You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: An02g14160-T-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: An02g14160-T-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
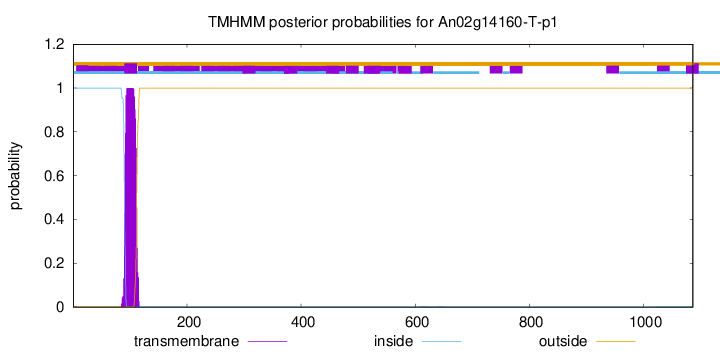
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus niger | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus niger | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | An02g14160-T-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | AA8|AA3|AA3 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Has domain(s) with predicted nucleic acid binding activity | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT69 | 144 | 409 | 1.2e-86 | 0.99581589958159 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 403053 | CAP59_mtransfer | 1.75e-102 | 144 | 403 | 1 | 225 | Cryptococcal mannosyltransferase 1. The capsule of pathogenic fungi is a complex polysaccharide whose formation is determined by a number of enzymes including, most importantly, alpha-1,3-mannosyltransferase 1, EC:2.4.1.-. |
| 240707 | RRM1_3_MRN1 | 4.61e-08 | 908 | 964 | 1 | 57 | RNA recognition motif 1 (RRM1) and 3 (RRM3) found in RNA-binding protein MRN1 and similar proteins. This subfamily corresponds to the RRM1 and RRM3 of MRN1, also termed multicopy suppressor of RSC-NHP6 synthetic lethality protein 1, or post-transcriptional regulator of 69 kDa, which is an RNA-binding protein found in yeast. Although its specific biological role remains unclear, MRN1 might be involved in translational regulation. Members in this family contain four copies of conserved RNA recognition motif (RRM), also known as RBD (RNA binding domain) or RNP (ribonucleoprotein domain). |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 1087 | 1 | 1087 | |
| 0.0 | 52 | 1087 | 46 | 984 | |
| 0.0 | 49 | 534 | 9 | 494 | |
| 0.0 | 49 | 534 | 9 | 494 | |
| 2.41e-239 | 51 | 530 | 46 | 541 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.999973 | 0.000067 |