You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: EXJ76045.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: EXJ76045.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Cladophialophora psammophila | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Herpotrichiellaceae; Cladophialophora; Cladophialophora psammophila | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | EXJ76045.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT57 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Peroxidase [Source:UniProtKB/TrEMBL;Acc:W9XFC3] | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA2 | 62 | 244 | 6.3e-23 | 0.6862745098039216 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 173829 | plant_peroxidase_like_1 | 1.23e-109 | 21 | 286 | 1 | 264 | Uncharacterized family of plant peroxidase-like proteins. This is a subgroup of heme-dependent peroxidases similar to plant peroxidases. Along with animal peroxidases, these enzymes belong to a group of peroxidases containing a heme prosthetic group (ferriprotoporphyrin IX) which catalyzes a multistep oxidative reaction involving hydrogen peroxide as the electron acceptor. The plant peroxidase-like superfamily is found in all three kingdoms of life and carries out a variety of biosynthetic and degradative functions. |
| 395089 | peroxidase | 9.33e-23 | 60 | 197 | 14 | 155 | Peroxidase. |
| 173823 | plant_peroxidase_like | 1.19e-19 | 60 | 284 | 16 | 253 | Heme-dependent peroxidases similar to plant peroxidases. Along with animal peroxidases, these enzymes belong to a group of peroxidases containing a heme prosthetic group (ferriprotoporphyrin IX), which catalyzes a multistep oxidative reaction involving hydrogen peroxide as the electron acceptor. The plant peroxidase-like superfamily is found in all three kingdoms of life and carries out a variety of biosynthetic and degradative functions. Several sub-families can be identified. Class I includes intracellular peroxidases present in fungi, plants, archaea and bacteria, called catalase-peroxidases, that can exhibit both catalase and broad-spectrum peroxidase activities depending on the steady-state concentration of hydrogen peroxide. Catalase-peroxidases are typically comprised of two homologous domains that probably arose via a single gene duplication event. Class II includes ligninase and other extracellular fungal peroxidases, while class III is comprised of classic extracellular plant peroxidases, like horseradish peroxidase. |
| 173825 | ascorbate_peroxidase | 7.08e-15 | 65 | 197 | 33 | 168 | Ascorbate peroxidases and cytochrome C peroxidases. Ascorbate peroxidases are a subgroup of heme-dependent peroxidases of the plant superfamily that share a heme prosthetic group and catalyze a multistep oxidative reaction involving hydrogen peroxide as the electron acceptor. Along with related catalase-peroxidases, ascorbate peroxidases belong to class I of the plant superfamily. Ascorbate peroxidases are found in the chloroplasts and/or cytosol of algae and plants, where they have been shown to control the concentration of lethal hydrogen peroxide molecules. The yeast cytochrome c peroxidase is a divergent member of the family; it forms a complex with cytochrome c to catalyze the reduction of hydrogen peroxide to water. |
| 173826 | ligninase | 1.04e-10 | 66 | 256 | 42 | 231 | Ligninase and other manganese-dependent fungal peroxidases. Ligninases and related extracellular fungal peroxidases belong to class II of the plant heme-dependent peroxidase superfamily. All members of the superfamily share a heme prosthetic group and catalyze a multistep oxidative reaction involving hydrogen peroxide as the electron acceptor. Class II peroxidases are fungal glycoproteins that have been implicated in the oxidative breakdown of lignin, the main cell wall component of woody plants. They contain four conserved disulphide bridges and two conserved calcium binding sites. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.03e-112 | 10 | 526 | 14 | 534 | |
| 6.40e-111 | 5 | 506 | 10 | 515 | |
| 6.67e-104 | 20 | 512 | 28 | 524 | |
| 3.07e-89 | 13 | 443 | 12 | 447 | |
| 4.49e-88 | 13 | 441 | 12 | 445 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.63e-95 | 20 | 519 | 22 | 509 | WSC domain-containing protein ARB_07870 OS=Arthroderma benhamiae (strain ATCC MYA-4681 / CBS 112371) OX=663331 GN=ARB_07870 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.08e-07 | 622 | 669 | 21 | 68 | Clock-controlled protein 6 OS=Neurospora crassa (strain ATCC 24698 / 74-OR23-1A / CBS 708.71 / DSM 1257 / FGSC 987) OX=367110 GN=ccg-6 PE=2 SV=2 |
|
| 1.12e-07 | 66 | 197 | 35 | 166 | Probable L-ascorbate peroxidase 4, peroxisomal OS=Oryza sativa subsp. japonica OX=39947 GN=APX4 PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 8.04e-07 | 62 | 194 | 114 | 247 | Putative L-ascorbate peroxidase 6 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=APX6 PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 2.01e-06 | 66 | 194 | 36 | 164 | Probable L-ascorbate peroxidase 3 OS=Oryza sativa subsp. indica OX=39946 GN=APX3 PE=2 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
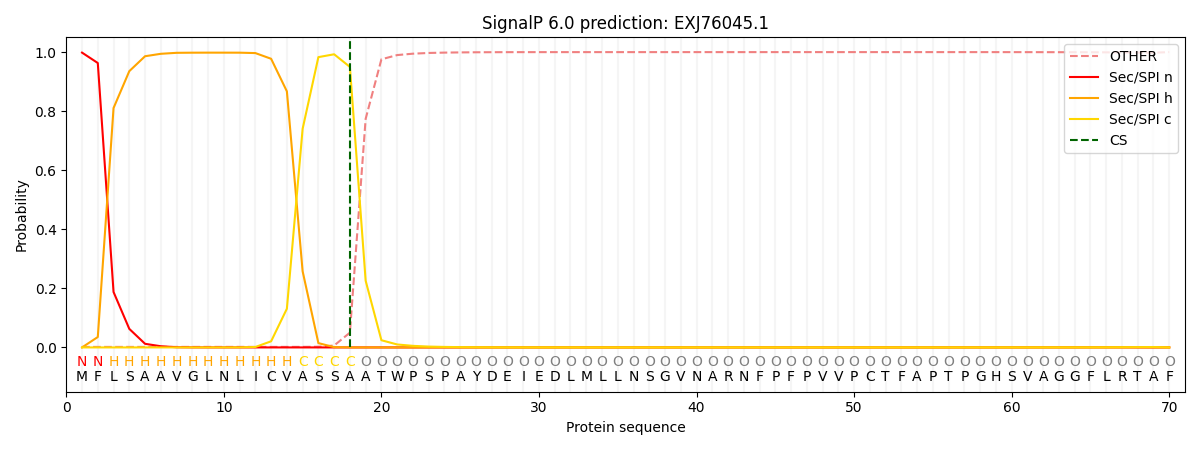
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.012916 | 0.987058 | CS pos: 18-19. Pr: 0.9499 |
