You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: AYO42799.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: AYO42799.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
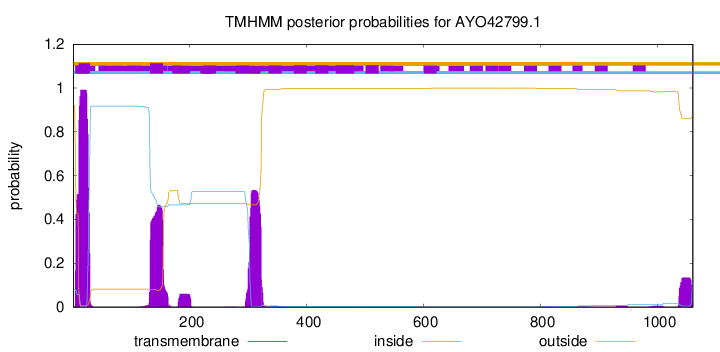
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Malassezia restricta | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Basidiomycota; Malasseziomycetes; ; Malasseziaceae; Malassezia; Malassezia restricta | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | AYO42799.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH8 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | putative unsaturated glucuronyl hydrolase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH105 | 759 | 995 | 2.3e-26 | 0.6716867469879518 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400034 | Glyco_hydro_88 | 2.96e-13 | 761 | 972 | 96 | 292 | Glycosyl Hydrolase Family 88. Unsaturated glucuronyl hydrolase catalyzes the hydrolytic release of unsaturated glucuronic acids from oligosaccharides (EC:3.2.1.-) produced by the reactions of polysaccharide lyases. |
| 226678 | YesR | 3.68e-13 | 761 | 1023 | 103 | 338 | Rhamnogalacturonyl hydrolase YesR [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| 341250 | LC-FACS_euk | 3.88e-09 | 375 | 555 | 249 | 399 | Eukaryotic long-chain fatty acid CoA synthetase (LC-FACS). The members of this family are eukaryotic fatty acid CoA synthetases that activate fatty acids with chain lengths of 12 to 20. LC-FACS catalyzes the formation of fatty acyl-CoA in a two-step reaction: the formation of a fatty acyl-AMP molecule as an intermediate, and the formation of a fatty acyl-CoA. This is a required step before free fatty acids can participate in most catabolic and anabolic reactions. Organisms tend to have multiple isoforms of LC-FACS genes with multiple splice variants. For example, nine genes are found in Arabidopsis and six genes are expressed in mammalian cells. |
| 395403 | AMP-binding | 3.97e-06 | 384 | 559 | 255 | 402 | AMP-binding enzyme. |
| 341228 | AFD_class_I | 3.99e-06 | 385 | 559 | 98 | 241 | Adenylate forming domain, Class I, also known as the ANL superfamily. This family is known as the ANL (acyl-CoA synthetases, the NRPS adenylation domains, and the Luciferase enzymes) superfamily. It includes acyl- and aryl-CoA ligases, as well as the adenylation domain of nonribosomal peptide synthetases and firefly luciferases.The adenylate-forming enzymes catalyze an ATP-dependent two-step reaction to first activate a carboxylate substrate as an adenylate and then transfer the carboxylate to the pantetheine group of either coenzyme A or an acyl-carrier protein. The active site of the domain is located at the interface of a large N-terminal subdomain and a smaller C-terminal subdomain. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 1061 | 1 | 1061 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 1061 | 1 | 1061 | |
| 0.0 | 3 | 1033 | 4 | 1045 | |
| 6.25e-156 | 8 | 1014 | 6 | 1025 | |
| 3.37e-153 | 8 | 1014 | 7 | 1023 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
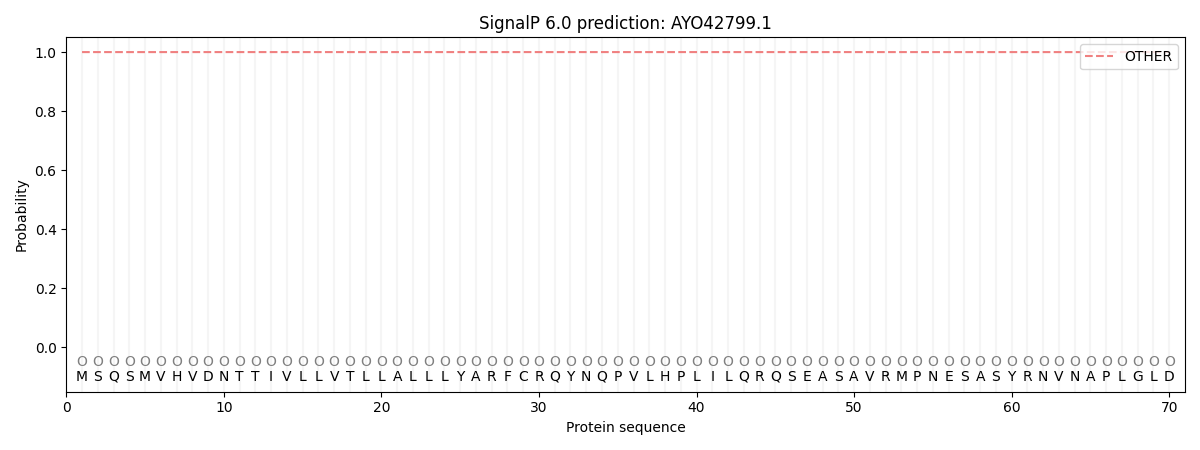
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000051 | 0.000001 |