You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: CC1G_05516-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: CC1G_05516-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Coprinopsis cinerea | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Basidiomycota; Agaricomycetes; ; Psathyrellaceae; Coprinopsis; Coprinopsis cinerea | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | CC1G_05516-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH10 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | alpha amylase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 1408451; End:1411129 Strand: + | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MKLPQLWTVS LSLFGLFLAL TYASPAPQHV KRAPQVSLIN HSYSNAVLSG TINVQNIAYS | 60 |
| KVVEVVWAVG DSWSDSQIIP ATYTSSGSNN FETWAFSGRA SGATQFYIRY TVSGQTYYDP | 120 |
| GNYQNHQVNR PPSNSQPPVV TSSTAVVPPP TSTTAPAPPP TGTVAPGNLP PIIPANIPYE | 180 |
| APATPPTGCN NFNGLDNCQG NSHEMAASSE RRRWQTPPRG DPAHEESFQD YSHLVGYADI | 240 |
| QYNSARNAAV VTVNAAHKEG ATLTYSFNGA EQSSPIFQVT NSLQTALAIT VTSSDGKKLV | 300 |
| LEPINFFWQH QSLSAAQSSF NNGQKGGIVE LFGWPWNDIA KECEFLGKAG YMGVKVWAPN | 360 |
| EHVWGSHYYE PDGQFRPWYF VYQPVSYRLQ SRMGTREELR NMINSCRRAG VRVYADAVIN | 420 |
| HMSGQGTDIQ NHRVGNCELY SGHNATENSP YYTSGNTFLI NPFTGTRPTL EFPAVPYGPT | 480 |
| DFHCERSLNS WTDGIVVTKG WLVGLTDLNT SKPYVQDRIA TYLTDLLSIG FSGFRVDAAK | 540 |
| HIGPQDMAQI LARLKNKMGG SLPDDFITWM EVIIGGEAAL MACSGGEWSW YTNFDNKMRA | 600 |
| AGLSNEDIQK VKIWSSDYPK EMPICGHWIL PPSRFAIQND DHDQQNDGSS SRDMADKGSV | 660 |
| LIKEKNVAAH RNFEVNLFAR RDNDWHIKLI LSSYMFMPNG GSGFPDGLSD CSLHYTGNQN | 720 |
| INGCKGVPKD TAYVANACGY TMQPGKYTRP HRDISIINAM RGWVGLGPTN ANALGIPGCQ | 780 |
| 780 |
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH13 | 350 | 649 | 9.3e-53 | 0.9182156133828996 |
| CBM21 | 38 | 128 | 9.4e-16 | 0.9345794392523364 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200456 | AmyAc_bac_euk_AmyA | 1.34e-142 | 325 | 766 | 1 | 329 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in bacterial and eukaryotic Alpha amylases (also called 1,4-alpha-D-glucan-4-glucanohydrolase). AmyA (EC 3.2.1.1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages of glycogen, starch, related polysaccharides, and some oligosaccharides. This group includes AmyA proteins from bacteria, fungi, mammals, insects, mollusks, and nematodes. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| 200454 | AmyAc_bac1_AmyA | 7.47e-35 | 332 | 576 | 8 | 213 | Alpha amylase catalytic domain found in bacterial Alpha-amylases (also called 1,4-alpha-D-glucan-4-glucanohydrolase). AmyA (EC 3.2.1.1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-(1,4) glycosidic linkages of glycogen, starch, related polysaccharides, and some oligosaccharides. This group includes Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Cyanobacteria. The Alpha-amylase family comprises the largest family of glycoside hydrolases (GH), with the majority of enzymes acting on starch, glycogen, and related oligo- and polysaccharides. These proteins catalyze the transformation of alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkages with retention of the anomeric center. The protein is described as having 3 domains: A, B, C. A is a (beta/alpha) 8-barrel; B is a loop between the beta 3 strand and alpha 3 helix of A; C is the C-terminal extension characterized by a Greek key. The majority of the enzymes have an active site cleft found between domains A and B where a triad of catalytic residues (Asp, Glu and Asp) performs catalysis. Other members of this family have lost the catalytic activity as in the case of the human 4F2hc, or only have 2 residues that serve as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, such as Thermus A4 beta-galactosidase with 2 Glu residues (GH42) and human alpha-galactosidase with 2 Asp residues (GH31). The family members are quite extensive and include: alpha amylase, maltosyltransferase, cyclodextrin glycotransferase, maltogenic amylase, neopullulanase, isoamylase, 1,4-alpha-D-glucan maltotetrahydrolase, 4-alpha-glucotransferase, oligo-1,6-glucosidase, amylosucrase, sucrose phosphorylase, and amylomaltase. |
| 214758 | Aamy | 1.68e-21 | 319 | 426 | 6 | 99 | Alpha-amylase domain. |
| 397445 | CBM_21 | 2.03e-17 | 32 | 129 | 3 | 113 | Carbohydrate/starch-binding module (family 21). This family consists of several eukaryotic proteins that are thought to be involved in the regulation of glycogen metabolism. For instance, the mouse PTG protein has been shown to interact with glycogen synthase, phosphorylase kinase, phosphorylase a: these three enzymes have key roles in the regulation of glycogen metabolism. PTG also binds the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1C) and localizes it to glycogen. Subsets of similar interactions have been observed with several other members of this family, such as the yeast PIG1, PIG2, GAC1 and GIP2 proteins. While the precise function of these proteins is not known, they may serve a scaffold function, bringing together the key enzymes in glycogen metabolism. This family is a carbohydrate binding domain. |
| 236518 | PRK09441 | 9.12e-12 | 392 | 545 | 76 | 241 | cytoplasmic alpha-amylase; Reviewed |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGX42980.1|CBM21|GH13 | 0.0 | 31 | 780 | 37 | 790 |
| QRW16798.1|CBM21|GH13 | 4.63e-255 | 35 | 779 | 34 | 783 |
| QRV88491.1|CBM21|GH13 | 1.99e-253 | 36 | 777 | 79 | 840 |
| QRV73700.1|CBM21|GH13 | 2.81e-253 | 36 | 777 | 79 | 840 |
| QRW02641.1|CBM21|GH13 | 2.81e-253 | 36 | 777 | 79 | 840 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1Q4N_X | 2.12e-44 | 321 | 645 | 4 | 302 | Chain X, Alpha-amylase, salivary [Homo sapiens] |
| 3DHP_A | 9.86e-44 | 321 | 645 | 4 | 302 | Chain A, Alpha-amylase 1 [Homo sapiens] |
| 1JXK_A | 4.20e-43 | 321 | 645 | 4 | 302 | Role of ethe mobile loop in the mehanism of human salivary amylase [Homo sapiens],1MFU_A Probing the role of a mobile loop in human salivary amylase: Structural studies on the loop-deleted mutant [Homo sapiens] |
| 1C8Q_A | 4.58e-43 | 321 | 645 | 4 | 302 | STRUCTURE SOLUTION AND REFINEMENT OF THE RECOMBINANT HUMAN SALIVARY AMYLASE [Homo sapiens],1MFV_A Probing the role of a mobile loop in human slaivary amylase: Structural studies on the loop-deleted enzyme [Homo sapiens],1SMD_A HUMAN SALIVARY AMYLASE [Homo sapiens],1XV8_A Crystal Structure of Human Salivary Alpha-Amylase Dimer [Homo sapiens],1XV8_B Crystal Structure of Human Salivary Alpha-Amylase Dimer [Homo sapiens] |
| 3BLK_A | 4.58e-43 | 321 | 645 | 4 | 302 | Chain A, Alpha-amylase 1 [Homo sapiens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|P19961|AMY2B_HUMAN | 5.62e-44 | 299 | 645 | 5 | 317 | Alpha-amylase 2B OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=AMY2B PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|P04746|AMYP_HUMAN | 4.83e-43 | 299 | 645 | 5 | 317 | Pancreatic alpha-amylase OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=AMY2A PE=1 SV=2 |
| sp|P00688|AMYP_MOUSE | 6.24e-43 | 299 | 645 | 5 | 314 | Pancreatic alpha-amylase OS=Mus musculus OX=10090 GN=Amy2 PE=1 SV=2 |
| sp|P0DTE7|AMY1B_HUMAN | 8.92e-43 | 300 | 645 | 6 | 317 | Alpha-amylase 1B OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=AMY1B PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|P0DTE8|AMY1C_HUMAN | 8.92e-43 | 300 | 645 | 6 | 317 | Alpha-amylase 1C OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=AMY1C PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
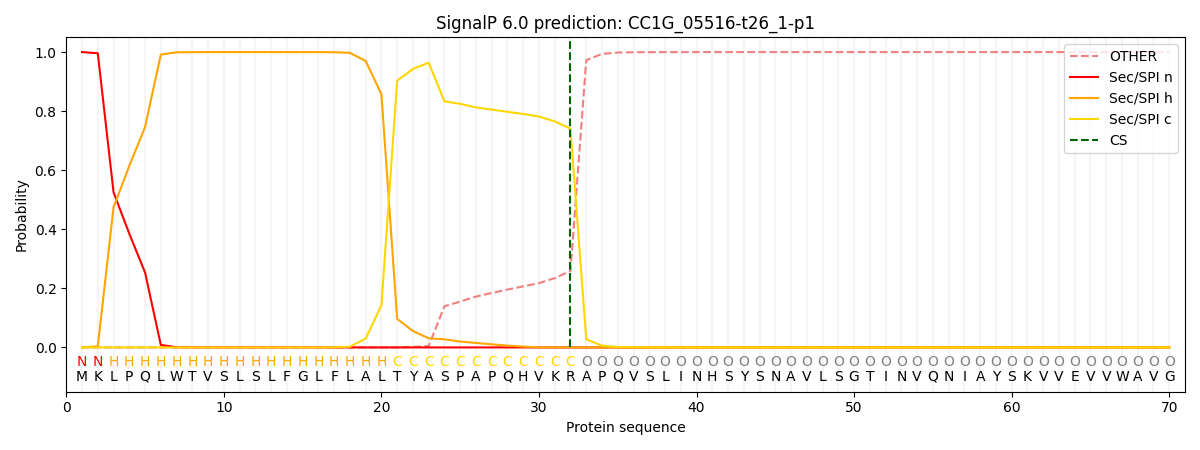
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000188 | 0.999820 | CS pos: 32-33. Pr: 0.7407 |
