You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: EKG16555.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: EKG16555.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Macrophomina phaseolina | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Dothideomycetes; ; Botryosphaeriaceae; Macrophomina; Macrophomina phaseolina | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | EKG16555.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH3 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Galactose-binding domain-like protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 4.2.2.23:4 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL4 | 20 | 519 | 1.1e-210 | 0.9959919839679359 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 401282 | RhgB_N | 1.30e-151 | 23 | 273 | 1 | 251 | Rhamnogalacturonan lyase B, N-terminal. Members of this family are found in both fungi, bacteria and wood-eating arthropods. The domain is found at the N-terminus of rhamnogalacturonase B, a member of the polysaccharide lyase family 4. The domain adopts a structure consisting of a beta super-sandwich, with eighteen strands in two beta-sheets. The three domains of the whole protein rhamnogalacturonan lyase (RGL4), are involved in the degradation of rhamnogalacturonan-I, RG-I, an important pectic plant cell-wall polysaccharide. The active-site residues are a lysine at position 169 in UniProtKB:Q00019 and a histidine at 229, Lys169 is likely to be a proton abstractor, His229 a proton donor in the mechanism. The substrate is a disaccharide, and RGL4, in contrast to other rhamnogalacturonan hydrolases, cleaves the alpha-1,4 linkages of RG-I between Rha and GalUA through a beta-elimination resulting in a double bond in the nonreducing GalUA residue, and is thus classified as a polysaccharide lyase (PL). |
| 199907 | RGL4_N | 4.98e-55 | 23 | 257 | 1 | 263 | N-terminal catalytic domain of rhamnogalacturonan lyase, a family 4 polysaccharide lyase. The rhamnogalacturonan lyase of the polysaccharide lyase family 4 (RGL4) is involved in the degradation of RG (rhamnogalacturonan) type-I, an important pectic plant cell wall polysaccharide, by cleaving the alpha-1,4 glycoside bond between L-rhamnose and D-galacturonic acids in the backbone of RG type-I through a beta-elimination reaction. RGL4 consists of three domains, an N-terminal catalytic domain, a middle domain with a FNIII type fold and a C-terminal domain with a jelly roll fold; the middle and C-terminal domains are both putative carbohydrate binding modules. There are two types of RG lyases, which both cleave the alpha-1,4 bonds of the RG-I main chain (RG chain) through the beta-elimination reaction, but belong to two structurally unrelated polysaccharide lyase (PL) families, 4 and 11. |
| 405384 | CBM-like | 6.69e-53 | 364 | 512 | 1 | 145 | Polysaccharide lyase family 4, domain III. CBM-like is domain III of rhamnogalacturonan lyase (RG-lyase). The full-length protein specifically recognizes and cleaves alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds between l-rhamnose and d-galacturonic acids in the backbone of rhamnogalacturonan-I, a major component of the plant cell wall polysaccharide, pectin. This domain possesses a jelly roll beta-sandwich fold structurally homologous to carbohydrate binding modules (CBMs), and it carries two sulfate ions and a hexa-coordinated calcium ion. |
| 199905 | RGL4_C | 4.72e-51 | 366 | 512 | 1 | 148 | C-terminal domain of rhamnogalacturonan lyase, a family 4 polysaccharide lyase. The rhamnogalacturonan lyase of the polysaccharide lyase family 4 (RGL4) is involved in the degradation of RG (rhamnogalacturonan) type-I, an important pectic plant cell wall polysaccharide, by cleaving the alpha-1,4 glycoside bond between L-rhamnose and D-galacturonic acids in the backbone of RG type-I through a beta-elimination reaction. RGL4 consists of three domains, an N-terminal catalytic domain, a middle domain with a FNIII type fold and a C-terminal domain with a jelly roll fold. Both the middle and the C-terminal domain are putative carbohydrate binding modules. There are two types of RG lyases, which both cleave the alpha-1,4 bonds of the RG-I main chain (RG chain) through the beta-elimination reaction, but belong to two structurally unrelated polysaccharide lyase (PL) families, 4 and 11. |
| 405387 | fn3_3 | 3.50e-22 | 279 | 352 | 1 | 74 | Polysaccharide lyase family 4, domain II. FnIII-like is domain II of rhamnogalacturonan lyase (RG-lyase). The full-length protein specifically recognizes and cleaves alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds between l-rhamnose and d-galacturonic acids in the backbone of rhamnogalacturonan-I, a major component of the plant cell wall polysaccharide, pectin. This domain displays an immunoglobulin-like or more specifically Fibronectin-III type fold and shows highest structural similarity to the C-terminal beta-sandwich subdomain of the pro-hormone/propeptide processing enzyme carboxypeptidase gp180 from duck. It serves to assist in producing the deep pocket, with domain III, into which the substrate fits. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.08e-241 | 1 | 528 | 1 | 526 | |
| 5.81e-240 | 7 | 524 | 7 | 524 | |
| 1.85e-238 | 1 | 528 | 1 | 530 | |
| 1.01e-234 | 21 | 528 | 20 | 526 | |
| 1.65e-233 | 13 | 528 | 12 | 526 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.85e-233 | 22 | 528 | 1 | 506 | Rhamnogalacturonan lyase from Aspergillus aculeatus [Aspergillus aculeatus] |
|
| 1.51e-232 | 22 | 528 | 1 | 506 | Rhamnogalacturonan lyase from Aspergillus aculeatus K150A active site mutant [Aspergillus aculeatus],2XHN_B Rhamnogalacturonan lyase from Aspergillus aculeatus K150A active site mutant [Aspergillus aculeatus],3NJV_A Rhamnogalacturonan lyase from Aspergillus aculeatus K150A substrate complex [Aspergillus aculeatus] |
|
| 6.11e-232 | 22 | 528 | 1 | 506 | Rhamnogalacturonan Lyase from Aspergillus aculeatus mutant H210A [Aspergillus aculeatus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.44e-242 | 7 | 524 | 7 | 522 | Probable rhamnogalacturonate lyase A OS=Aspergillus niger (strain CBS 513.88 / FGSC A1513) OX=425011 GN=rglA PE=3 SV=2 |
|
| 3.67e-238 | 15 | 524 | 14 | 522 | Probable rhamnogalacturonate lyase A OS=Aspergillus terreus (strain NIH 2624 / FGSC A1156) OX=341663 GN=rglA PE=3 SV=2 |
|
| 4.64e-233 | 21 | 528 | 19 | 525 | Rhamnogalacturonate lyase A OS=Aspergillus aculeatus OX=5053 GN=rglA PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.12e-231 | 2 | 528 | 1 | 526 | Probable rhamnogalacturonate lyase A OS=Aspergillus oryzae (strain ATCC 42149 / RIB 40) OX=510516 GN=rglA PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 1.84e-230 | 2 | 528 | 1 | 526 | Probable rhamnogalacturonate lyase A OS=Aspergillus flavus (strain ATCC 200026 / FGSC A1120 / IAM 13836 / NRRL 3357 / JCM 12722 / SRRC 167) OX=332952 GN=rglA PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
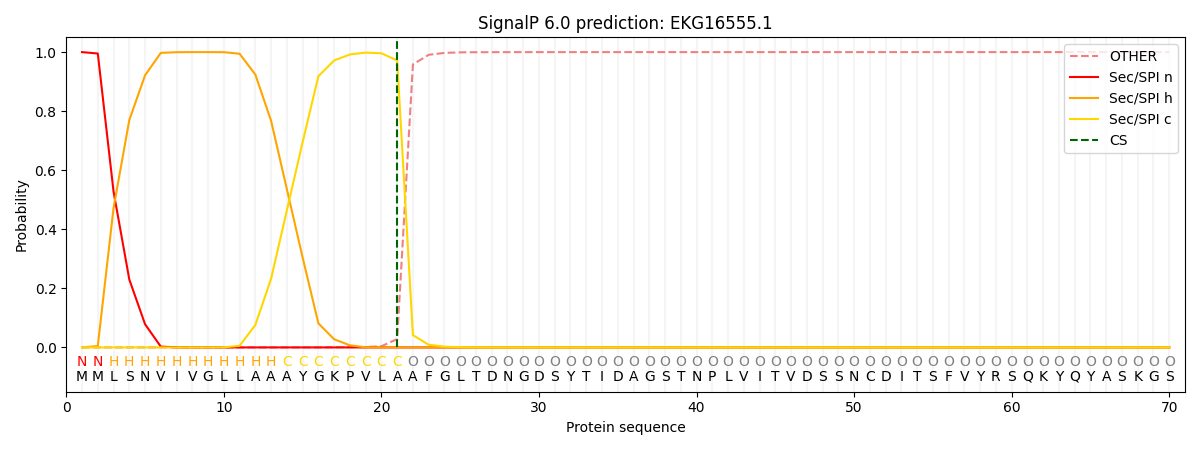
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000286 | 0.999691 | CS pos: 21-22. Pr: 0.9718 |
