You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: FPRO_14931-t41_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: FPRO_14931-t41_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Fusarium proliferatum | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Sordariomycetes; ; Nectriaceae; Fusarium; Fusarium proliferatum | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | FPRO_14931-t41_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT2 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | uncharacterized protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH24 | 101 | 241 | 5.6e-36 | 0.9781021897810219 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 381599 | lyz_endolysin_autolysin | 3.32e-49 | 104 | 244 | 2 | 134 | endolysin and autolysin. The dsDNA phages of eubacteria use endolysins or muralytic enzymes in conjunction with hollin, a small membrane protein, to degrade the peptidoglycan found in bacterial cell walls. Similarly, bacteria produce autolysins to facilitate the biosynthesis of its cell wall heteropolymer peptidoglycan and cell division. Endolysins and autolysins are found in viruses and bacteria, respectively. Both endolysin and autolysin enzymes cleave the glycosidic beta 1,4-bonds between the N-acetylmuramic acid and the N-acetylglucosamine of the peptidoglycan. |
| 381620 | lyz_P1 | 2.40e-33 | 100 | 244 | 3 | 138 | P1 lysozyme Lyz-like proteins. Enterobacteria phage P1 lysozyme Lyz is secreted to the Escherichia coli periplasm where it is membrane bound and inactive. Activation involves the release from the membrane, an intramolecular thiol-disulfide isomerization and extensive structural rearrangement of the N-terminal region. The dsDNA phages of eubacteria use endolysins or muralytic enzymes in conjunction with hollin, a small membrane protein, to degrade the peptidoglycan found in bacterial cell walls. Similarly, bacteria produce autolysins to facilitate the biosynthesis of its cell wall heteropolymer peptidoglycan and cell division. Endolysins and autolysins are found in viruses and bacteria, respectively. Both endolysin and autolysin enzymes cleave the glycosidic beta 1,4-bonds between the N-acetylmuramic acid and the N-acetylglucosamine of the peptidoglycan. |
| 226295 | RrrD | 1.95e-27 | 104 | 248 | 12 | 150 | Phage-related lysozyme (muramidase), GH24 family [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
| 381619 | endolysin_R21-like | 1.03e-23 | 101 | 244 | 6 | 140 | endolysin R21-like proteins. Unlike T4 E phage lysozyme, the endolysin R21 from Enterobacteria phage P21 has an N-terminal SAR (signal-arrest-release) domain that anchors the endolysin to the membrane in an inactive form, which act to prevent premature lysis of the infected bacterium. The dsDNA phages of eubacteria use endolysins or muralytic enzymes in conjunction with hollin, a small membrane protein, to degrade the peptidoglycan found in bacterial cell walls. Similarly, bacteria produce autolysins to facilitate the biosynthesis of its cell wall heteropolymer peptidoglycan and cell division. Endolysins and autolysins are found in viruses and bacteria, respectively. Both endolysin and autolysin enzymes cleave the glycosidic beta 1,4-bonds between the N-acetylmuramic acid and the N-acetylglucosamine of the peptidoglycan. |
| 411609 | sporang_Gsm | 8.60e-08 | 29 | 128 | 4 | 101 | sporangiospore maturation cell wall hydrolase GsmA. The peptidoglycan-hydrolyzing enzyme GsmA occurs in some sporangia-forming members of the Actinobacteria, such as Actinoplanes missouriensis, and is required for proper separation of spores. GsmA proteins have one or two SH3 domains N-terminal to the hydrolase domain. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.29e-177 | 1 | 258 | 1 | 258 | |
| 4.29e-177 | 1 | 258 | 1 | 258 | |
| 1.75e-176 | 1 | 258 | 1 | 258 | |
| 3.53e-176 | 1 | 258 | 1 | 258 | |
| 5.01e-112 | 1 | 258 | 1 | 261 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.10e-13 | 104 | 244 | 57 | 192 | Chain A, Lysozyme [Acinetobacter baumannii] |
|
| 3.70e-09 | 98 | 248 | 5 | 149 | Chain A, Lysozyme [Asticcacaulis excentricus],6H9D_B Chain B, Lysozyme [Asticcacaulis excentricus],6H9D_C Chain C, Lysozyme [Asticcacaulis excentricus] |
|
| 1.16e-08 | 104 | 244 | 14 | 152 | Chain A, Endolysin [Escherichia coli O157 typing phage 15],7M5I_B Chain B, Endolysin [Escherichia coli O157 typing phage 15] |
|
| 1.39e-07 | 111 | 244 | 10 | 134 | Chain A, Lysozyme [Enterobacteria phage P21],3HDF_B Chain B, Lysozyme [Enterobacteria phage P21] |
|
| 2.10e-07 | 111 | 244 | 35 | 159 | Chain A, Lysozyme [Enterobacteria phage P21],3HDE_B Chain B, Lysozyme [Enterobacteria phage P21],3HDE_C Chain C, Lysozyme [Enterobacteria phage P21],3HDE_D Chain D, Lysozyme [Enterobacteria phage P21] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.93e-12 | 102 | 244 | 6 | 141 | Endolysin OS=Bacillus phage B103 OX=10778 GN=15 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 2.48e-11 | 102 | 244 | 6 | 141 | Endolysin OS=Bacillus phage PZA OX=10757 GN=15 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 2.48e-11 | 102 | 244 | 6 | 141 | Endolysin OS=Bacillus phage phi29 OX=10756 GN=15 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 3.57e-08 | 111 | 244 | 37 | 161 | SAR-endolysin OS=Bacteriophage PS119 OX=83128 GN=19 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 2.01e-06 | 111 | 244 | 35 | 159 | Lysozyme RrrD OS=Escherichia coli (strain K12) OX=83333 GN=rrrD PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
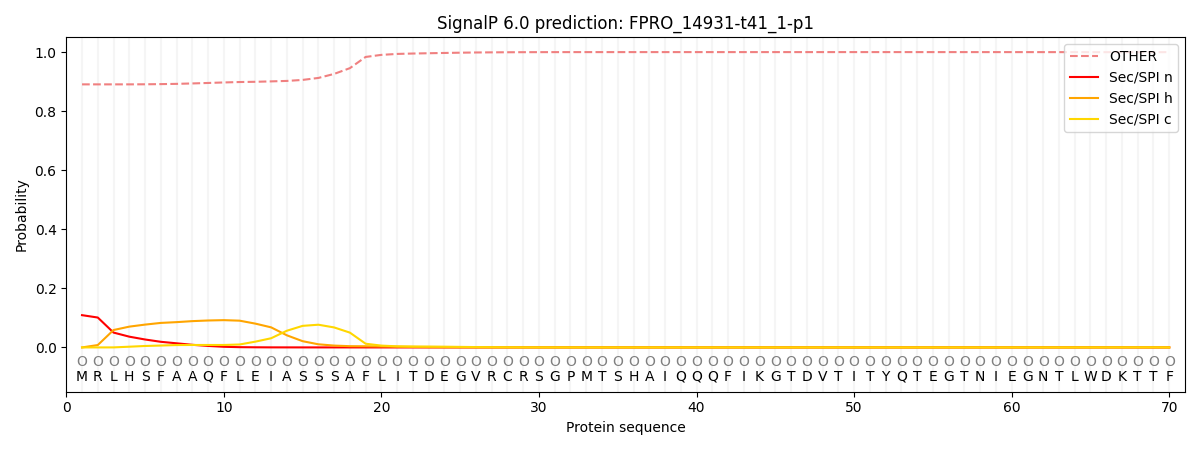
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.895929 | 0.104089 |
