You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: EAQ91088.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: EAQ91088.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Chaetomium globosum | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Sordariomycetes; ; Chaetomiaceae; Chaetomium; Chaetomium globosum | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | EAQ91088.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH7 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | conserved hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH131 | 466 | 653 | 2.1e-84 | 0.792156862745098 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 408085 | GH131_N | 1.79e-54 | 474 | 648 | 60 | 251 | Glycoside hydrolase 131 catalytic N-terminal domain. This is the N-terminal domain found in glycoside hydrolase family 131 (GH131A) protein observed in Coprinopsis cinerea. GH131A exhibits bifunctional exo-beta-1,3-/-1,6- and endo-beta-1,4 activity toward beta-glucan. This domain is catalytic in nature though the catalytic mechanism of C. cinerea GH131A is different from that of typical glycosidases that use a pair of carboxylic acid residues as the catalytic residues. In the case of GH131A, Glu98 and His218 may form a catalytic dyad and Glu98 may activate His218 during catalysis. |
| 340871 | MFS_SLC45_SUC | 4.52e-36 | 9 | 406 | 121 | 421 | Solute carrier family 45 and similar sugar transporters of the Major Facilitator Superfamily of transporters. This group includes the solute carrier 45 (SLC45) family as well as plant sucrose transporters (SUCs or SUTs) and similar proteins such as Schizosaccharomyces pombe general alpha-glucoside permease. the SLC45 family is composed of four (A1-A4) vertebrate proteins as well as related insect proteins such as Drosophila sucrose transporter SCRT or Slc45-1. Members of this group transport sucrose and other sugars like maltose into the cell, with the concomitant uptake of protons (symport system). Plant sucrose transporters are crucial to carbon partitioning, playing a key role in phloem loading/unloading. They play a key role in loading and unloading of sucrose into the phloem and as a result, they control sucrose distribution throughout the whole plant and drive the osmotic flow system in the phloem. They also play a role in the exchange of sucrose between beneficial symbionts (mycorrhiza and Rhizobium) as well as pathogens such as nematodes and parasitic fungi. There are nine sucrose transporter genes in Arabidopsis and five in rice. Vertebrate SLC45 family proteins have been implicated in the regulation of glucose homoeostasis in the brain (SLC45A1), with skin and hair pigmentation (SLC45A2), and with prostate cancer and myelination (SLC45A3). Mutations in SLC45A2, also called MATP (membrane-associated transporter protein) or melanoma antigen AIM1, cause oculocutaneous albinism type 4 (OCA4), an autosomal recessive disorder of melanin biosynthesis that results in congenital hypopigmentation of ocular and cutaneous tissues. The SLC45 family and related sugar transporters belong to the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins, which are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
| 273545 | GPH_sucrose | 4.02e-12 | 11 | 200 | 132 | 328 | GPH family sucrose/H+ symporter. This model represents sucrose/proton symporters, found in plants, from the Glycoside-Pentoside-Hexuronide (GPH)/cation symporter family. These proteins are predicted to have 12 transmembrane domains. Members may export sucrose (e.g. SUT1, SUT4) from green parts to the phloem for long-distance transport or import sucrose (e.g SUT2) to sucrose sinks such as the tap root of the carrot. |
| 349949 | MFS | 1.26e-04 | 16 | 202 | 107 | 264 | Major Facilitator Superfamily. The Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) is a large and diverse group of secondary transporters that includes uniporters, symporters, and antiporters. MFS proteins facilitate the transport across cytoplasmic or internal membranes of a variety of substrates including ions, sugar phosphates, drugs, neurotransmitters, nucleosides, amino acids, and peptides. They do so using the electrochemical potential of the transported substrates. Uniporters transport a single substrate, while symporters and antiporters transport two substrates in the same or in opposite directions, respectively, across membranes. MFS proteins are typically 400 to 600 amino acids in length, and the majority contain 12 transmembrane alpha helices (TMs) connected by hydrophilic loops. The N- and C-terminal halves of these proteins display weak similarity and may be the result of a gene duplication/fusion event. Based on kinetic studies and the structures of a few bacterial superfamily members, GlpT (glycerol-3-phosphate transporter), LacY (lactose permease), and EmrD (multidrug transporter), MFS proteins are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. Bacterial members function primarily for nutrient uptake, and as drug-efflux pumps to confer antibiotic resistance. Some MFS proteins have medical significance in humans such as the glucose transporter Glut4, which is impaired in type II diabetes, and glucose-6-phosphate transporter (G6PT), which causes glycogen storage disease when mutated. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.46e-226 | 9 | 640 | 208 | 883 | |
| 4.43e-119 | 470 | 655 | 75 | 260 | |
| 2.66e-111 | 470 | 654 | 77 | 261 | |
| 7.72e-105 | 470 | 656 | 82 | 270 | |
| 7.72e-105 | 470 | 656 | 82 | 270 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.55e-95 | 470 | 655 | 59 | 244 | Chain A, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE3_B Chain B, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE3_C Chain C, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE3_D Chain D, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE4_A Chain A, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE4_B Chain B, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE4_C Chain C, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina],4LE4_D Chain D, Beta-glucanase [Podospora anserina] |
|
| 6.60e-49 | 466 | 652 | 55 | 232 | Chain A, Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the glycoside hydrolase family 131 protein from Coprinopsis cinerea [Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130],3W9A_B Chain B, Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the glycoside hydrolase family 131 protein from Coprinopsis cinerea [Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130],3W9A_C Chain C, Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the glycoside hydrolase family 131 protein from Coprinopsis cinerea [Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130],3W9A_D Chain D, Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the glycoside hydrolase family 131 protein from Coprinopsis cinerea [Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.46e-48 | 10 | 406 | 160 | 543 | General alpha-glucoside permease OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=sut1 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 1.05e-08 | 9 | 189 | 156 | 342 | Sucrose transport protein SUC2 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=SUC2 PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 6.83e-08 | 242 | 431 | 98 | 249 | Probable MFS transporter cctQ OS=Talaromyces islandicus OX=28573 GN=cctQ PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 1.68e-07 | 9 | 207 | 158 | 353 | Sucrose transport protein SUC5 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=SUC5 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 3.43e-06 | 9 | 152 | 157 | 308 | Sucrose transport protein SUC9 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=SUC9 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
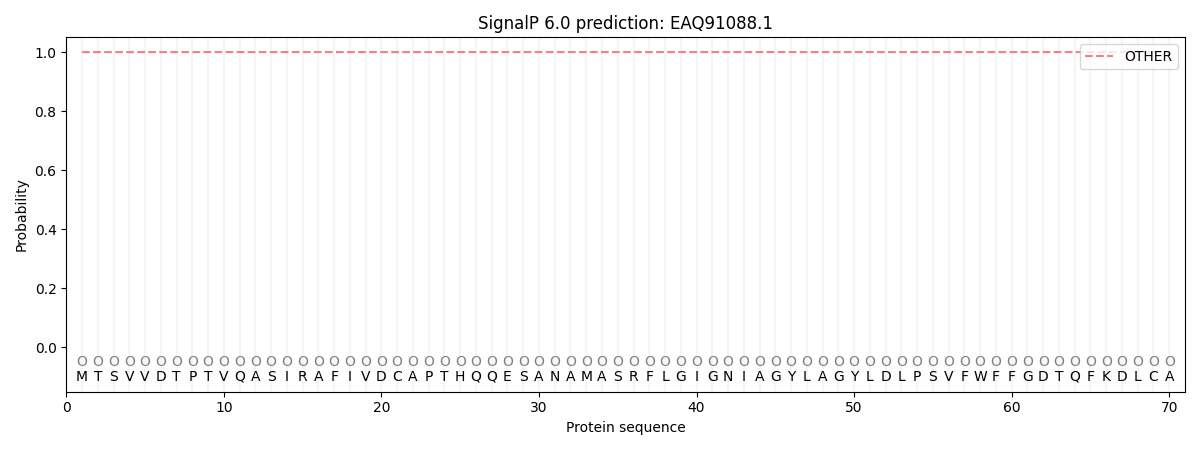
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.999994 | 0.000014 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
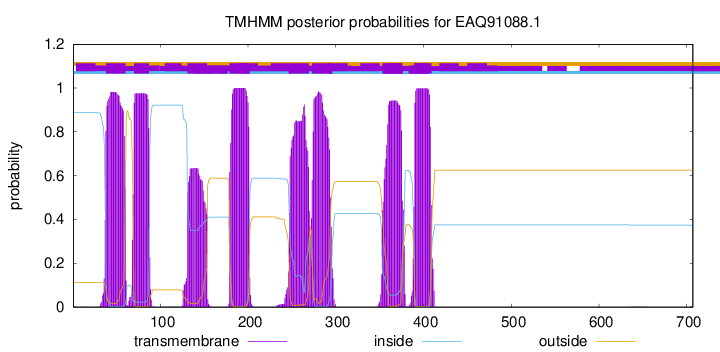
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 38 | 60 |
| 70 | 87 |
| 131 | 153 |
| 179 | 201 |
| 247 | 269 |
| 273 | 295 |
| 353 | 375 |
| 390 | 409 |
