You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: EEQ33548.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: EEQ33548.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Microsporum canis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Arthrodermataceae; Microsporum; Microsporum canis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | EEQ33548.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT2 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | glucoamylase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.3:94 | 3.2.1.3:71 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH15 | 42 | 449 | 4.6e-76 | 0.9861495844875346 |
| CBM20 | 512 | 599 | 2.5e-26 | 0.9444444444444444 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 395586 | Glyco_hydro_15 | 3.17e-122 | 40 | 449 | 4 | 415 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 15. In higher organisms this family is represented by phosphorylase kinase subunits. |
| 99886 | CBM20_glucoamylase | 2.19e-35 | 503 | 610 | 1 | 106 | Glucoamylase (glucan1,4-alpha-glucosidase), C-terminal CBM20 (carbohydrate-binding module, family 20) domain. Glucoamylases are inverting, exo-acting starch hydrolases that hydrolyze starch and related polysaccharides by releasing the nonreducing end glucose. They are mainly active on alpha-1,4-glycosidic bonds but also have some activity towards 1,6-glycosidic bonds occurring in natural oligosaccharides. The ability of glucoamylases to cleave 1-6-glycosidic binds is called "debranching activity" and is of importance in industrial applications, where complete degradation of starch to glucose is needed. Most glucoamylases are multidomain proteins containing an N-terminal catalytic domain, a C-terminal CBM20 domain, and a highly O-glycosylated linker region that connects the two. The CBM20 domain is found in a large number of starch degrading enzymes including alpha-amylase, beta-amylase, glucoamylase, and CGTase (cyclodextrin glucanotransferase). CBM20 is also present in proteins that have a regulatory role in starch metabolism in plants (e.g. alpha-amylase) or glycogen metabolism in mammals (e.g. laforin). CBM20 folds as an antiparallel beta-barrel structure with two starch binding sites. These two sites are thought to differ functionally with site 1 acting as the initial starch recognition site and site 2 involved in the specific recognition of appropriate regions of starch. |
| 395557 | CBM_20 | 2.18e-33 | 513 | 602 | 3 | 92 | Starch binding domain. |
| 119437 | CBM20 | 8.49e-26 | 513 | 610 | 2 | 96 | The family 20 carbohydrate-binding module (CBM20), also known as the starch-binding domain, is found in a large number of starch degrading enzymes including alpha-amylase, beta-amylase, glucoamylase, and CGTase (cyclodextrin glucanotransferase). CBM20 is also present in proteins that have a regulatory role in starch metabolism in plants (e.g. alpha-amylase) or glycogen metabolism in mammals (e.g. laforin). CBM20 folds as an antiparallel beta-barrel structure with two starch binding sites. These two sites are thought to differ functionally with site 1 acting as the initial starch recognition site and site 2 involved in the specific recognition of appropriate regions of starch. |
| 99883 | CBM20_alpha_amylase | 1.79e-25 | 512 | 611 | 2 | 95 | Alpha-amylase, C-terminal CBM20 (carbohydrate-binding module, family 20) domain. This domain is found in several bacterial and fungal alpha-amylases including the maltopentaose-forming amylases (G5-amylases). Most alpha-amylases have, in addition to the C-terminal CBM20 domain, an N-terminal catalytic domain belonging to glycosyl hydrolase family 13, which hydrolyzes internal alpha-1,4-glucosidic bonds in starch and related saccharides, yielding maltotriose and maltose. Two types of soluble substrates are used by alpha-amylases including long substrates (e.g. amylose) and short substrates (e.g. maltodextrins or maltooligosaccharides). The CBM20 domain is found in a large number of starch degrading enzymes including alpha-amylase, beta-amylase, glucoamylase, and CGTase (cyclodextrin glucanotransferase). CBM20 is also present in proteins that have a regulatory role in starch metabolism in plants (e.g. alpha-amylase) or glycogen metabolism in mammals (e.g. laforin). CBM20 folds as an antiparallel beta-barrel structure with two starch binding sites. These two sites are thought to differ functionally with site 1 acting as the initial starch recognition site and site 2 involved in the specific recognition of appropriate regions of starch. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.77e-254 | 22 | 611 | 26 | 618 | |
| 1.77e-254 | 22 | 611 | 26 | 618 | |
| 1.77e-254 | 22 | 611 | 26 | 618 | |
| 1.77e-254 | 22 | 611 | 26 | 618 | |
| 2.58e-252 | 40 | 611 | 17 | 591 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.98e-224 | 42 | 611 | 17 | 616 | Structure of the catalytic domain of Aspergillus niger Glucoamylase [Aspergillus niger] |
|
| 2.13e-204 | 40 | 611 | 14 | 598 | Chain A, GLUCOAMYLASE [Trichoderma reesei],2VN7_A Chain A, GLUCOAMYLASE [Trichoderma reesei] |
|
| 7.24e-204 | 39 | 611 | 19 | 593 | Crystal structure of Penicillium oxalicum Glucoamylase [Penicillium oxalicum 114-2] |
|
| 2.91e-197 | 42 | 491 | 17 | 466 | Refined structure for the complex of acarbose with glucoamylase from Aspergillus awamori var. x100 to 2.4 angstroms resolution [Aspergillus awamori],1DOG_A REFINED STRUCTURE FOR THE COMPLEX OF 1-DEOXYNOJIRIMYCIN WITH GLUCOAMYLASE FROM (ASPERGILLUS AWAMORI) VAR. X100 TO 2.4 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION [Aspergillus awamori],1GLM_A REFINED CRYSTAL STRUCTURES OF GLUCOAMYLASE FROM ASPERGILLUS AWAMORI VAR. X100 [Aspergillus awamori],3GLY_A REFINED CRYSTAL STRUCTURES OF GLUCOAMYLASE FROM ASPERGILLUS AWAMORI VAR. X100 [Aspergillus awamori] |
|
| 3.01e-197 | 42 | 491 | 17 | 466 | GLUCOAMYLASE-471 COMPLEXED WITH ACARBOSE [Aspergillus awamori] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 611 | 1 | 610 | Glucoamylase ARB_02327-1 OS=Arthroderma benhamiae (strain ATCC MYA-4681 / CBS 112371) OX=663331 GN=ARB_02327-1 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 3.45e-248 | 16 | 611 | 16 | 612 | Glucoamylase OS=Aspergillus oryzae (strain ATCC 42149 / RIB 40) OX=510516 GN=glaA PE=2 SV=2 |
|
| 7.93e-229 | 42 | 611 | 41 | 639 | Glucoamylase OS=Aspergillus usamii OX=186680 GN=glaA PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 6.88e-225 | 42 | 611 | 41 | 639 | Glucoamylase I OS=Aspergillus kawachii OX=1069201 GN=gaI PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 2.33e-223 | 42 | 611 | 41 | 640 | Glucoamylase OS=Aspergillus awamori OX=105351 GN=GLAA PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
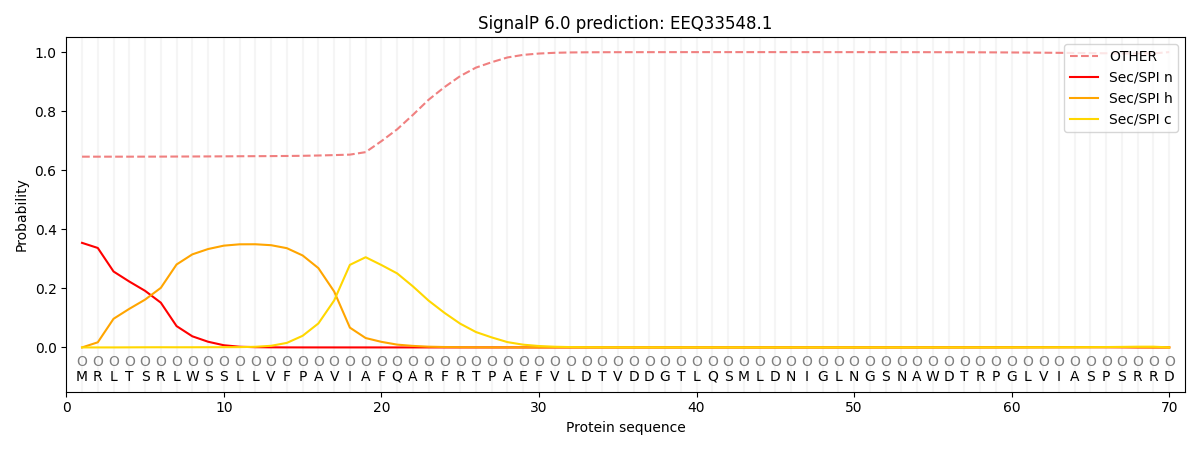
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.667125 | 0.332868 |
