You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: ASPGLDRAFT_1512325-t33_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: ASPGLDRAFT_1512325-t33_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus glaucus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus glaucus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | ASPGLDRAFT_1512325-t33_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH105 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.40:5 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH78 | 244 | 625 | 6.7e-75 | 0.7321428571428571 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 407469 | Bac_rhamnosid6H | 1.86e-07 | 241 | 428 | 26 | 224 | Bacterial alpha-L-rhamnosidase 6 hairpin glycosidase domain. This family consists of bacterial rhamnosidase A and B enzymes. L-Rhamnose is abundant in biomass as a common constituent of glycolipids and glycosides, such as plant pigments, pectic polysaccharides, gums or biosurfactants. Some rhamnosides are important bioactive compounds. For example, terpenyl glycosides, the glycosidic precursor of aromatic terpenoids, act as important flavouring substances in grapes. Other rhamnosides act as cytotoxic rhamnosylated terpenoids, as signal substances in plants or play a role in the antigenicity of pathogenic bacteria. |
| 273702 | oligosac_amyl | 3.08e-05 | 293 | 421 | 340 | 461 | oligosaccharide amylase. The name of this type of amylase is based on the characterization of an glucoamylase family enzyme from Thermoactinomyces vulgaris. The T. vulgaris enzyme was expressed in E. coli and, like other glucoamylases, it releases beta-D-glucose from starch. However, unlike previously characterized glucoamylases, this T. vulgaris amylase hydrolyzes maltooligosaccharides (maltotetraose, maltose) more efficiently than starch (1), indicating this enzyme belongs to a class of glucoamylase-type enzymes with oligosaccharide-metabolizing activity. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 658 | 1 | 658 | |
| 0.0 | 2 | 658 | 5 | 659 | |
| 0.0 | 2 | 658 | 5 | 659 | |
| 0.0 | 2 | 658 | 5 | 659 | |
| 0.0 | 2 | 658 | 5 | 659 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.55e-13 | 69 | 550 | 94 | 531 | Chain A, Alpha-L-rhamnosidase [Klebsiella oxytoca],4XHC_B Chain B, Alpha-L-rhamnosidase [Klebsiella oxytoca] |
|
| 7.86e-13 | 70 | 583 | 194 | 658 | Crystal structure of a putative alpha-rhamnosidase from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
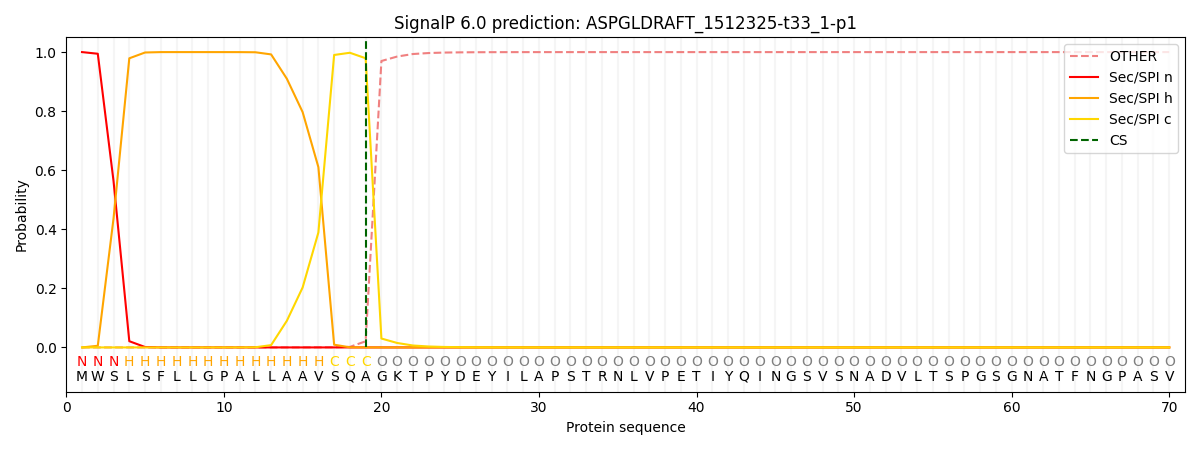
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000221 | 0.999777 | CS pos: 19-20. Pr: 0.9792 |
