You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: ATY64613.1
You are here: Home > Sequence: ATY64613.1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
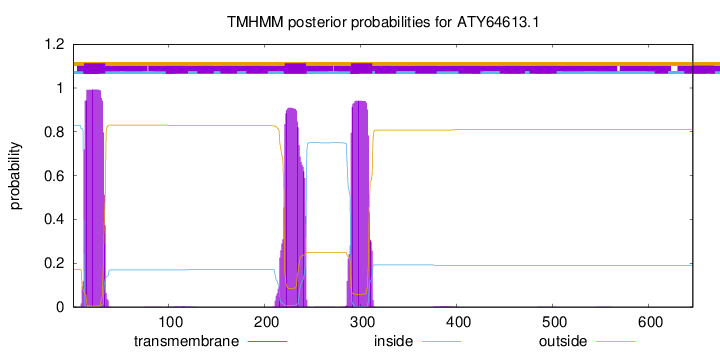
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Cordyceps militaris | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Sordariomycetes; ; Cordycipitaceae; Cordyceps; Cordyceps militaris | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | ATY64613.1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT71 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Glycosyltransferase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 2941962; End:2944204 Strand: - | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MAMGFLKKAS RLALLVSAAS TLFLFLSLYH ILSPSIASPE RLKAAADTVD HCHTPRNNTK | 60 |
| PRIPNKIHQI WKDKDLSTYP LTASTGAWES TFENKNYTIR LWTEQDIVNL VKASYPWFLS | 120 |
| TYESYKYNIQ RADVARLMVV HHEGGLYADL DAHPSPDTSA ESINCLQSLG YQVIIAPTSE | 180 |
| DRGISNHFFM AERDAEFLLW ALHEAKKRAT SLSGRFMLPY VAVFWSTGPM MITSVMNEYA | 240 |
| WLYNQASETK SMAVLKDSFL HSFLHHAAGR SWHGSDGRAL NYIADHFNDV LAPVLLFLVA | 300 |
| VATAVILARR WGQVRPHIYN IVPYQTPEVM ASPPSQSHGS HQPIELKNDT LPSWLRFRIW | 360 |
| ASQFLYRGRN RGGNRRNIVR LPFGKVAKLW TTMNELAAME YVRQHTSIPI PKLYEVYRHK | 420 |
| NGTISLVMEG LPGNGSDYAR MGPREVEAFG RELSGYILQL RSLEPPEAGF VGSVTGGPLV | 480 |
| DHRVGHIPFG PFHSVANFHF YLRLGSRLQD WTKGEVVKRV HAESHNYKVK FTHADLNPRN | 540 |
| IQYYKGKIVG IIDWEFAGWY PEYWEYTKML WADAPNYEPF FRAVEGEPSI EKYREEIEAE | 600 |
| RDIWRLISHW RYDDYYGEQE KRDAVYAALG EDVARKASMQ QALQTT | 646 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 226297 | OCH1 | 3.63e-19 | 63 | 354 | 82 | 338 | Mannosyltransferase OCH1 or related enzyme [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
| 270690 | APH_ChoK_like | 1.00e-15 | 378 | 571 | 24 | 154 | Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase and Choline Kinase family. This family is composed of APH, ChoK, ethanolamine kinase (ETNK), macrolide 2'-phosphotransferase (MPH2'), an unusual homoserine kinase, and uncharacterized proteins with similarity to the N-terminal domain of acyl-CoA dehydrogenase 10 (ACAD10). The members of this family catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP (or CTP) to small molecule substrates such as aminoglycosides, macrolides, choline, ethanolamine, and homoserine. Phosphorylation of the antibiotics, aminoglycosides and macrolides, leads to their inactivation and to bacterial antibiotic resistance. Phosphorylation of choline, ethanolamine, and homoserine serves as precursors to the synthesis of important biological compounds, such as the major phospholipids, phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine and the amino acids, threonine, methionine, and isoleucine. The APH/ChoK family is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other kinases, such as the typical serine/threonine/tyrosine protein kinases (PKs), RIO kinases, actin-fragmin kinase (AFK), and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). |
| 398274 | Gly_transf_sug | 9.32e-11 | 86 | 154 | 6 | 79 | Glycosyltransferase sugar-binding region containing DXD motif. The DXD motif is a short conserved motif found in many families of glycosyltransferases, which add a range of different sugars to other sugars, phosphates and proteins. DXD-containing glycosyltransferases all use nucleoside diphosphate sugars as donors and require divalent cations, usually manganese. The DXD motif is expected to play a carbohydrate binding role in sugar-nucleoside diphosphate and manganese dependent glycosyltransferases. |
| 396281 | APH | 1.75e-09 | 378 | 583 | 24 | 222 | Phosphotransferase enzyme family. This family consists of bacterial antibiotic resistance proteins, which confer resistance to various aminoglycosides they include: aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase or kanamycin kinase / neomycin-kanamycin phosphotransferase and streptomycin 3''-kinase or streptomycin 3''-phosphotransferase. The aminoglycoside phosphotransferases inactivate aminoglycoside antibiotics via phosphorylation. This family also includes homoserine kinase. This family is related to fructosamine kinase pfam03881. |
| 270702 | HomoserineK_II | 6.71e-04 | 533 | 561 | 183 | 211 | Type II Homoserine Kinase. This subfamily is composed of unusual homoserine kinases, from a subset of bacteria, which have a Protein Kinase fold. These proteins do not bear any similarity to the GHMP family homoserine kinases present in most bacteria and eukaryotes. Homoserine kinase catalyzes the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to L-homoserine producing L-homoserine phosphate, an intermediate in the production of the amino acids threonine, methionine, and isoleucine. The Type II homoserine kinase subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other kinases, such as the typical serine/threonine/tyrosine protein kinases (PKs), RIO kinases, actin-fragmin kinase (AFK), and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATY64613.1|GT32 | 0.0 | 1 | 646 | 1 | 646 |
| UQC87643.1|GT32 | 2.04e-83 | 54 | 313 | 62 | 323 |
| UNI15388.1|GT32 | 1.98e-82 | 57 | 310 | 51 | 302 |
| BCS10670.1|GT32 | 1.74e-81 | 47 | 312 | 22 | 286 |
| BCR98326.1|GT32 | 4.52e-81 | 47 | 312 | 52 | 316 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|O14084|IMT1_SCHPO | 4.12e-26 | 27 | 291 | 27 | 280 | Inositol phosphoceramide mannosyltransferase 1 OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=imt1 PE=3 SV=2 |
| sp|Q10323|IMT3_SCHPO | 1.16e-21 | 53 | 287 | 47 | 269 | Inositol phosphoceramide mannosyltransferase 3 OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=SPAC17G8.11c PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|P33300|SUR1_YEAST | 4.21e-20 | 60 | 297 | 51 | 276 | Mannosyl phosphorylinositol ceramide synthase SUR1 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=SUR1 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|P38287|CSH1_YEAST | 3.08e-19 | 63 | 297 | 62 | 284 | Mannosyl phosphorylinositol ceramide synthase CSH1 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=CSH1 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|Q9UT67|IMT2_SCHPO | 3.03e-18 | 60 | 291 | 79 | 300 | Inositol phosphoceramide mannosyltransferase 2 OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=SPCC4F11.04c PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
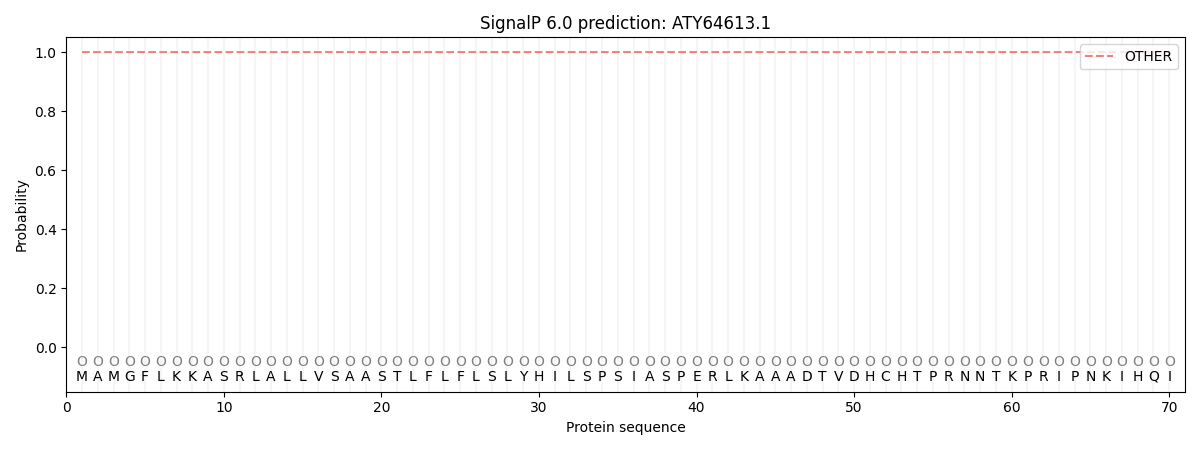
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000020 | 0.000000 |