You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: ATEG_10016-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: ATEG_10016-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus terreus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus terreus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | ATEG_10016-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT35 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | conserved hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE12 | 28 | 224 | 1.4e-41 | 0.9809523809523809 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 238859 | Rhamnogalacturan_acetylesterase_like | 3.03e-53 | 25 | 225 | 1 | 198 | Rhamnogalacturan_acetylesterase_like subgroup of SGNH-hydrolases. Rhamnogalacturan acetylesterase removes acetyl esters from rhamnogalacturonan substrates, and renders them susceptible to degradation by rhamnogalacturonases. Rhamnogalacturonans are highly branched regions in pectic polysaccharides, consisting of repeating -(1,2)-L-Rha-(1,4)-D-GalUA disaccharide units, with many rhamnose residues substituted by neutral oligosaccharides such as arabinans, galactans and arabinogalactans. Extracellular enzymes participating in the degradation of plant cell wall polymers, such as Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase, would typically be found in saprophytic and plant pathogenic fungi and bacteria. |
| 340891 | MFS_FucP_MFSD4_like | 1.63e-22 | 320 | 542 | 3 | 217 | Bacterial fucose permease, eukaryotic Major facilitator superfamily domain-containing protein 4, and similar proteins. This family is composed of bacterial L-fucose permease (FucP), eukaryotic Major facilitator superfamily domain-containing protein 4 (MFSD4) proteins, and similar proteins. L-fucose permease facilitates the uptake of L-fucose across the boundary membrane with the concomitant transport of protons into the cell; it can also transport L-galactose and D-arabinose. The MFSD4 subfamily consists of two vertebrate members: MFSD4A and MFSD4B. The function of MFSD4A is unknown. MFSD4B is more commonly know as Sodium-dependent glucose transporter 1 (NaGLT1), a primary fructose transporter in rat renal brush-border membranes that also facilitates sodium-independent urea uptake. The FucP/MFSD4 family belongs to the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of membrane transport proteins, which are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. |
| 349949 | MFS | 5.25e-12 | 318 | 538 | 1 | 224 | Major Facilitator Superfamily. The Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) is a large and diverse group of secondary transporters that includes uniporters, symporters, and antiporters. MFS proteins facilitate the transport across cytoplasmic or internal membranes of a variety of substrates including ions, sugar phosphates, drugs, neurotransmitters, nucleosides, amino acids, and peptides. They do so using the electrochemical potential of the transported substrates. Uniporters transport a single substrate, while symporters and antiporters transport two substrates in the same or in opposite directions, respectively, across membranes. MFS proteins are typically 400 to 600 amino acids in length, and the majority contain 12 transmembrane alpha helices (TMs) connected by hydrophilic loops. The N- and C-terminal halves of these proteins display weak similarity and may be the result of a gene duplication/fusion event. Based on kinetic studies and the structures of a few bacterial superfamily members, GlpT (glycerol-3-phosphate transporter), LacY (lactose permease), and EmrD (multidrug transporter), MFS proteins are thought to function through a single substrate binding site, alternating-access mechanism involving a rocker-switch type of movement. Bacterial members function primarily for nutrient uptake, and as drug-efflux pumps to confer antibiotic resistance. Some MFS proteins have medical significance in humans such as the glucose transporter Glut4, which is impaired in type II diabetes, and glucose-6-phosphate transporter (G6PT), which causes glycogen storage disease when mutated. |
| 238141 | SGNH_hydrolase | 6.28e-11 | 28 | 224 | 2 | 187 | SGNH_hydrolase, or GDSL_hydrolase, is a diverse family of lipases and esterases. The tertiary fold of the enzyme is substantially different from that of the alpha/beta hydrolase family and unique among all known hydrolases; its active site closely resembles the typical Ser-His-Asp(Glu) triad from other serine hydrolases, but may lack the carboxlic acid. |
| 223809 | FucP | 8.90e-11 | 322 | 544 | 22 | 256 | Fucose permease [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.00e-112 | 1 | 256 | 1 | 259 | |
| 2.00e-112 | 1 | 256 | 1 | 259 | |
| 3.21e-111 | 1 | 256 | 1 | 259 | |
| 3.21e-111 | 1 | 256 | 1 | 259 | |
| 1.98e-109 | 1 | 256 | 1 | 259 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.13e-13 | 294 | 544 | 60 | 321 | Bypass of stop codon protein 6 OS=Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) OX=559292 GN=BSC6 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 8.89e-09 | 23 | 226 | 4 | 213 | Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase RhgT OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=rhgT PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
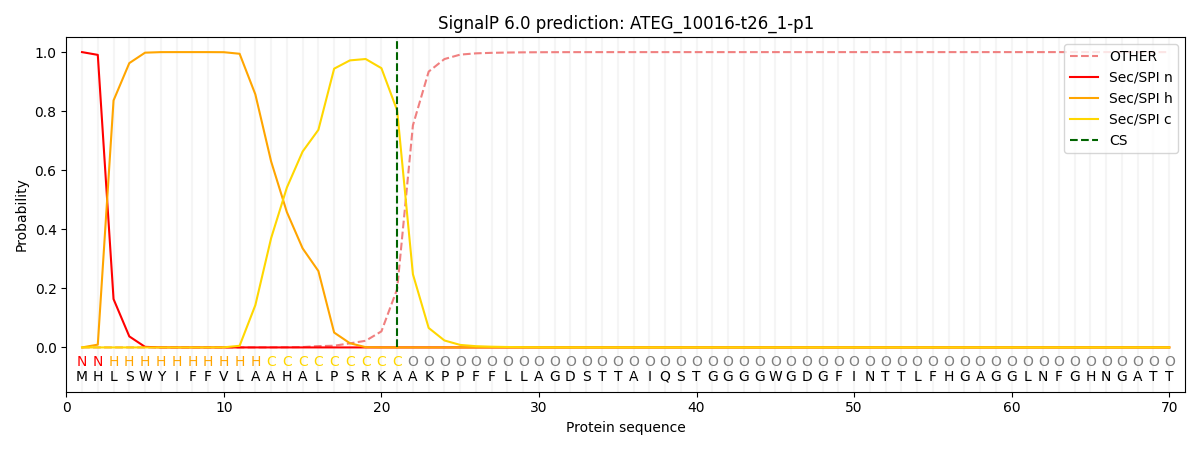
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000265 | 0.999701 | CS pos: 21-22. Pr: 0.8022 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
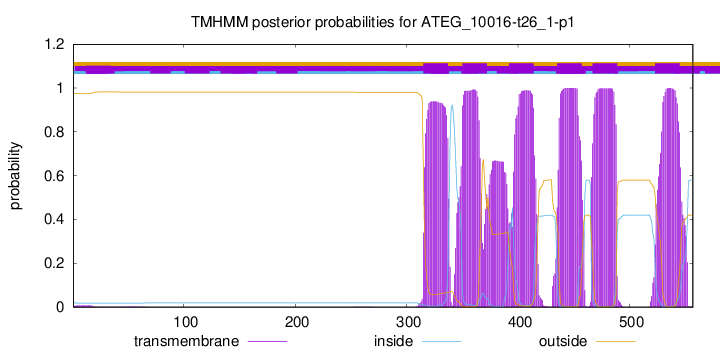
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 315 | 337 |
| 350 | 372 |
| 392 | 414 |
| 435 | 457 |
| 467 | 489 |
| 523 | 545 |
