You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: CIMG_02314-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: CIMG_02314-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
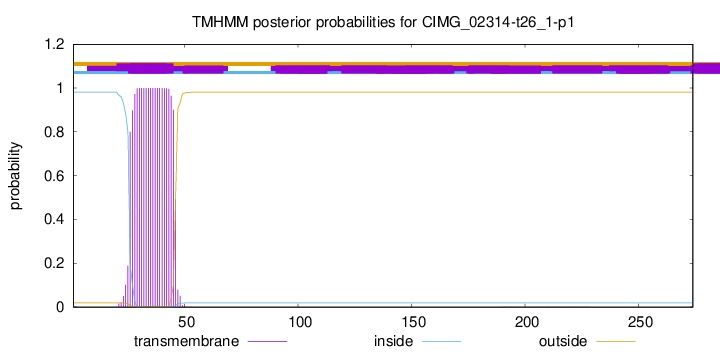
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Coccidioides immitis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Onygenaceae; Coccidioides; Coccidioides immitis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | CIMG_02314-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE4 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | polysaccharide deacetylase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE4 | 68 | 196 | 2.7e-19 | 0.9307692307692308 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200581 | CE4_NodB_like_2 | 6.23e-83 | 72 | 259 | 1 | 190 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of uncharacterized chitin deacetylases and hypothetical proteins. This family includes some uncharacterized chitin deacetylases and hypothetical proteins, mainly from eukaryotes. Although their biological function is unknown, members in this family show high sequence homology to the catalytic NodB homology domain of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum chitin deacetylase (endo-chitin de-N-acetylase, ClCDA, EC 3.5.1.41), which catalyzes the hydrolysis of N-acetamido groups of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in chitin, converting it to chitosan in fungal cell walls. Like ClCDA, this family is a member the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. |
| 213022 | CE4_NodB_like_6s_7s | 3.44e-39 | 72 | 247 | 1 | 171 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of rhizobial NodB-like proteins. This family belongs to the large and functionally diverse carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily, whose members show strong sequence similarity with some variability due to their distinct carbohydrate substrates. It includes many rhizobial NodB chitooligosaccharide N-deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.-)-like proteins, mainly from bacteria and eukaryotes, such as chitin deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.41), bacterial peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.-), and acetylxylan esterases (EC 3.1.1.72), which catalyze the N- or O-deacetylation of substrates such as acetylated chitin, peptidoglycan, and acetylated xylan. All members of this family contain a catalytic NodB homology domain with the same overall topology and a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold with 6- or 7 strands. Their catalytic activity is dependent on the presence of a divalent cation, preferably cobalt or zinc, and they employ a conserved His-His-Asp zinc-binding triad closely associated with the conserved catalytic base (aspartic acid) and acid (histidine) to carry out acid/base catalysis. Several family members show diversity both in metal ion specificities and in the residues that coordinate the metal. |
| 200578 | CE4_CtAXE_like | 1.88e-32 | 72 | 259 | 1 | 180 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of Clostridium thermocellum acetylxylan esterase and its bacterial homologs. This family is represented by Clostridium thermocellum acetylxylan esterase (CtAXE, EC 3.1.1.72), a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. CtAXE deacetylates O-acetylated xylan, a key component of plant cell walls. It shows no detectable activity on generic esterase substrates including para-nitrophenyl acetate. It is specific for sugar-based substrates and will precipitate acetylxylan, as a consequence of deacetylation. CtAXE is a monomeric protein containing a catalytic NodB homology domain with the same overall topology and a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold as other CE4 esterases. However, due to differences in the topography of the substrate-binding groove, the chemistry of the active center, and metal ion coordination, CtAXE has different metal ion preference and lacks activity on N-acetyl substrates. It is significantly activated by Co2+. Moreover, CtAXE displays distinctly different ligand coordination to the metal ion, utilizing an aspartate, a histidine, and four water molecules, as opposed to the conserved His-His-Asp zinc-binding triad of other CE4 esterases. |
| 200574 | CE4_BsYlxY_like | 2.77e-29 | 69 | 260 | 3 | 188 | Putative catalytic NodB homology domain of uncharacterized protein YlxY from Bacillus subtilis and its bacterial homologs. The Bacillus subtilis genome contains six polysaccharide deacetylase gene homologs: pdaA, pdaB (previously known as ybaN), yheN, yjeA, yxkH and ylxY. This family is represented by Bacillus subtilis putative polysaccharide deacetylase BsYlxY, encoded by the ylxY gene, which is a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. Although its biological function still remains unknown, BsYlxY shows high sequence homology to the catalytic domain of Bacillus subtilis pdaB gene encoding a putative polysaccharide deacetylase (BsPdaB), which is essential for the maintenance of spores after the late stage of sporulation and is highly conserved in spore-forming bacteria. However, disruption of the ylxY gene in B. subtilis did not cause any sporulation defect. Moreover, the Asp residue in the classical His-His-Asp zinc-binding motif of CE4 esterases is mutated to a Val residue in this family. Other catalytically relevant residues of CE4 esterases are also not conserved, which suggest that members of this family may be inactive. |
| 396211 | Polysacc_deac_1 | 6.43e-29 | 66 | 195 | 1 | 124 | Polysaccharide deacetylase. This domain is found in polysaccharide deacetylase. This family of polysaccharide deacetylases includes NodB (nodulation protein B from Rhizobium) which is a chitooligosaccharide deacetylase. It also includes chitin deacetylase from yeast, and endoxylanases which hydrolyzes glucosidic bonds in xylan. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.57e-97 | 11 | 264 | 932 | 1185 | |
| 2.84e-96 | 18 | 260 | 5 | 249 | |
| 2.84e-96 | 18 | 260 | 5 | 249 | |
| 1.45e-95 | 38 | 260 | 11 | 235 | |
| 1.45e-95 | 38 | 260 | 11 | 235 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.63e-27 | 50 | 262 | 83 | 302 | Chain A, Predicted xylanase/chitin deacetylase [Caldanaerobacter subterraneus subsp. tengcongensis MB4] |
|
| 5.78e-21 | 55 | 264 | 68 | 271 | Crystal structure of a BA3943 mutant,a CE4 family pseudoenzyme with restored enzymatic activity. [Bacillus anthracis] |
|
| 6.94e-19 | 55 | 264 | 69 | 272 | Crystal structure of a BA3943 mutant,a CE4 family pseudoenzyme [Bacillus anthracis] |
|
| 1.21e-18 | 56 | 264 | 41 | 246 | Structure of a family 4 carbohydrate esterase from Bacillus anthracis [Bacillus anthracis str. Ames] |
|
| 3.95e-18 | 55 | 264 | 69 | 272 | Chain A, Putative polysaccharide deacetylase [Bacillus anthracis] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.83e-25 | 63 | 260 | 13 | 209 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase BC_3618 OS=Bacillus cereus (strain ATCC 14579 / DSM 31 / CCUG 7414 / JCM 2152 / NBRC 15305 / NCIMB 9373 / NCTC 2599 / NRRL B-3711) OX=226900 GN=BC_3618 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 4.36e-18 | 70 | 262 | 65 | 256 | Uncharacterized 30.6 kDa protein in fumA 3'region OS=Geobacillus stearothermophilus OX=1422 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 3.55e-16 | 69 | 260 | 37 | 228 | Chitin deacetylase OS=Emericella nidulans (strain FGSC A4 / ATCC 38163 / CBS 112.46 / NRRL 194 / M139) OX=227321 GN=cda PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 4.90e-15 | 55 | 262 | 113 | 314 | Uncharacterized protein YlxY OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=ylxY PE=3 SV=2 |
|
| 9.87e-15 | 72 | 260 | 268 | 448 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase OS=Streptococcus pneumoniae (strain ATCC BAA-255 / R6) OX=171101 GN=pgdA PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
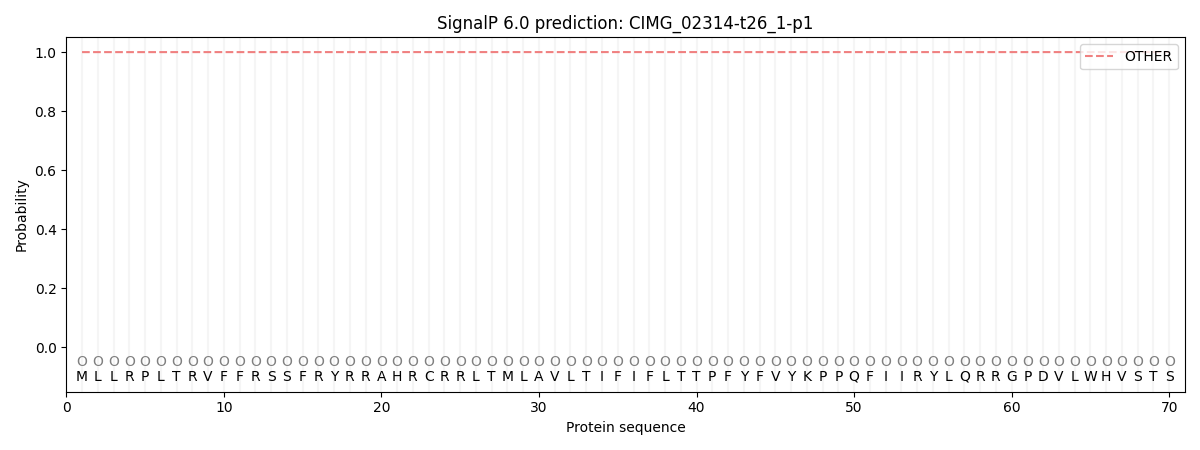
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000013 | 0.000015 |