You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: FPRO_09787-t41_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: FPRO_09787-t41_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Fusarium proliferatum | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Sordariomycetes; ; Nectriaceae; Fusarium; Fusarium proliferatum | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | FPRO_09787-t41_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH20 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | related to glucan 1,3-beta-glucosidase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.39:20 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH81 | 171 | 847 | 9.4e-210 | 0.9839228295819936 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 227785 | Acf2 | 0.0 | 106 | 852 | 20 | 756 | Endoglucanase Acf2 [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| 407548 | Glyco_hydro81C | 0.0 | 495 | 845 | 1 | 349 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 81 C-terminal domain. Family of eukaryotic beta-1,3-glucanases. Within the Aspergillus fumigatus protein, two perfectly conserved Glu residues (E550 or E554) have been proposed as putative nucleophiles of the active site of the Engl1 endoglucanase, while the proton donor would be D475. The endo-beta-1,3-glucanase activity is essential for efficient spore release. This entry represents the helical C-terminal domain. |
| 397619 | Glyco_hydro_81 | 1.43e-144 | 167 | 489 | 1 | 321 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 81. Family of eukaryotic beta-1,3-glucanases. Within the Aspergillus fumigatus protein ENGL1, two perfectly conserved Glu residues (E550 or E554) have been proposed as putative nucleophiles of the active site of the Engl1 endoglucanase, while the proton donor would be D475. The endo-beta-1,3-glucanase activity is essential for efficient spore release. |
| 411776 | SP2_N | 6.46e-04 | 112 | 185 | 1 | 73 | N-terminal domain of transcription factor Specificity Protein (SP) 2. Specificity Proteins (SPs) are transcription factors that are involved in many cellular processes, including cell differentiation, cell growth, apoptosis, immune responses, response to DNA damage, and chromatin remodeling. SP2 contains the least conserved DNA-binding domain within the SP subfamily of proteins, and its DNA sequence specificity differs from the other SP proteins. It localizes primarily within subnuclear foci associated with the nuclear matrix, and can activate, or in some cases, repress expression from different promoters. The transcription factor SP2 serves as a paradigm for indirect genomic binding. It does not require its DNA-binding domain for genomic DNA binding and occupies target promoters independently of whether they contain a cognate DNA-binding motif. SP2 belongs to a family of proteins, called the SP/Kruppel or Krueppel-like Factor (KLF) family, characterized by a C-terminal DNA-binding domain of 81 amino acids consisting of three Kruppel-like C2H2 zinc fingers. These factors bind to a loose consensus motif, namely NNRCRCCYY (where N is any nucleotide; R is A/G, and Y is C/T), such as the recurring motifs in GC and GT boxes (5'-GGGGCGGGG-3' and 5-GGTGTGGGG-3') that are present in promoters and more distal regulatory elements of mammalian genes. SP factors preferentially bind GC boxes, while KLFs bind CACCC boxes. Another characteristic hallmark of SP factors is the presence of the Buttonhead (BTD) box CXCPXC, just N-terminal to the zinc fingers. The function of the BTD box is unknown, but it is thought to play an important physiological role. Another feature of most SP factors is the presence of a conserved amino acid stretch, the so-called SP box, located close to the N-terminus. SP factors may be separated into three groups based on their domain architecture and the similarity of their N-terminal transactivation domains: SP1-4, SP5, and SP6-9. The transactivation domains between the three groups are not homologous to one another. SP1-4 have similar N-terminal transactivation domains characterized by glutamine-rich regions, which, in most cases, have adjacent serine/threonine-rich regions. This model represents the N-terminal domain of SP2. |
| 200437 | ADF_drebrin_like | 0.004 | 340 | 397 | 21 | 84 | ADF homology domain of drebrin and actin-binding protein 1 (abp1). Actin depolymerization factor/cofilin-like domains (ADF domains) are present in a family of essential eukaryotic actin regulatory proteins. Many of these proteins enhance the turnover rate of actin and interact with actin monomers as well as actin filaments. Abp1 and drebrin (developmentally regulated brain protein) are multidomain proteins with an N-terminal ADF homology domain and one or more C-terminal SH3 domains. They have been shown to interact with polymeric F-actin, but not with monomeric G-actin, and do not appear to promote the disassembly of actin filaments. Drebrin rather stabilizes actin filaments by inducing changes in the helical twist and may promote or interfere with the interactions of other proteins with actin filaments. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 854 | 1 | 854 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 854 | 1 | 854 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 854 | 1 | 854 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 854 | 1 | 854 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 854 | 1 | 854 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.08e-84 | 153 | 831 | 7 | 703 | The structure of a glycoside hydrolase family 81 endo-[beta]-1,3-glucanase [Rhizomucor miehei],4K3A_B The structure of a glycoside hydrolase family 81 endo-[beta]-1,3-glucanase [Rhizomucor miehei] |
|
| 1.15e-83 | 153 | 831 | 32 | 728 | Crystal structure of GH family 81 beta-1,3-glucanase from Rhizomucr miehei complexed with laminaripentaose [Rhizomucor miehei],5XBZ_B Crystal structure of GH family 81 beta-1,3-glucanase from Rhizomucr miehei complexed with laminaripentaose [Rhizomucor miehei],5XC2_A Crystal structure of GH family 81 beta-1,3-glucanase from Rhizomucr miehei complexed with laminarihexaose [Rhizomucor miehei],5XC2_B Crystal structure of GH family 81 beta-1,3-glucanase from Rhizomucr miehei complexed with laminarihexaose [Rhizomucor miehei],5XC2_C Crystal structure of GH family 81 beta-1,3-glucanase from Rhizomucr miehei complexed with laminarihexaose [Rhizomucor miehei],5XC2_D Crystal structure of GH family 81 beta-1,3-glucanase from Rhizomucr miehei complexed with laminarihexaose [Rhizomucor miehei] |
|
| 1.32e-82 | 153 | 831 | 7 | 703 | The structure of a glycoside hydrolase family 81 endo-[beta]-1,3-glucanase [Rhizomucor miehei],4K35_B The structure of a glycoside hydrolase family 81 endo-[beta]-1,3-glucanase [Rhizomucor miehei] |
|
| 1.53e-24 | 460 | 828 | 285 | 637 | Chain A, Glycoside hydrolase family 81 [Acetivibrio thermocellus ATCC 27405] |
|
| 8.12e-17 | 526 | 771 | 361 | 604 | Chain A, Glycoside Hydrolase [Halalkalibacterium halodurans C-125] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.42e-224 | 113 | 849 | 162 | 900 | Probable endo-1,3(4)-beta-glucanase ARB_01444 OS=Arthroderma benhamiae (strain ATCC MYA-4681 / CBS 112371) OX=663331 GN=ARB_01444 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 8.67e-173 | 147 | 852 | 7 | 703 | Ascus wall endo-1,3(4)-beta-glucanase OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=eng2 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 4.93e-151 | 146 | 851 | 46 | 737 | Primary septum endo-1,3(4)-beta-glucanase OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=eng1 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 1.62e-141 | 146 | 851 | 401 | 1112 | Endo-1,3(4)-beta-glucanase 1 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=DSE4 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.32e-140 | 146 | 850 | 74 | 777 | Endo-1,3(4)-beta-glucanase 2 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=ACF2 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
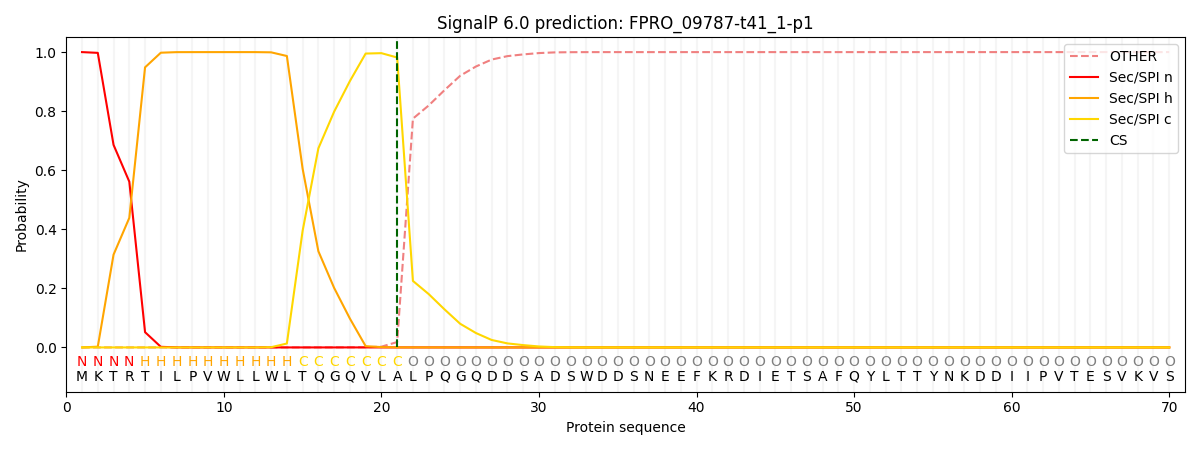
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000193 | 0.999790 | CS pos: 21-22. Pr: 0.9817 |
