You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: CPAR2_401310-T-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: CPAR2_401310-T-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
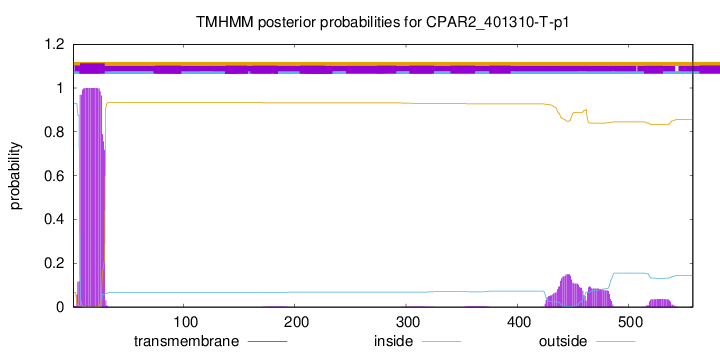
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Candida parapsilosis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Saccharomycetes; ; Debaryomycetaceae; Candida; Candida parapsilosis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | CPAR2_401310-T-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH76 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | UDP-glucose:ceramide glucosyltransferase, expression increased in fluconazole and voriconazole resistant strains | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 2.4.1.80:3 | 2.4.1.-:1 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT21 | 73 | 423 | 1.5e-92 | 0.9957081545064378 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 133012 | Glucosylceramide_synthase | 4.59e-54 | 73 | 423 | 1 | 196 | Glucosylceramide synthase catalyzes the first glycosylation step of glycosphingolipid synthesis. UDP-glucose:N-acylsphingosine D-glucosyltransferase (glucosylceramide synthase or ceramide glucosyltransferase) catalyzes the first glycosylation step of glycosphingolipid synthesis. Its product, glucosylceramide, serves as the core of more than 300 glycosphingolipids (GSL). GSLs are a group of membrane components that have the lipid portion embedded in the outer plasma membrane leaflet and the sugar chains extended to the outer environment. Several lines of evidence suggest the importance of GSLs in various cellular processes such as differentiation, adhesion, proliferation, and cell-cell recognition. In pathogenic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans, glucosylceramide serves as an antigen that elicits an antibody response in patients and it is essential for fungal growth in host extracellular environment. |
| 404400 | Glyco_transf_21 | 2.03e-13 | 149 | 421 | 9 | 174 | Glycosyl transferase family 21. This is a family of ceramide beta-glucosyltransferases - EC:2.4.1.80. |
| 224136 | BcsA | 8.01e-05 | 75 | 192 | 56 | 159 | Glycosyltransferase, catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase and poly-beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine synthase [Cell motility]. |
| 404520 | Glyco_tranf_2_3 | 5.32e-04 | 75 | 207 | 4 | 134 | Glycosyltransferase like family 2. Members of this family of prokaryotic proteins include putative glucosyltransferase, which are involved in bacterial capsule biosynthesis. |
| 341145 | RMtype1_S_EcoJA65PI-TRD1-CR1_like | 0.005 | 66 | 100 | 84 | 118 | Type I restriction-modification system specificity (S) subunit Target Recognition Domain-ConseRved domain (TRD-CR), similar to S.EcoJA65PI TRD1-CR1, S.Fco49512ORF2615P TRD1-CR1, and S.SonIV TRD2-CR2. Escherichia coli UCD_JA65_pb S subunit (S.EcoJA65PI) recognizes 5'... AGCANNNNNNTGA ... 3' while Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 S subunit (S.SonIV) recognizes 5'... TACNNNNNNGTNGT ... 3'. The recognition sequence of Flavobacterium columnare S subunit (S.Fco49512ORF2615P) is undetermined. The restriction-modification (RM) system S subunit consists of two variable target recognition domains (TRD1 and 2) and two conserved regions (CR1 and CR2) which separate the TRDs. The TRDs each bind to different specific sequences in the DNA. For example, S.EcoJA65PI TRD1 recognizes AGCA/TGCT and S.EcoJA65PI TRD2 recognizes TCA/TGA; S.SonIV TRD1 recognizes TAC/GTA and S.SonIV TRD2 recognizes ACNAC/GTNGT. RM systems protect a bacterial cell against invasion of foreign DNA by endonucleolytic cleavage of DNA that lacks a site specific modification. The host genome is protected from cleavage by methylation of specific nucleotides in the target sites. In type I systems, both restriction and modification activities are present in one enzyme complex composed of one DNA specificity (S) subunit (this family), two modification (M) subunits and two restriction (R) subunits. This model contains both TRD1-CR1 and TRD2-CR2. It may also include TRD-CR-like sequence-recognition domains of various type II restriction enzymes and methyltransferases and type I DNA methyltransferases. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 558 | 1 | 558 | |
| 0.0 | 2 | 558 | 7 | 560 | |
| 4.06e-238 | 1 | 558 | 8 | 544 | |
| 5.77e-237 | 9 | 558 | 16 | 540 | |
| 2.07e-205 | 3 | 558 | 12 | 500 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.22e-239 | 1 | 558 | 8 | 544 | Ceramide glucosyltransferase OS=Candida albicans (strain SC5314 / ATCC MYA-2876) OX=237561 GN=HSX11 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 2.94e-140 | 12 | 558 | 49 | 509 | Ceramide glucosyltransferase OS=Komagataella phaffii (strain GS115 / ATCC 20864) OX=644223 GN=PAS_chr3_0357 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.56e-76 | 75 | 558 | 53 | 501 | Ceramide glucosyltransferase OS=Gibberella zeae (strain ATCC MYA-4620 / CBS 123657 / FGSC 9075 / NRRL 31084 / PH-1) OX=229533 GN=GCS1 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 6.32e-72 | 75 | 558 | 54 | 476 | Ceramide glucosyltransferase OS=Magnaporthe oryzae (strain 70-15 / ATCC MYA-4617 / FGSC 8958) OX=242507 GN=MGG_10668 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 9.81e-60 | 74 | 549 | 56 | 437 | Ceramide glucosyltransferase OS=Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii serotype A (strain H99 / ATCC 208821 / CBS 10515 / FGSC 9487) OX=235443 GN=GCS1 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
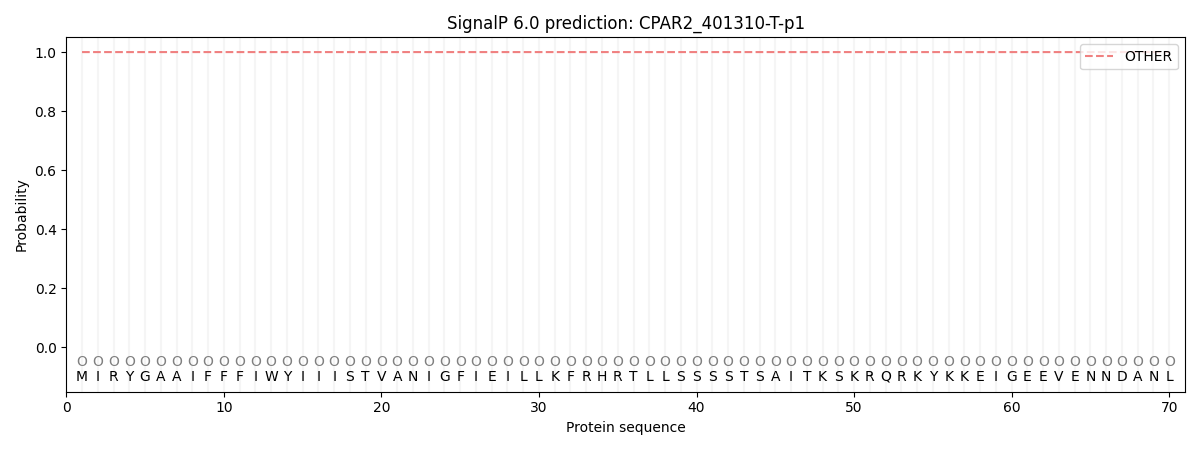
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000048 | 0.000010 |