You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: ATEG_07121-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: ATEG_07121-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
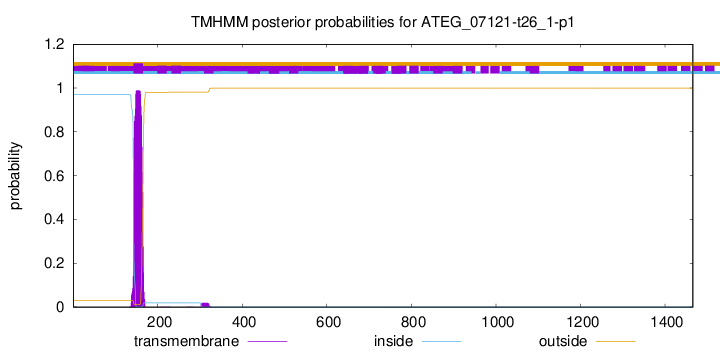
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus terreus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus terreus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | ATEG_07121-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH43|CBM91 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.21:13 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH3 | 248 | 462 | 2.1e-56 | 0.9768518518518519 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 224389 | BglX | 1.16e-43 | 271 | 600 | 81 | 366 | Periplasmic beta-glucosidase and related glycosidases [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| 271038 | STKc_SRPK | 1.44e-42 | 1129 | 1459 | 56 | 320 | Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Serine-aRginine Protein Kinase. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. SRPKs phosphorylate and regulate splicing factors from the SR protein family by specifically phosphorylating multiple serine residues residing in SR/RS dipeptide motifs (also known as RS domains). Phosphorylation of the RS domains enhances interaction with transportin SR and facilitates entry of the SR proteins into the nucleus. SRPKs contain a nonconserved insert domain, within the well-conserved catalytic kinase domain, that regulates their subcellular localization. They play important roles in mediating pre-mRNA processing and mRNA maturation, as well as other cellular functions such as chromatin reorganization, cell cycle and p53 regulation, and metabolic signaling. Vertebrates contain three distinct SRPKs, called SRPK1-3. The SRPK homolog in budding yeast, Sky1p, recognizes and phosphorylates its substrate Npl3p, which lacks a classic RS domain but contains a single RS dipeptide at the C-terminus of its RGG domain. Npl3p is a shuttling heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) that exports a distinct class of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. The SRPK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. |
| 396478 | Glyco_hydro_3_C | 3.23e-42 | 570 | 809 | 1 | 216 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 3 C-terminal domain. This domain is involved in catalysis and may be involved in binding beta-glucan. This domain is found associated with pfam00933. |
| 185053 | PRK15098 | 5.23e-36 | 269 | 1043 | 116 | 751 | beta-glucosidase BglX. |
| 271036 | PKc_CLK | 3.81e-35 | 1126 | 1459 | 55 | 332 | Catalytic domain of the Dual-specificity protein kinases, CDC-like kinases. Dual-specificity PKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine (S/T) as well as tyrosine residues on protein substrates. CLKs are involved in the phosphorylation and regulation of serine/arginine-rich (SR) proteins, which play a crucial role in pre-mRNA splicing by directing splice site selection. SR proteins are phosphorylated first by SR protein kinases (SRPKs) at the N-terminus, which leads to its assembly into nuclear speckles where splicing factors are stored. CLKs phosphorylate the C-terminal part of SR proteins, causing the nuclear speckles to dissolve and splicing factors to be recruited at sites of active transcription. Based on a conserved "EHLAMMERILG" signature motif which may be crucial for substrate specificity, CLKs are also referred to as LAMMER kinases. CLKs autophosphorylate at tyrosine residues and phosphorylate their substrates exclusively on S/T residues. In Drosophila, the CLK homolog DOA (Darkener of apricot) is essential for embryogenesis and its mutation leads to defects in sexual differentiation, eye formation, and neuronal development. In fission yeast, the CLK homolog Lkh1 is a negative regulator of filamentous growth and asexual flocculation, and is also involved in oxidative stress response. Vertebrates contain mutliple CLK proteins and mammals have four (CLK1-4). The CLK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 1045 | 1 | 1038 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 1045 | 1 | 1038 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 1045 | 1 | 1038 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 1045 | 1 | 1038 | |
| 0.0 | 6 | 1045 | 15 | 1035 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.33e-229 | 186 | 1045 | 9 | 830 | Three-dimensional structures of two heavily N-glycosylated Aspergillus sp. Family GH3 beta-D-glucosidases [Aspergillus fumigatus],5FJI_B Three-dimensional structures of two heavily N-glycosylated Aspergillus sp. Family GH3 beta-D-glucosidases [Aspergillus fumigatus] |
|
| 5.45e-228 | 186 | 1045 | 10 | 828 | Three-dimensional structures of two heavily N-glycosylated Aspergillus sp. Family GH3 beta-D-glucosidases [Aspergillus oryzae],5FJJ_B Three-dimensional structures of two heavily N-glycosylated Aspergillus sp. Family GH3 beta-D-glucosidases [Aspergillus oryzae],5FJJ_C Three-dimensional structures of two heavily N-glycosylated Aspergillus sp. Family GH3 beta-D-glucosidases [Aspergillus oryzae],5FJJ_D Three-dimensional structures of two heavily N-glycosylated Aspergillus sp. Family GH3 beta-D-glucosidases [Aspergillus oryzae] |
|
| 6.86e-225 | 186 | 1045 | 9 | 827 | Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus [Aspergillus aculeatus],4IIB_B Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus [Aspergillus aculeatus],4IIC_A Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus in complex with isofagomine [Aspergillus aculeatus],4IIC_B Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus in complex with isofagomine [Aspergillus aculeatus],4IID_A Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus in complex with 1-deoxynojirimycin [Aspergillus aculeatus],4IID_B Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus in complex with 1-deoxynojirimycin [Aspergillus aculeatus],4IIE_A Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus in complex with calystegine B(2) [Aspergillus aculeatus],4IIE_B Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus in complex with calystegine B(2) [Aspergillus aculeatus],4IIF_A Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus in complex with castanospermine [Aspergillus aculeatus],4IIF_B Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus in complex with castanospermine [Aspergillus aculeatus],4IIG_A Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus in complex with D-glucose [Aspergillus aculeatus],4IIG_B Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus in complex with D-glucose [Aspergillus aculeatus],4IIH_A Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus in complex with thiocellobiose [Aspergillus aculeatus],4IIH_B Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus in complex with thiocellobiose [Aspergillus aculeatus] |
|
| 5.35e-222 | 186 | 1045 | 28 | 841 | Chain A, Beta-glucosidase [Rasamsonia emersonii],5JU6_B Chain B, Beta-glucosidase [Rasamsonia emersonii],5JU6_C Chain C, Beta-glucosidase [Rasamsonia emersonii],5JU6_D Chain D, Beta-glucosidase [Rasamsonia emersonii] |
|
| 4.52e-220 | 198 | 1045 | 20 | 825 | Chain A, Beta-glucosidase [Thermochaetoides thermophila] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 6 | 1045 | 25 | 1023 | Probable beta-glucosidase E OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain ATCC MYA-4609 / Af293 / CBS 101355 / FGSC A1100) OX=330879 GN=bglE PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 0.0 | 12 | 1045 | 5 | 1011 | Probable beta-glucosidase E OS=Emericella nidulans (strain FGSC A4 / ATCC 38163 / CBS 112.46 / NRRL 194 / M139) OX=227321 GN=bglE PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 0.0 | 6 | 1045 | 28 | 1040 | Probable beta-glucosidase E OS=Aspergillus clavatus (strain ATCC 1007 / CBS 513.65 / DSM 816 / NCTC 3887 / NRRL 1 / QM 1276 / 107) OX=344612 GN=bglE PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 0.0 | 6 | 1045 | 25 | 1023 | Probable beta-glucosidase E OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain CEA10 / CBS 144.89 / FGSC A1163) OX=451804 GN=bglE PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 0.0 | 1 | 1045 | 1 | 1038 | Probable beta-glucosidase E OS=Aspergillus oryzae (strain ATCC 42149 / RIB 40) OX=510516 GN=bglE PE=3 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
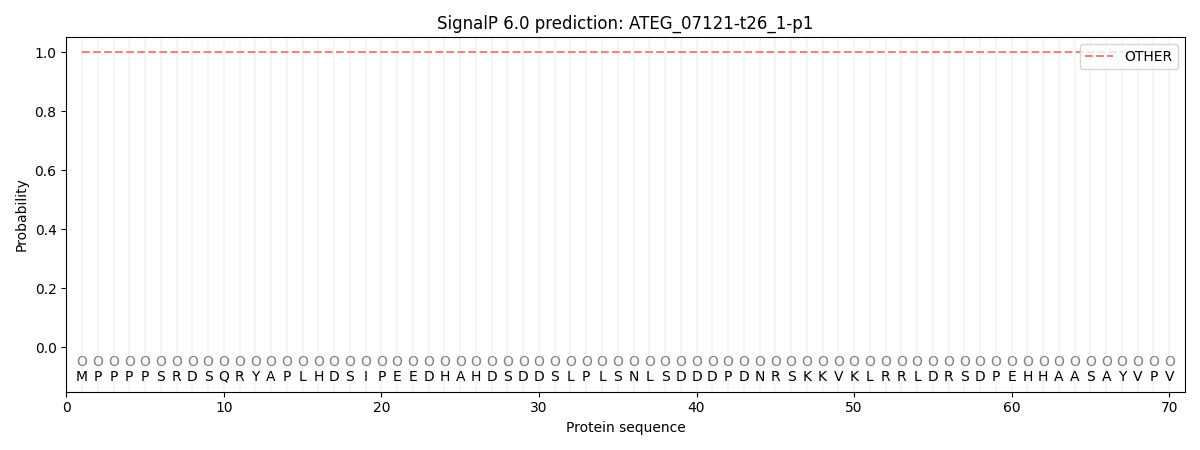
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 1.000067 | 0.000000 |