You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: EPrPRT00000016087-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: EPrPRT00000016087-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Pythium arrhenomanes | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Pythiaceae; Pythium; Pythium arrhenomanes | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | EPrPRT00000016087-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH131 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Thioredoxin. | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 2.4.1.265:13 | 2.4.1.-:9 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT57 | 510 | 1016 | 3e-140 | 0.9854469854469855 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 397324 | Alg6_Alg8 | 7.84e-151 | 509 | 1016 | 1 | 472 | ALG6, ALG8 glycosyltransferase family. N-linked (asparagine-linked) glycosylation of proteins is mediated by a highly conserved pathway in eukaryotes, in which a lipid (dolichol phosphate)-linked oligosaccharide is assembled at the endoplasmic reticulum membrane prior to the transfer of the oligosaccharide moiety to the target asparagine residues. This oligosaccharide is composed of Glc(3)Man(9)GlcNAc(2). The addition of the three glucose residues is the final series of steps in the synthesis of the oligosaccharide precursor. Alg6 transfers the first glucose residue, and Alg8 transfers the second one. In the human alg6 gene, a C->T transition, which causes Ala333 to be replaced with Val, has been identified as the cause of a congenital disorder of glycosylation, designated as type Ic OMIM:603147. |
| 239259 | PDI_a_family | 4.13e-29 | 144 | 251 | 1 | 101 | Protein Disulfide Isomerase (PDIa) family, redox active TRX domains; composed of eukaryotic proteins involved in oxidative protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by acting as catalysts and folding assistants. Members of this family include PDI and PDI-related proteins like ERp72, ERp57 (or ERp60), ERp44, P5, PDIR, ERp46 and the transmembrane PDIs. PDI, ERp57, ERp72, P5, PDIR and ERp46 are all oxidases, catalyzing the formation of disulfide bonds of newly synthesized polypeptides in the ER. They also exhibit reductase activity in acting as isomerases to correct any non-native disulfide bonds, as well as chaperone activity to prevent protein aggregation and facilitate the folding of newly synthesized proteins. These proteins usually contain multiple copies of a redox active TRX (a) domain containing a CXXC motif, and may also contain one or more redox inactive TRX-like (b) domains. Only one a domain is required for the oxidase function but multiple copies are necessary for the isomerase function. The different types of PDIs may show different substrate specificities and tissue-specific expression, or may be induced by stress. PDIs are in their reduced form at steady state and are oxidized to the active form by Ero1, which is localized in the ER through ERp44. Some members of this family also contain a DnaJ domain in addition to the redox active a domains; examples are ERdj5 and Pfj2. Also included in the family is the redox inactive N-terminal TRX-like domain of ERp29. |
| 400361 | COPIIcoated_ERV | 2.83e-27 | 303 | 472 | 53 | 223 | Endoplasmic reticulum vesicle transporter. This family is conserved from plants and fungi to humans. Erv46 works in close conjunction with Erv41 and together they form a complex which cycles between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex. Erv46-41 interacts strongly with the endoplasmic reticulum glucosidase II. Mammalian glucosidase II comprises a catalytic alpha-subunit and a 58 kDa beta subunit, which is required for ER localization. All proteins identified biochemically as Erv41p-Erv46p interactors are localized to the early secretory pathway and are involved in protein maturation and processing in the ER and/or sorting into COPII vesicles for transport to the Golgi. |
| 404692 | ERGIC_N | 1.16e-23 | 4 | 94 | 1 | 91 | Endoplasmic Reticulum-Golgi Intermediate Compartment (ERGIC). This family is the N-terminal of ERGIC proteins, ER-Golgi intermediate compartment clusters, otherwise known as Ervs, and is associated with family COPIIcoated_ERV, pfam07970. |
| 273454 | pdi_dom | 8.54e-22 | 146 | 252 | 1 | 99 | protein disulfide-isomerase domain. This model describes a domain of eukaryotic protein disulfide isomerases, generally found in two copies. The high cutoff for total score reflects the expectation of finding both copies. The domain is similar to thioredoxin but the redox-active disulfide region motif is APWCGHCK. [Protein fate, Protein folding and stabilization] |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.20e-219 | 494 | 1034 | 10 | 568 | |
| 6.90e-128 | 502 | 1015 | 12 | 495 | |
| 5.05e-92 | 513 | 1016 | 25 | 507 | |
| 1.88e-91 | 513 | 1016 | 25 | 507 | |
| 1.88e-91 | 513 | 1016 | 25 | 507 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.23e-15 | 524 | 919 | 87 | 433 | Cryo-EM structure of yeast ALG6 in complex with 6AG9 Fab and Dol25-P-Glc [Saccharomyces cerevisiae],6SNI_X Cryo-EM structure of nanodisc reconstituted yeast ALG6 in complex with 6AG9 Fab [Saccharomyces cerevisiae] |
|
| 5.44e-12 | 146 | 251 | 12 | 109 | Chain A, Protein disulfide-isomerase A4 [Mus musculus] |
|
| 7.66e-12 | 146 | 251 | 19 | 117 | Crystal Structure of Yeast Protein Disulfide Isomerase [Saccharomyces cerevisiae],3BOA_A Crystal structure of yeast protein disulfide isomerase. [Saccharomyces cerevisiae] |
|
| 8.03e-12 | 146 | 251 | 135 | 232 | Crystal structure of the a0a fragment of ERp72 [Homo sapiens] |
|
| 1.38e-11 | 146 | 251 | 12 | 112 | Chain A, PROTEIN DISULFIDE ISOMERASE [Homo sapiens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.34e-92 | 513 | 1016 | 25 | 507 | Probable dolichyl pyrophosphate Glc1Man9GlcNAc2 alpha-1,3-glucosyltransferase OS=Mus musculus OX=10090 GN=Alg8 PE=2 SV=2 |
|
| 3.31e-90 | 513 | 1016 | 25 | 507 | Probable dolichyl pyrophosphate Glc1Man9GlcNAc2 alpha-1,3-glucosyltransferase OS=Bos taurus OX=9913 GN=ALG8 PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 1.35e-89 | 506 | 1016 | 16 | 497 | Probable dolichyl pyrophosphate Glc1Man9GlcNAc2 alpha-1,3-glucosyltransferase OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=At2g44660 PE=2 SV=3 |
|
| 6.30e-89 | 513 | 1016 | 25 | 507 | Probable dolichyl pyrophosphate Glc1Man9GlcNAc2 alpha-1,3-glucosyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=ALG8 PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 2.64e-78 | 508 | 1016 | 14 | 495 | Dolichyl pyrophosphate Glc1Man9GlcNAc2 alpha-1,3-glucosyltransferase OS=Neurospora crassa (strain ATCC 24698 / 74-OR23-1A / CBS 708.71 / DSM 1257 / FGSC 987) OX=367110 GN=alg-8 PE=3 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
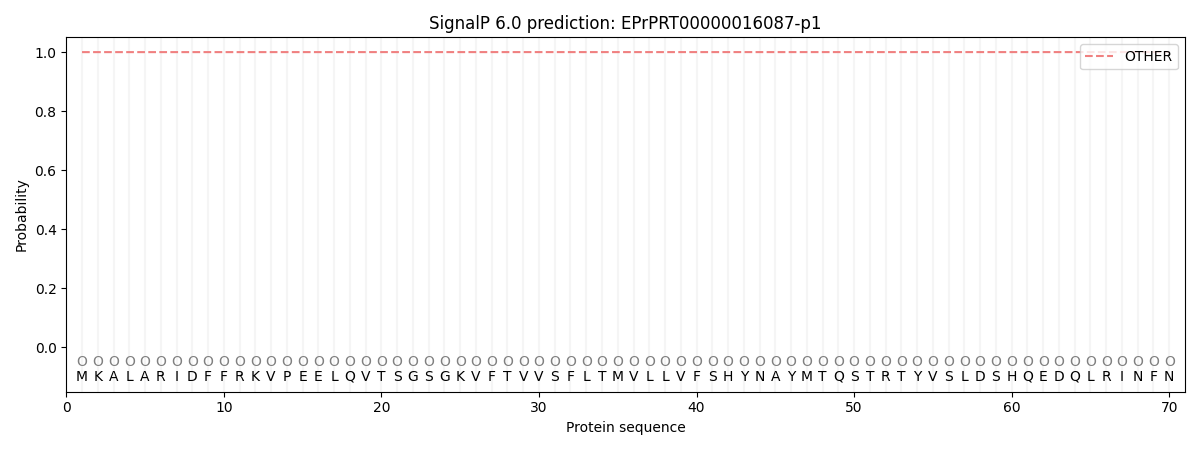
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000000 | 0.000007 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
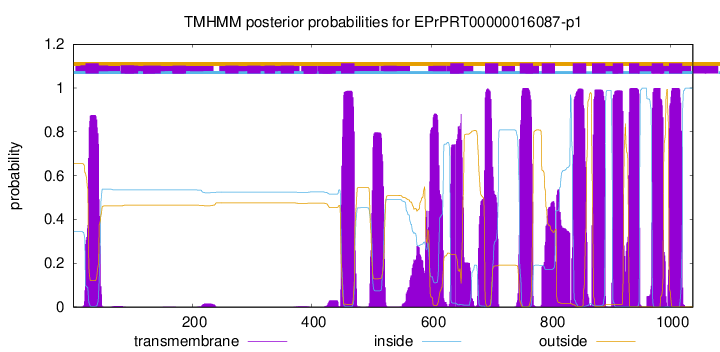
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 21 | 43 |
| 449 | 471 |
| 632 | 654 |
| 690 | 712 |
| 748 | 770 |
| 785 | 807 |
| 837 | 859 |
| 869 | 891 |
| 904 | 921 |
| 931 | 948 |
| 969 | 988 |
| 998 | 1020 |
