You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: ATEG_00186-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: ATEG_00186-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus terreus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus terreus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | ATEG_00186-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | AA11 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | predicted protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.55:25 | 3.2.1.-:1 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH62 | 33 | 315 | 1.2e-115 | 0.9928057553956835 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 350101 | GH62 | 1.42e-170 | 34 | 343 | 1 | 304 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 62, characterized arabinofuranosidases. The glycosyl hydrolase family 62 (GH62) includes eukaryotic (mostly fungal) and prokaryotic enzymes which are characterized arabinofuranosidases (alpha-L-arabinofuranosidases; EC 3.2.1.55) that specifically cleave either alpha-1,2 or alpha-1,3-L-arabinofuranose side chains from xylans. These enzymes show significantly different substrate preference with rather low specific activity towards natural substrates and differ in catalytic efficiency. They do not act on xylose moieties in xylan that are adorned with an arabinose side chain at both O2 and O3 positions, nor do they display any non-specific arabinofuranosidase activity. The synergistic action in biomass degradation makes GH62 promising candidates for biotechnological improvements of biofuel production and in various biorefinery applications. These enzymes also contain carbohydrate binding modules (CBMs) that bind cellulose or xylan. |
| 281639 | Glyco_hydro_62 | 1.77e-64 | 34 | 314 | 3 | 271 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 62. Family of alpha -L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55). This enzyme hydrolyzed aryl alpha-L-arabinofuranosides and cleaves arabinosyl side chains from arabinoxylan and arabinan. |
| 350092 | GH_F | 6.73e-11 | 60 | 306 | 1 | 242 | Glycosyl hydrolase families 43 and 62 form CAZY clan GH-F. This glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62). GH43 includes enzymes with beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37), beta-1,3-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.-), alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55), arabinanase (EC 3.2.1.99), xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8), endo-alpha-L-arabinanases (beta-xylanases) and galactan 1,3-beta-galactosidase (EC 3.2.1.145) activities. GH62 includes enzymes characterized as arabinofuranosidases (alpha-L-arabinofuranosidases; EC 3.2.1.55) that specifically cleave either alpha-1,2 or alpha-1,3-L-arabinofuranose side chains from xylans. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many of the enzymes in this family display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. GH62 are also predicted to be inverting enzymes. A common structural feature of both, GH43 and GH62 enzymes, is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| 350153 | GH43_GsAbnA-like | 6.14e-04 | 61 | 140 | 3 | 95 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as Geobacillus stearothermophilus endo-alpha-1,5-L-arabinanase AbnA. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes mostly enzymes with alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (ABF; EC 3.2.1.55) and endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (ABN; EC 3.2.1.99) activities. It includes Geobacillus stearothermophilus T-6 NCIMB 40222 AbnA, Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168 (Abn2;YxiA;J3A;BSU39330) (Arb43B), and Thermotoga petrophila RKU-1 (AbnA;TpABN;Tpet_0637). These are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. The GH43 ABN enzymes hydrolyze alpha-1,5-L-arabinofuranoside linkages while the ABF enzymes cleave arabinose side chains so that the combined actions of these two enzymes reduce arabinan to L-arabinose and/or arabinooligosaccharides. Many of these enzymes are different from other arabinases; they are organized into two different domains with a divalent metal cluster close to the catalytic residues to guarantee the correct protonation state of the catalytic residues and consequently the enzyme activity. These arabinan-degrading enzymes are important in the food industry for efficient production of L-arabinose from agricultural waste; L-arabinose is often used as a bioactive sweetener. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| 350097 | GH43_Bt3655-like | 0.005 | 40 | 158 | 125 | 237 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 arabinofuranosidase Bt3655. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43)-like family includes the characterized arabinofuranosidases (EC 3.2.1.55): Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 (Bt3655;BT_3655) and Penicillium chrysogenum 31B Abf43B, as well as Bifidobacterium adolescentis ATCC 15703 beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37) BAD_1527. It belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) which includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62) families. GH43 includes enzymes with beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37), beta-1,3-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.-), alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55), arabinanase (EC 3.2.1.99), xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8), endo-alpha-L-arabinanases (beta-xylanases) and galactan 1,3-beta-galactosidase (EC 3.2.1.145) activities. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.34e-180 | 33 | 348 | 58 | 372 | |
| 1.28e-179 | 33 | 348 | 82 | 396 | |
| 2.41e-178 | 25 | 348 | 18 | 341 | |
| 1.43e-177 | 25 | 348 | 9 | 332 | |
| 2.16e-168 | 33 | 346 | 32 | 345 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.00e-166 | 34 | 348 | 1 | 316 | Chain A, Glycosyl hydrolase family 62 protein [Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130],5B6S_B Chain B, Glycosyl hydrolase family 62 protein [Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130],5B6T_A Chain A, Glycosyl hydrolase family 62 protein [Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130],5B6T_B Chain B, Glycosyl hydrolase family 62 protein [Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130] |
|
| 2.40e-148 | 24 | 348 | 10 | 337 | Chain A, GH62 arabinofuranosidase [Podospora anserina],4N4B_A Chain A, GH62 arabinofuranosidase [Podospora anserina] |
|
| 7.30e-136 | 37 | 343 | 23 | 342 | Crystal structure of GH62 hydrolase in complex with xylotriose [Mycothermus thermophilus] |
|
| 1.38e-133 | 37 | 343 | 23 | 342 | Crystal structure of GH62 hydrolase from thermophilic fungus Scytalidium thermophilum [Mycothermus thermophilus] |
|
| 1.48e-71 | 34 | 341 | 141 | 434 | Crystal Structure of Streptomyces coelicolor alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)],3WMZ_A Crystal Structure of Streptomyces coelicolor alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase ethylmercury derivative [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)],3WN0_A Crystal Structure of Streptomyces coelicolor alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase in complex with L-arabinose [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)],3WN1_A Crystal Structure of Streptomyces coelicolor alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase in complex with xylotriose [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)],3WN2_A Crystal Structure of Streptomyces coelicolor alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase in complex with xylohexaose [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.08e-71 | 34 | 341 | 323 | 615 | Alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase C OS=Cellvibrio japonicus (strain Ueda107) OX=498211 GN=xynC PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 3.13e-71 | 31 | 341 | 27 | 328 | Probable alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase axhA OS=Aspergillus tubingensis OX=5068 GN=axhA PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.95e-70 | 34 | 341 | 178 | 471 | Extracellular exo-alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase OS=Streptomyces coelicolor (strain ATCC BAA-471 / A3(2) / M145) OX=100226 GN=abfB PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.20e-69 | 26 | 341 | 22 | 324 | Probable alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase axhA-1 OS=Emericella nidulans (strain FGSC A4 / ATCC 38163 / CBS 112.46 / NRRL 194 / M139) OX=227321 GN=axhA-1 PE=3 SV=2 |
|
| 4.23e-69 | 34 | 341 | 178 | 471 | Extracellular exo-alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase OS=Streptomyces lividans OX=1916 GN=abfB PE=1 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
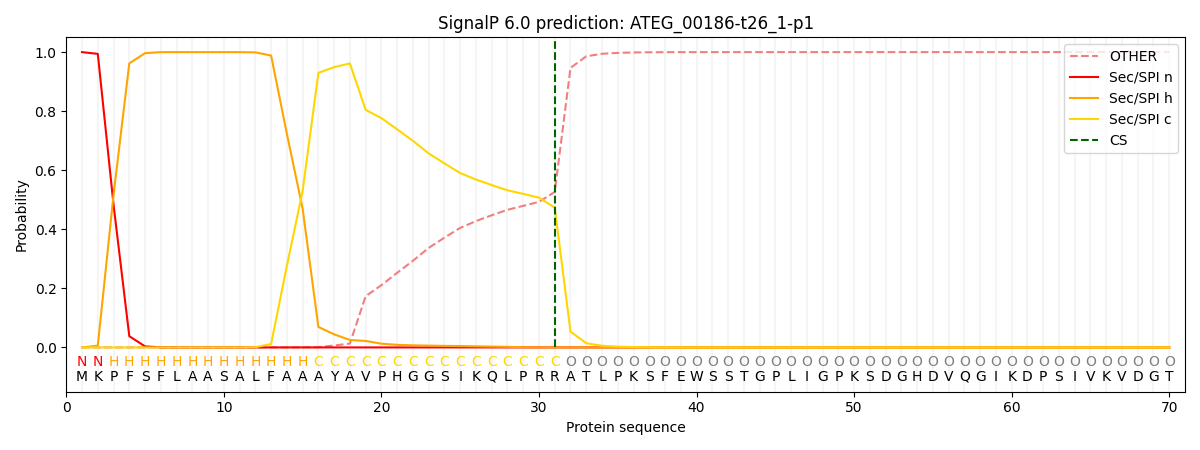
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000272 | 0.999700 | CS pos: 31-32. Pr: 0.4736 |
