You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: FUN_008344-T1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: FUN_008344-T1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Rhizophagus irregularis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Mucoromycota; Glomeromycetes; ; Glomeraceae; Rhizophagus; Rhizophagus irregularis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | FUN_008344-T1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH13 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 2.4.1.16:11 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT2 | 719 | 1215 | 1.9e-234 | 0.9639468690702088 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 367353 | Chitin_synth_2 | 0.0 | 700 | 1214 | 1 | 524 | Chitin synthase. Members of this family are fungal chitin synthase EC:2.4.1.16 enzymes. They catalyze chitin synthesis as follows: UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine + {(1,4)-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)}(N) <=> UDP + {(1,4)-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)}(N+1). |
| 133033 | Chitin_synth_C | 2.72e-89 | 732 | 1070 | 2 | 244 | C-terminal domain of Chitin Synthase catalyzes the incorporation of GlcNAc from substrate UDP-GlcNAc into chitin. Chitin synthase, also called UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:chitin 4-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase, catalyzes the incorporation of GlcNAc from substrate UDP-GlcNAc into chitin, which is a linear homopolymer of GlcNAc residues formed by covalent beta-1,4 linkages. Chitin is an important component of the cell wall of fungi and bacteria and it is synthesized on the cytoplasmic surface of the cell membrane by membrane bound chitin synthases. Studies with fungi have revealed that most of them contain more than one chitin synthase gene. At least five subclasses of chitin synthases have been identified. |
| 293786 | ANK | 1.15e-30 | 100 | 198 | 1 | 98 | ankyrin repeats. Ankyrin repeats are one of the most abundant repeat motifs, and generally function as scaffolds for protein-protein interactions in processes including cell cycle, transcriptional regulation, signal transduction, vesicular trafficking, and inflammatory response. Although predominantly found in eukaryotic proteins, they are also found in some bacterial and viral proteins. Less is known of their physiological roles in prokaryotes. Some bacterial ANK proteins play key roles in microbial pathogenesis by mimicking or manipulating host function(s). The pathogen Providencia alcalifaciens N-formyltransferase ankyrin repeats function in small molecule binding and allosteric control. Ankyrin-repeat proteins have been associated with a number of human diseases. |
| 293786 | ANK | 2.20e-28 | 136 | 230 | 4 | 97 | ankyrin repeats. Ankyrin repeats are one of the most abundant repeat motifs, and generally function as scaffolds for protein-protein interactions in processes including cell cycle, transcriptional regulation, signal transduction, vesicular trafficking, and inflammatory response. Although predominantly found in eukaryotic proteins, they are also found in some bacterial and viral proteins. Less is known of their physiological roles in prokaryotes. Some bacterial ANK proteins play key roles in microbial pathogenesis by mimicking or manipulating host function(s). The pathogen Providencia alcalifaciens N-formyltransferase ankyrin repeats function in small molecule binding and allosteric control. Ankyrin-repeat proteins have been associated with a number of human diseases. |
| 293786 | ANK | 5.80e-27 | 66 | 165 | 1 | 98 | ankyrin repeats. Ankyrin repeats are one of the most abundant repeat motifs, and generally function as scaffolds for protein-protein interactions in processes including cell cycle, transcriptional regulation, signal transduction, vesicular trafficking, and inflammatory response. Although predominantly found in eukaryotic proteins, they are also found in some bacterial and viral proteins. Less is known of their physiological roles in prokaryotes. Some bacterial ANK proteins play key roles in microbial pathogenesis by mimicking or manipulating host function(s). The pathogen Providencia alcalifaciens N-formyltransferase ankyrin repeats function in small molecule binding and allosteric control. Ankyrin-repeat proteins have been associated with a number of human diseases. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.68e-222 | 391 | 1186 | 71 | 880 | |
| 3.43e-212 | 404 | 1221 | 185 | 1171 | |
| 4.35e-209 | 406 | 1214 | 117 | 966 | |
| 2.20e-205 | 401 | 1214 | 293 | 1264 | |
| 1.10e-203 | 407 | 1214 | 119 | 1096 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.72e-190 | 407 | 1211 | 187 | 1161 | Chitin synthase D OS=Emericella nidulans (strain FGSC A4 / ATCC 38163 / CBS 112.46 / NRRL 194 / M139) OX=227321 GN=chsD PE=1 SV=4 |
|
| 4.36e-190 | 407 | 1214 | 331 | 1296 | Chitin synthase 5 OS=Ustilago maydis (strain 521 / FGSC 9021) OX=237631 GN=CHS5 PE=3 SV=3 |
|
| 1.19e-187 | 404 | 1214 | 210 | 1191 | Chitin synthase 3 OS=Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii serotype A (strain H99 / ATCC 208821 / CBS 10515 / FGSC 9487) OX=235443 GN=CHS3 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.87e-187 | 407 | 1214 | 169 | 1148 | Chitin synthase 3 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=CHS3 PE=1 SV=3 |
|
| 8.05e-187 | 407 | 1214 | 211 | 1186 | Chitin synthase 4 OS=Neurospora crassa (strain ATCC 24698 / 74-OR23-1A / CBS 708.71 / DSM 1257 / FGSC 987) OX=367110 GN=chs-4 PE=3 SV=3 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000046 | 0.000000 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
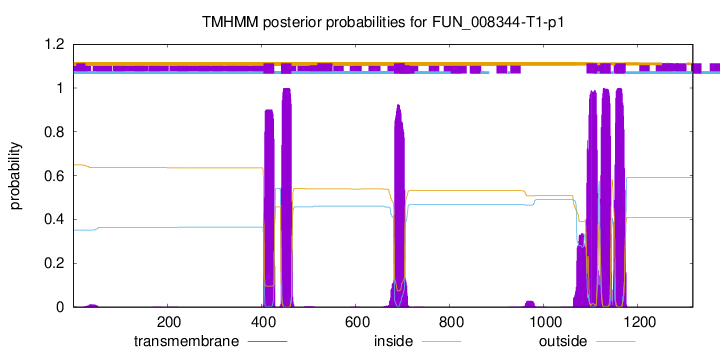
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 405 | 427 |
| 442 | 464 |
| 682 | 704 |
| 1091 | 1113 |
| 1120 | 1142 |
| 1152 | 1174 |
