You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: CCG81822.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: CCG81822.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Taphrina deformans | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Taphrinomycetes; ; Taphrinaceae; Taphrina; Taphrina deformans | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | CCG81822.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH135 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Glyco_trans_2-like domain-containing protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT2 | 394 | 607 | 3.9e-41 | 0.8883248730964467 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 404513 | Glyco_trans_2_3 | 1.47e-40 | 393 | 599 | 1 | 194 | Glycosyl transferase family group 2. Members of this family of prokaryotic proteins include putative glucosyltransferases, which are involved in bacterial capsule biosynthesis. |
| 224136 | BcsA | 4.57e-12 | 390 | 636 | 137 | 362 | Glycosyltransferase, catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase and poly-beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine synthase [Cell motility]. |
| 133043 | CESA_CelA_like | 1.51e-08 | 243 | 511 | 1 | 198 | CESA_CelA_like are involved in the elongation of the glucan chain of cellulose. Family of proteins related to Agrobacterium tumefaciens CelA and Gluconacetobacter xylinus BscA. These proteins are involved in the elongation of the glucan chain of cellulose, an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues. They are putative catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase, which is a glycosyltransferase using UDP-glucose as the substrate. The catalytic subunit is an integral membrane protein with 6 transmembrane segments and it is postulated that the protein is anchored in the membrane at the N-terminal end. |
| 133045 | CESA_like | 1.53e-07 | 390 | 499 | 78 | 180 | CESA_like is the cellulose synthase superfamily. The cellulose synthase (CESA) superfamily includes a wide variety of glycosyltransferase family 2 enzymes that share the common characteristic of catalyzing the elongation of polysaccharide chains. The members include cellulose synthase catalytic subunit, chitin synthase, glucan biosynthesis protein and other families of CESA-like proteins. Cellulose synthase catalyzes the polymerization reaction of cellulose, an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues in plants, most algae, some bacteria and fungi, and even some animals. In bacteria, algae and lower eukaryotes, there is a second unrelated type of cellulose synthase (Type II), which produces acylated cellulose, a derivative of cellulose. Chitin synthase catalyzes the incorporation of GlcNAc from substrate UDP-GlcNAc into chitin, which is a linear homopolymer of beta-(1,4)-linked GlcNAc residues and Glucan Biosynthesis protein catalyzes the elongation of beta-1,2 polyglucose chains of Glucan. |
| 404520 | Glyco_tranf_2_3 | 3.52e-04 | 390 | 539 | 87 | 228 | Glycosyltransferase like family 2. Members of this family of prokaryotic proteins include putative glucosyltransferase, which are involved in bacterial capsule biosynthesis. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.97e-207 | 24 | 769 | 131 | 872 | |
| 2.99e-206 | 24 | 769 | 133 | 874 | |
| 2.99e-206 | 24 | 769 | 133 | 874 | |
| 2.99e-206 | 24 | 769 | 133 | 874 | |
| 6.55e-206 | 24 | 769 | 136 | 877 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000043 | 0.000000 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
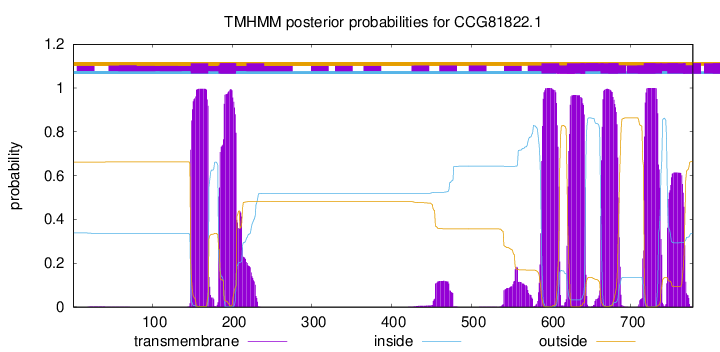
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 746 | 768 |
| 148 | 170 |
| 185 | 204 |
| 588 | 610 |
| 620 | 642 |
| 662 | 684 |
| 717 | 739 |
