You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: ASPTUDRAFT_174662-t33_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: ASPTUDRAFT_174662-t33_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus tubingensis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus tubingensis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | ASPTUDRAFT_174662-t33_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH13 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH31 | 269 | 746 | 8.2e-69 | 0.9859484777517564 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 236691 | PRK10426 | 0.0 | 26 | 751 | 4 | 626 | alpha-glucosidase; Provisional |
| 269880 | GH31_glucosidase_YihQ | 1.84e-149 | 286 | 635 | 1 | 325 | alpha-glucosidase YihQ-like. YihQ is a bacterial alpha-glucosidase with a conserved glycosyl hydrolase family 31 (GH31) domain that catalyzes the release of an alpha-glucosyl residue from the non-reducing end of alpha-glucoside substrates such as alpha-glucosyl fluoride. Orthologs of YihQ that have not yet been functionally characterized are present in plants and fungi. YihQ has sequence similarity to other GH31 enzymes such as CtsZ, a 6-alpha-glucosyltransferase from Bacillus globisporus, and YicI, an alpha-xylosidase from Echerichia coli. These latter two belong to different GH31 subfamilies than YihQ. In bacteria, YihQ (along with YihO) is important for bacterial O-antigen capsule assembly and translocation. |
| 224418 | YicI | 3.56e-66 | 128 | 749 | 122 | 671 | Alpha-glucosidase, glycosyl hydrolase family GH31 [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| 395838 | Glyco_hydro_31 | 1.08e-41 | 272 | 746 | 6 | 440 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 31. Glycosyl hydrolases are key enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism. Family 31 comprises of enzymes that are, or similar to, alpha- galactosidases. |
| 269878 | GH31_NET37 | 1.60e-34 | 353 | 707 | 49 | 361 | glucosidase NET37. NET37 (also known as KIAA1161) is a human lamina-associated nuclear envelope transmembrane protein. A member of the glycosyl hydrolase family 31 (GH31) , it has been shown to be required for myogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells. Related proteins are found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Enzymes of the GH31 family possess a wide range of different hydrolytic activities including alpha-glucosidase (glucoamylase and sucrase-isomaltase), alpha-xylosidase, 6-alpha-glucosyltransferase, 3-alpha-isomaltosyltransferase and alpha-1,4-glucan lyase. All GH31 enzymes cleave a terminal carbohydrate moiety from a substrate that varies considerably in size, depending on the enzyme, and may be either a starch or a glycoprotein. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 768 | 1 | 768 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 768 | 1 | 768 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 768 | 1 | 768 | |
| 0.0 | 4 | 768 | 6 | 770 | |
| 0.0 | 4 | 768 | 6 | 770 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.97e-99 | 31 | 741 | 9 | 661 | A bacterial protein structure in glycoside hydrolase family 31 [Escherichia coli K-12],5AED_B A bacterial protein structure in glycoside hydrolase family 31 [Escherichia coli K-12],5AEG_A A bacterial protein structure in glycoside hydrolase family 31. [Escherichia coli K-12],5AEG_B A bacterial protein structure in glycoside hydrolase family 31. [Escherichia coli K-12],5OHT_A A GH31 family sulfoquinovosidase from E. coli in complex with aza-sugar inhibitor IFGSQ [Escherichia coli K-12],5OHT_B A GH31 family sulfoquinovosidase from E. coli in complex with aza-sugar inhibitor IFGSQ [Escherichia coli K-12] |
|
| 1.05e-98 | 31 | 741 | 9 | 661 | A bacterial protein structure in glycoside hydrolase family 31 [Escherichia coli K-12],5AEE_B A bacterial protein structure in glycoside hydrolase family 31 [Escherichia coli K-12] |
|
| 2.25e-88 | 33 | 766 | 1 | 669 | Chain A, Alpha-glucosidase [[Eubacterium] rectale],6PNR_C Chain C, Alpha-glucosidase [[Eubacterium] rectale] |
|
| 3.03e-85 | 33 | 767 | 1 | 672 | Chain A, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],5OHY_B Chain B, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],5OHY_C Chain C, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],5OHY_D Chain D, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens] |
|
| 1.58e-84 | 33 | 767 | 1 | 672 | Chain A, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],5OHS_B Chain B, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],5OHS_C Chain C, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],5OHS_D Chain D, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],5OHS_E Chain E, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],5OHS_F Chain F, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],5OHS_G Chain G, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],5OHS_H Chain H, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],7OFX_A Chain A, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],7OFX_B Chain B, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],7OFX_C Chain C, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens],7OFX_D Chain D, Alpha-glucosidase yihQ [Agrobacterium tumefaciens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.29e-99 | 31 | 741 | 9 | 661 | Sulfoquinovosidase OS=Escherichia coli (strain K12) OX=83333 GN=yihQ PE=1 SV=3 |
|
| 2.54e-15 | 141 | 706 | 126 | 633 | Oligosaccharide 4-alpha-D-glucosyltransferase OS=Cellvibrio japonicus (strain Ueda107) OX=498211 GN=agd31B PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 2.04e-11 | 287 | 714 | 313 | 687 | Myogenesis-regulating glycosidase OS=Mus musculus OX=10090 GN=Myorg PE=1 SV=2 |
|
| 7.01e-11 | 314 | 754 | 380 | 783 | Probable glucan 1,3-alpha-glucosidase OS=Oryza sativa subsp. japonica OX=39947 GN=Os03g0216600 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 1.89e-09 | 431 | 749 | 507 | 811 | Neutral alpha-glucosidase AB OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=GANAB PE=1 SV=3 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
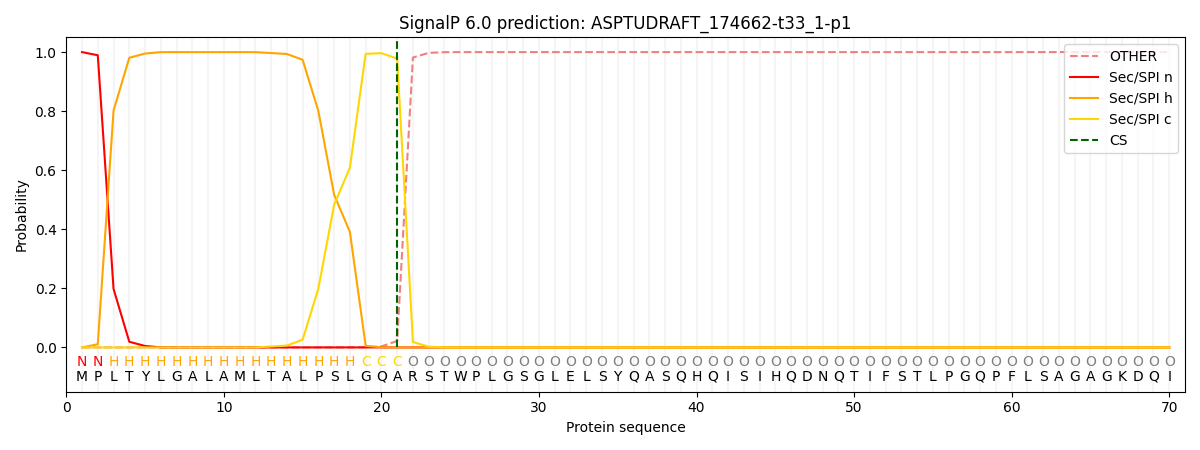
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000223 | 0.999759 | CS pos: 21-22. Pr: 0.9781 |
