You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: EPrPIT00000017120-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: EPrPIT00000017120-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Globisporangium irregulare | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Oomycota; NA; ; Pythiaceae; Globisporangium; Globisporangium irregulare | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | EPrPIT00000017120-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE4 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Callose synthase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 6253; End:13055 Strand: + | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MATREQNESY NRGGGSEYRK RASSNYFELD ADRRRNKSER TERFSTRLTS LDVQQPPLSS | 60 |
| KSSEGKFTDD DESSIDACSE MLHAKFGFQE GSVANQREHP SDAPDQYIVE LHKKLFSNYR | 120 |
| DWCKFLNAQP VHFRGTSAAQ VKHPLHMDLM LYFLVWGEAA NLRHMPECLC YIYHQMMTLV | 180 |
| NADPNIQERK PEGWYLENVV RPIWSECSNM QRRNNLKKPL EHVQIRNYDD INEYFWKQHC | 240 |
| LSIDITQVGR ELTQNHGKTF YEHRSIFTLV LNYYRIFQFN LMFMNLLTVL AFAVTISPDG | 300 |
| GKGGFVQFGR IGDVVEPYTT RDLKLAVVSI PFSHALLAFL KCVLEACHGW HLLIAKEKSA | 360 |
| SSSRSLTYGS ALVIRMLWNG GFAVLFGFMI FVPLNELRDT ALLDQFLPIT GGFFVPGLLV | 420 |
| LLVQAFSPQL ISGTFAAKFV REGESCYVGR NMAPPFSYQI KYITFWLFLW TIKALTSYFI | 480 |
| LVRPLMLPTL AIYSMKLEYQ SSLVSFHNMG VILSLWLPVV FIFNYDTQIY FTIFQALLGA | 540 |
| FKGVLMKTGE IRGVKEMSKA FRVAPQLFDQ KVVTTLARAS DASANGNDSS RPSALAAAYE | 600 |
| SQMMLRFVVV WNEIVNSFRE GDLLDDKEAA ILQYDIRSNG EVFEPVFLSA GKLGEAMNLT | 660 |
| IKTAKEGKGE SQLRVALVES DCLSALRSFY TASFYVLTSL FGNDDADVLE GFRMIEDIAS | 720 |
| AGGFMKSFHV RELVRLRAAV VDLLEEILEL PDPEVQSQHM PGARVHTMGV VRNFVSKMEV | 780 |
| FLNTLQAFCV DPALQRKFSN SKFCSSTNGY LYASRGLVNL FCNDSSMGAA TRACLLLSLE | 840 |
| RSEAMPRCTE AQRRLGFFMK SLVMDIPQLQ AIKEMXXXXS FSVVTPFYAE TVLFSLEDLN | 900 |
| NPLVNHPIFE KVEEDGKNLT ILKYLTKIHE EEWLNFLERM DVSSPEEAQK QYPLDIRLWA | 960 |
| SYRGQTLART VQGMMMYEDA IKILHWLEIG SSPGKSAEQK QTQLQDMVRL KFSYICACQV | 1020 |
| YGKHRKENKQ QADDIDYLLQ EYPNLRVAYV DTIDMQSGEK TYDTVLIKSE NGEIAEVYRY | 1080 |
| QLPGDPVLGE GKPENQNNAL QFTRGEFVQT IDMNQQHYFE ECLKMPQMLR TADLHPSKKP | 1140 |
| VSIIGMREHI FTGNASSLAK FKTWQELVFV TLSQRVLADP LYVRMHYGHP DVFDKVIALT | 1200 |
| RGGVSKASKG INLSEDVFAG FNSTLRGGVV THVEFMQCGK GRDVALSQIS MFEGKLANGA | 1260 |
| GETSLAREAH RMGQFMDFFR LNSMYYSHTG FYFATWMTIV TTFVYMYSKV YMALAGVQEQ | 1320 |
| VIYKMESQDI INLNDNFDFV DRAYHDSDAV INTQYYIQAG LFLSLPLIAV YFGEMGIRRG | 1380 |
| LVQLIEMIIT GGPAFFIFQV GTTMHYFDNN LLHGEAQYKA TGRGFKITRE TFVLLYKAYA | 1440 |
| NSHYRKAFEL IGLCLVYLTF GSFNICKRDG PVTESLSSDF CETSQGFGVQ TFAIWVISVL | 1500 |
| WLMSPYIFNT DGLDWEKTKA DVKAWTVWMY ADESFKDEDL PMNGGWISWW KGELSLYHNT | 1560 |
| KPIARFTVLL RESRHFLLMW YVITLRWNAL AVALVFGAVI STVLILGVIG AAGTAMKGTP | 1620 |
| APVRAGLYLA SITACLVAYF VIARVVLDAS MDSSLSLFFG YMGGLYGLNE MIRMWSFKNS | 1680 |
| SIASVGMFQQ LAFLFDFVFC TAMIIPLFIM SGIPFLNIIQ TRMMYNKGFS EVVSASSQYA | 1740 |
| FSLAAFMGIL GGTGCGWIFH LFTTLESTPG FISYVTTYEL LDGKAGDGTT TYVFYFACVG | 1800 |
| GTMIAGITNF FIGRRLSIIC GGVLAMLGMV SVSAVQTSGE NFLFPGVGLL GCAVFVATVI | 1860 |
| LSIVTPAVYI FPESPYWVYL REGLEACERC LAVLRRKEGF LLSLFLMLVS GLFLGALNMY | 1920 |
| MSQKFSSIEN AQYMFVNCVS LQFLGALFSF FFMDRVDHRR ILFCTLIPIA ALVAILGVNV | 1980 |
| NTGTWKDDAE YLMLRIVGLL LYFFAGLGIT SVLWVSCVGF FRTSQRAFYT NLFFMVFFLV | 2040 |
| PVLSLFIRVS TSYADKQYIY LYALSGCCVV VLLLLFGVGT QKNGMLCTKA EMEAERARIR | 2100 |
| RTRQTRRSAR TPGSARSRNL SRSRGKSHSN YQVYESPAGG MP | 2142 |
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 2.4.1.34:28 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT48 | 845 | 1591 | 8e-271 | 0.9621109607577808 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 396784 | Glucan_synthase | 0.0 | 846 | 1548 | 3 | 714 | 1,3-beta-glucan synthase component. This family consists of various 1,3-beta-glucan synthase components including Gls1, Gls2 and Gls3 from yeast. 1,3-beta-glucan synthase EC:2.4.1.34 also known as callose synthase catalyzes the formation of a beta-1,3-glucan polymer that is a major component of the fungal cell wall. The reaction catalyzed is:- UDP-glucose + {(1,3)-beta-D-glucosyl}(N) <=> UDP + {(1,3)-beta-D-glucosyl}(N+1). |
| 405046 | FKS1_dom1 | 6.16e-30 | 151 | 242 | 8 | 106 | 1,3-beta-glucan synthase subunit FKS1, domain-1. The FKS1_dom1 domain is likely to be the 'Class I' region just N-terminal to the first set of transmembrane helices that is involved in 1,3-beta-glucan synthesis itself. This family is found on proteins with family Glucan_synthase, pfam02364. |
| 340874 | MFS_SV2_like | 3.90e-05 | 1691 | 2047 | 6 | 323 | Metazoan Synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2 (SV2) and related small molecule transporters of the Major Facilitator Superfamily. This family is composed of metazoan synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2 (SV2) and related small molecule transporters including those that transport inorganic phosphate (Pht), aromatic compounds (PcaK and related proteins), proline/betaine (ProP), alpha-ketoglutarate (KgtP), citrate (CitA), shikimate (ShiA), and cis,cis-muconate (MucK), among others. SV2 is a transporter-like protein that serves as the receptor for botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT/A), one of seven neurotoxins produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. BoNT/A blocks neurotransmitter release by cleaving synaptosome-associated protein of 25 kD (SNAP-25) within presynaptic nerve terminals. Also included in this family is synaptic vesicle 2 (SV2)-related protein (SVOP) and similar proteins. SVOP is a transporter-like nucleotide binding protein that localizes to neurotransmitter-containing vesicles. The SV2-like family belongs to the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins, which are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
| 349949 | MFS | 2.65e-04 | 1780 | 2051 | 76 | 356 | Major Facilitator Superfamily. The Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) is a large and diverse group of secondary transporters that includes uniporters, symporters, and antiporters. MFS proteins facilitate the transport across cytoplasmic or internal membranes of a variety of substrates including ions, sugar phosphates, drugs, neurotransmitters, nucleosides, amino acids, and peptides. They do so using the electrochemical potential of the transported substrates. Uniporters transport a single substrate, while symporters and antiporters transport two substrates in the same or in opposite directions, respectively, across membranes. MFS proteins are typically 400 to 600 amino acids in length, and the majority contain 12 transmembrane alpha helices (TMs) connected by hydrophilic loops. The N- and C-terminal halves of these proteins display weak similarity and may be the result of a gene duplication/fusion event. Based on kinetic studies and the structures of a few bacterial superfamily members, GlpT (glycerol-3-phosphate transporter), LacY (lactose permease), and EmrD (multidrug transporter), MFS proteins are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. Bacterial members function primarily for nutrient uptake, and as drug-efflux pumps to confer antibiotic resistance. Some MFS proteins have medical significance in humans such as the glucose transporter Glut4, which is impaired in type II diabetes, and glucose-6-phosphate transporter (G6PT), which causes glycogen storage disease when mutated. |
| 395036 | Sugar_tr | 3.02e-04 | 1735 | 2047 | 96 | 409 | Sugar (and other) transporter. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIZ28646.1|GT48 | 0.0 | 14 | 2142 | 9 | 2225 |
| CCA22009.1|GT48 | 0.0 | 19 | 2138 | 11 | 2219 |
| CCA17033.1|GT48 | 0.0 | 19 | 2140 | 12 | 2233 |
| UIZ28580.1|GT48 | 0.0 | 19 | 2142 | 11 | 2240 |
| CCA17037.1|GT48 | 0.0 | 21 | 2138 | 10 | 2241 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|Q9LXT9|CALS3_ARATH | 3.41e-226 | 64 | 1553 | 227 | 1751 | Callose synthase 3 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS3 PE=3 SV=3 |
| sp|Q9SJM0|CALSA_ARATH | 5.80e-224 | 80 | 1736 | 265 | 1892 | Callose synthase 10 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS10 PE=2 SV=5 |
| sp|Q9SFU6|CALS9_ARATH | 8.31e-224 | 80 | 1736 | 253 | 1878 | Callose synthase 9 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS9 PE=2 SV=2 |
| sp|Q9SL03|CALS2_ARATH | 5.27e-222 | 80 | 1561 | 235 | 1754 | Callose synthase 2 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS2 PE=2 SV=3 |
| sp|Q9SHJ3|CALS7_ARATH | 3.13e-221 | 80 | 1736 | 258 | 1918 | Callose synthase 7 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CALS7 PE=3 SV=3 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000038 | 0.000000 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
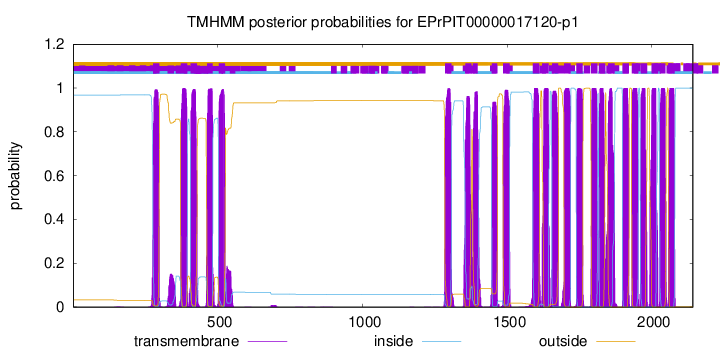
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 276 | 298 |
| 372 | 394 |
| 406 | 428 |
| 463 | 482 |
| 503 | 525 |
| 1285 | 1307 |
| 1355 | 1377 |
| 1381 | 1398 |
| 1447 | 1466 |
| 1486 | 1508 |
| 1589 | 1611 |
| 1621 | 1643 |
| 1655 | 1677 |
| 1697 | 1719 |
| 1739 | 1761 |
| 1790 | 1812 |
| 1817 | 1839 |
| 1849 | 1871 |
| 1899 | 1921 |
| 1931 | 1953 |
| 1962 | 1984 |
| 1999 | 2021 |
| 2028 | 2047 |
| 2057 | 2079 |
