C-type). N-type and M-type kinesins are (+) end-directed motors, while C-type kinesins are (-) end-directed motors, i.e. they transport cargo towards the (-) end of the microtubule. Kinesin motor domains hydrolyze ATP at a rate of about 80 per second, and move along the microtubule at a speed of about 6400 Angstroms per second. To achieve that, kinesin head groups work in pairs. Upon replacing ADP with ATP, a kinesin motor domain increases its affinity for microtubule binding and locks in place. Also, the neck linker binds to the motor domain, which repositions the other head domain through the coiled-coil domain close to a second tubulin dimer, about 80 Angstroms along the microtubule. Meanwhile, ATP hydrolysis takes place, and when the second head domain binds to the microtubule, the first domain again replaces ADP with ATP, triggering a conformational change that pulls the first domain forward. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDS14181.1|GH18 | 3.40e-136 | 776 | 1162 | 4 | 400 |
| BAA13489.1|GH18|3.2.1.14 | 6.75e-133 | 775 | 1166 | 2 | 400 |
| UJO23513.1|GH18 | 1.10e-124 | 787 | 1164 | 11 | 398 |
| QPG94099.1|GH18 | 4.57e-123 | 778 | 1165 | 1 | 390 |
| UOP57070.1|GH18 | 6.94e-123 | 783 | 1164 | 63 | 445 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1D2K_A | 3.26e-122 | 788 | 1164 | 8 | 389 | Chain A, CHITINASE 1 [Coccidioides immitis],1LL4_A Chain A, Chitinase 1 [Coccidioides immitis],1LL4_B Chain B, Chitinase 1 [Coccidioides immitis],1LL4_C Chain C, Chitinase 1 [Coccidioides immitis],1LL4_D Chain D, Chitinase 1 [Coccidioides immitis] |
| 1LL7_A | 8.89e-122 | 788 | 1164 | 8 | 389 | Chain A, CHITINASE 1 [Coccidioides immitis],1LL7_B Chain B, CHITINASE 1 [Coccidioides immitis] |
| 1LL6_A | 1.74e-121 | 788 | 1164 | 8 | 389 | Chain A, CHITINASE 1 [Coccidioides immitis],1LL6_B Chain B, CHITINASE 1 [Coccidioides immitis],1LL6_C Chain C, CHITINASE 1 [Coccidioides immitis],1LL6_D Chain D, CHITINASE 1 [Coccidioides immitis] |
| 1WNO_A | 2.30e-116 | 779 | 1166 | 1 | 394 | Crystal structure of a native chitinase from Aspergillus fumigatus YJ-407 [Aspergillus fumigatus],1WNO_B Crystal structure of a native chitinase from Aspergillus fumigatus YJ-407 [Aspergillus fumigatus] |
| 6IGY_A | 2.70e-116 | 787 | 1165 | 20 | 403 | Crystal structure of Aspergillus niger chitinase B [Aspergillus niger] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|Q1E3R8|CHI1_COCIM | 1.00e-121 | 745 | 1164 | 9 | 424 | Endochitinase 1 OS=Coccidioides immitis (strain RS) OX=246410 GN=CTS1 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|P0CB51|CHI1_COCPS | 1.40e-121 | 779 | 1164 | 34 | 424 | Endochitinase 1 OS=Coccidioides posadasii (strain RMSCC 757 / Silveira) OX=443226 GN=CTS1 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|C5P230|CHI1_COCP7 | 1.96e-121 | 745 | 1164 | 9 | 424 | Endochitinase 1 OS=Coccidioides posadasii (strain C735) OX=222929 GN=CTS1 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|E9QRF2|CHIB1_ASPFU | 1.51e-115 | 779 | 1166 | 39 | 432 | Endochitinase B1 OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain ATCC MYA-4609 / Af293 / CBS 101355 / FGSC A1100) OX=330879 GN=chiB1 PE=3 SV=1 |
| sp|Q873X9|CHIB1_ASPFM | 1.51e-115 | 779 | 1166 | 39 | 432 | Endochitinase B1 OS=Neosartorya fumigata OX=746128 GN=chiB1 PE=1 SV=1 |
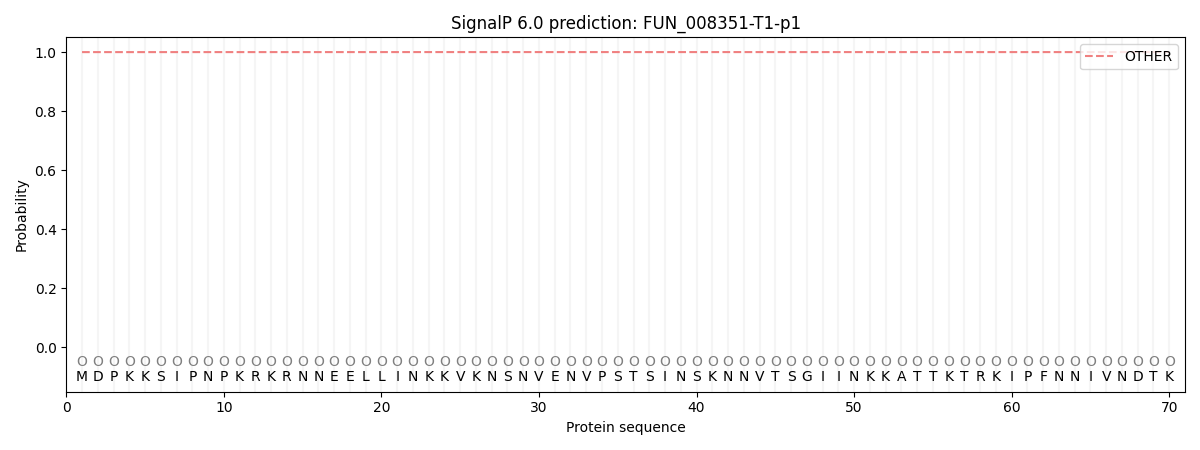
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000045 | 0.000000 |