You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: ASPCADRAFT_204675-t33_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: ASPCADRAFT_204675-t33_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus carbonarius | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus carbonarius | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | ASPCADRAFT_204675-t33_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH18 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | glycoside hydrolase family 32 protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.80:10 | 3.2.1.65:10 | 3.2.1.26:7 | 3.2.1.153:5 | 3.2.1.64:3 | 2.4.1.99:3 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH32 | 31 | 371 | 4.7e-93 | 0.9965870307167235 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 350134 | GH32_Inu-like | 5.31e-146 | 37 | 358 | 2 | 289 | glycoside hydrolase family 32 protein such as Aspergillus ficuum endo-inulinase (Inu2). This subfamily of glycosyl hydrolase family GH32 includes endo-inulinase (inu2, EC 3.2.1.7), exo-inulinase (Inu1, EC 3.2.1.80), invertase (EC 3.2.1.26), and levan fructotransferase (LftA, EC 4.2.2.16), among others. These enzymes cleave sucrose into fructose and glucose via beta-fructofuranosidase activity, producing invert sugar that is a mixture of dextrorotatory D-glucose and levorotatory D-fructose, thus named invertase (EC 3.2.1.26). These retaining enzymes (i.e. they retain the configuration at anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) catalyze hydrolysis in two steps involving a covalent glycosyl enzyme intermediate: an aspartate located close to the N-terminus acts as the catalytic nucleophile and a glutamate acts as the general acid/base; a conserved aspartate residue in the Arg-Asp-Pro (RDP) motif stabilizes the transition state. These enzymes are predicted to display a 5-fold beta-propeller fold as found for GH43 and CH68. The breakdown of sucrose is widely used as a carbon or energy source by bacteria, fungi, and plants. Invertase is used commercially in the confectionery industry, since fructose has a sweeter taste than sucrose and a lower tendency to crystallize. A common structural feature of all these enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain, similar to GH43, that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| 214757 | Glyco_32 | 3.84e-139 | 31 | 496 | 1 | 437 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 32. |
| 224536 | SacC | 9.66e-111 | 22 | 532 | 24 | 484 | Sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase SacC, GH32 family [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| 395193 | Glyco_hydro_32N | 2.78e-109 | 31 | 371 | 1 | 308 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 32 N-terminal domain. This domain corresponds to the N-terminal domain of glycosyl hydrolase family 32 which forms a five bladed beta propeller structure. |
| 350093 | GH_J | 2.89e-109 | 40 | 357 | 1 | 292 | Glycosyl hydrolase families 32 and 68, which form the clan GH-J. This glycosyl hydrolase family clan J (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) includes family 32 (GH32) and 68 (GH68). GH32 enzymes include invertase (EC 3.2.1.26) and other other fructofuranosidases such as inulinase (EC 3.2.1.7), exo-inulinase (EC 3.2.1.80), levanase (EC 3.2.1.65), and transfructosidases such sucrose:sucrose 1-fructosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.99), fructan:fructan 1-fructosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.100), sucrose:fructan 6-fructosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.10), fructan:fructan 6G-fructosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.243) and levan fructosyltransferases (EC 2.4.1.-). The GH68 family consists of frucosyltransferases (FTFs) that include levansucrase (EC 2.4.1.10, also known as beta-D-fructofuranosyl transferase), beta-fructofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.26) and inulosucrase (EC 2.4.1.9). GH32 and GH68 family enzymes are retaining enzymes (i.e. they retain the configuration at anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) and catalyze hydrolysis in two steps involving a covalent glycosyl enzyme intermediate: an aspartate located close to the N-terminus acts as the catalytic nucleophile and a glutamate acts as the general acid/base; a conserved aspartate residue in the Arg-Asp-Pro (RDP) motif stabilizes the transition state. A common structural feature of all these enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain, similar to GH43, that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 537 | 1 | 537 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 537 | 1 | 537 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 537 | 1 | 537 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 537 | 1 | 537 | |
| 0.0 | 1 | 537 | 1 | 537 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 20 | 537 | 1 | 518 | Crystal structure of exo-inulinase from Aspergillus awamori in spacegroup P21 [Aspergillus awamori],1Y9G_A Crystal structure of exo-inulinase from Aspergillus awamori complexed with fructose [Aspergillus awamori],1Y9M_A Crystal structure of exo-inulinase from Aspergillus awamori in spacegroup P212121 [Aspergillus awamori] |
|
| 6.70e-87 | 26 | 532 | 28 | 513 | First crystal structure of an endo-inulinase, from Aspergillus ficuum: structural analysis and comparison with other GH32 enzymes. [Aspergillus ficuum],3SC7_X First crystal structure of an endo-inulinase, from Aspergillus ficuum: structural analysis and comparison with other GH32 enzymes. [Aspergillus ficuum] |
|
| 1.87e-79 | 31 | 505 | 14 | 476 | Chain A, Invertase [Schwanniomyces occidentalis],3KF3_B Chain B, Invertase [Schwanniomyces occidentalis] |
|
| 2.01e-79 | 31 | 505 | 17 | 479 | Chain A, Invertase [Schwanniomyces occidentalis],3KF5_B Chain B, Invertase [Schwanniomyces occidentalis] |
|
| 2.74e-78 | 31 | 505 | 40 | 502 | Chain A, Fructofuranosidase [Schwanniomyces occidentalis],3U75_B Chain B, Fructofuranosidase [Schwanniomyces occidentalis],3U75_C Chain C, Fructofuranosidase [Schwanniomyces occidentalis],3U75_D Chain D, Fructofuranosidase [Schwanniomyces occidentalis] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1 | 537 | 1 | 537 | Extracellular exo-inulinase inuE OS=Aspergillus niger (strain CBS 513.88 / FGSC A1513) OX=425011 GN=inuE PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 0.0 | 1 | 537 | 1 | 537 | Extracellular exo-inulinase inuE OS=Aspergillus niger OX=5061 GN=inuE PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 0.0 | 1 | 537 | 1 | 537 | Extracellular exo-inulinase inuE OS=Aspergillus awamori OX=105351 GN=inuE PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 0.0 | 1 | 537 | 1 | 537 | Extracellular exo-inulinase inuE OS=Aspergillus ficuum OX=5058 GN=exoI PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 3.02e-204 | 6 | 537 | 8 | 703 | Putative glycosyl hydrolase ecdE OS=Aspergillus rugulosus OX=41736 GN=ecdE PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
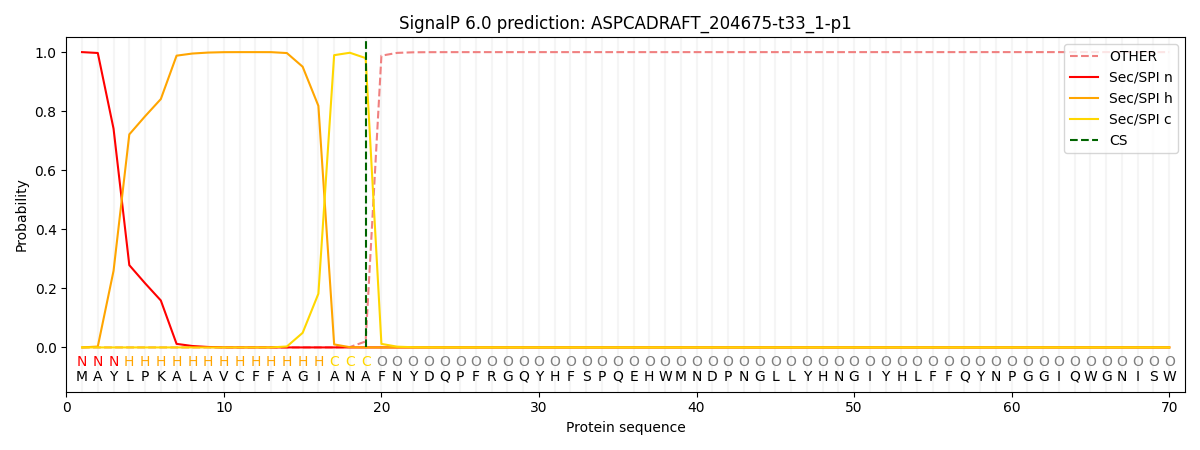
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000218 | 0.999730 | CS pos: 19-20. Pr: 0.9797 |
