You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: CAP99360:RNA-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: CAP99360:RNA-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
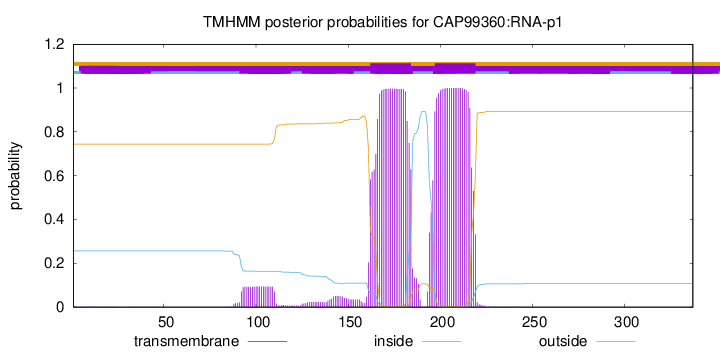
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Penicillium rubens | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Penicillium; Penicillium rubens | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | CAP99360:RNA-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT62 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | unspecified product | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT109 | 11 | 328 | 6e-121 | 0.7664233576642335 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 409190 | PGAP4-like_fungal | 1.81e-149 | 11 | 298 | 87 | 375 | uncharacterized fungal proteins similar to Post-GPI attachment to proteins factor 4. This subfamily contains uncharacterized fungal proteins with similarity to animal post-GPI attachment to proteins factor 4 (PGAP4), also known as post-GPI attachment to proteins GalNAc transferase 4 or transmembrane protein 246 (TMEM246). PGAP4 has been shown to be a Golgi-resident GPI-GalNAc transferase. Many eukaryotic proteins are anchored to the cell surface through glycolipid glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI). GPIs have a conserved core but exhibit diverse N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) modifications. PGAP4 knockout cells lose GPI-GalNAc structures. PGAP4 is most likely involved in the initial steps of GPI-GalNAc biosynthesis. In contrast to other Golgi glycotransferases, it contains three transmembrane domains. Proteins from this subfamily contain the putative catalytic site of PGAP4 and may have similar activities. |
| 409189 | PGAP4-like | 3.96e-36 | 13 | 295 | 85 | 361 | Post-GPI attachment to proteins factor 4 and similar proteins. This family includes post-GPI attachment to proteins factor 4 (PGAP4), also known as post-GPI attachment to proteins GalNAc transferase 4 or transmembrane protein 246 (TMEM246). PGAP4 has been shown to be a Golgi-resident GPI-GalNAc transferase. Many eukaryotic proteins are anchored to the cell surface through glycolipid glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI). GPIs have a conserved core but exhibit diverse N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) modifications. PGAP4 knockout cells lose GPI-GalNAc structures. PGAP4 is most likely involved in the initial steps of GPI-GalNAc biosynthesis. In contrast to other Golgi glycotransferases, it contains three transmembrane domains. This family also includes uncharacterized fungal proteins with similarity to PGAP4. |
| 409191 | PGAP4 | 8.47e-20 | 73 | 295 | 148 | 376 | Post-GPI attachment to proteins factor 4. Post-GPI attachment to proteins factor 4 (PGAP4), also known as post-GPI attachment to proteins GalNAc transferase 4 or transmembrane protein 246 (TMEM246), has been shown to be a Golgi-resident GPI-GalNAc transferase. Many eukaryotic proteins are anchored to the cell surface through glycolipid glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI). GPIs have a conserved core but exhibit diverse N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) modifications. PGAP4 knockout cells lose GPI-GalNAc structures. PGAP4 is most likely involved in the initial steps of GPI-GalNAc biosynthesis. In contrast to other Golgi glycotransferases (GTs), it contains three transmembrane domains. Structural modeling suggests that PGAP4 adopts a GT-A fold split by an insertion of tandem transmembrane domains. |
| 225843 | COG3306 | 6.06e-06 | 16 | 231 | 1 | 210 | Glycosyltransferase involved in LPS biosynthesis, GR25 family [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
| 133474 | Glyco_transf_25 | 1.85e-05 | 24 | 120 | 6 | 99 | Glycosyltransferase family 25 [lipooligosaccharide (LOS) biosynthesis protein] is a family of glycosyltransferases involved in LOS biosynthesis. The members include the beta(1,4) galactosyltransferases: Lgt2 of Moraxella catarrhalis, LgtB and LgtE of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Lic2A of Haemophilus influenzae. M. catarrhalis Lgt2 catalyzes the addition of galactose (Gal) to the growing chain of LOS on the cell surface. N. gonorrhoeae LgtB and LgtE link Gal-beta(1,4) to GlcNAc (N-acetylglucosamine) and Glc (glucose), respectively. The genes encoding LgtB and LgtE are two genes of a five gene locus involved in the synthesis of gonococcal LOS. LgtE is believed to perform the first step in LOS biosynthesis. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.50e-253 | 1 | 337 | 1 | 337 | |
| 2.12e-128 | 12 | 323 | 111 | 420 | |
| 3.42e-128 | 11 | 327 | 111 | 426 | |
| 3.42e-128 | 11 | 327 | 111 | 426 | |
| 2.77e-127 | 11 | 327 | 111 | 426 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000028 | 0.000000 |