You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: AN6470-T-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: AN6470-T-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Aspergillus nidulans | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Ascomycota; Eurotiomycetes; ; Aspergillaceae; Aspergillus; Aspergillus nidulans | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | AN6470-T-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH5 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Protein with lysozyme activity, involved in carbohydrate catabolism | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 3.2.1.17:41 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH25 | 21 | 198 | 2.2e-49 | 0.9830508474576272 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 119374 | GH25_CH-type | 3.73e-113 | 17 | 210 | 1 | 199 | CH-type (Chalaropsis-type) lysozymes represent one of four functionally-defined classes of peptidoglycan hydrolases (also referred to as endo-N-acetylmuramidases) that cleave bacterial cell wall peptidoglycans. CH-type lysozymes exhibit both lysozyme (acetylmuramidase) and diacetylmuramidase activity. The first member of this family to be described was a muramidase from the fungus Chalaropsis. However, a majority of the CH-type lysozymes are found in bacteriophages and Gram-positive bacteria such as Streptomyces and Clostridium. CH-type lysozymes have a single glycosyl hydrolase family 25 (GH25) domain with an unusual beta/alpha-barrel fold in which the last strand of the barrel is antiparallel to strands beta7 and beta1. Most CH-type lysozymes appear to lack the cell wall-binding domain found in other GH25 muramidases. |
| 395941 | Glyco_hydro_25 | 1.81e-57 | 21 | 199 | 2 | 180 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 25. |
| 119373 | GH25_muramidase | 7.18e-50 | 18 | 198 | 1 | 176 | Endo-N-acetylmuramidases (muramidases) are lysozymes (also referred to as peptidoglycan hydrolases) that degrade bacterial cell walls by catalyzing the hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues. This family of muramidases contains a glycosyl hydrolase family 25 (GH25) catalytic domain and is found in bacteria, fungi, slime molds, round worms, protozoans and bacteriophages. The bacteriophage members are referred to as endolysins which are involved in lysing the host cell at the end of the replication cycle to allow release of mature phage particles. Endolysins are typically modular enzymes consisting of a catalytically active domain that hydrolyzes the peptidoglycan cell wall and a cell wall-binding domain that anchors the protein to the cell wall. Endolysins generally have narrow substrate specificities with either intra-species or intra-genus bacteriolytic activity. |
| 119384 | GH25_YegX-like | 1.01e-38 | 19 | 193 | 2 | 177 | YegX is an uncharacterized bacterial protein with a glycosyl hydrolase family 25 (GH25) catalytic domain that is similar in sequence to the CH-type (Chalaropsis-type) lysozymes of the GH25 family of endolysins. |
| 119385 | GH25_Lyc-like | 6.61e-30 | 18 | 193 | 1 | 169 | Lyc muramidase is an autolytic lysozyme (autolysin) from Clostridium acetobutylicum encoded by the lyc gene. Lyc has a glycosyl hydrolase family 25 (GH25) catalytic domain. Endo-N-acetylmuramidases are lysozymes (also referred to as peptidoglycan hydrolases) that degrade bacterial cell walls by catalyzing the hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.31e-166 | 1 | 216 | 1 | 216 | |
| 1.31e-166 | 1 | 216 | 1 | 216 | |
| 1.07e-131 | 1 | 215 | 1 | 215 | |
| 8.82e-131 | 1 | 215 | 1 | 215 | |
| 4.84e-126 | 1 | 215 | 1 | 215 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.52e-96 | 16 | 216 | 1 | 206 | Chain A, muramidase [Trichobolus zukalii],6ZMV_B Chain B, muramidase [Trichobolus zukalii] |
|
| 6.20e-86 | 17 | 216 | 2 | 207 | Chain A, muramidase [Sodiomyces alcalophilus] |
|
| 9.40e-86 | 17 | 216 | 4 | 210 | The structure of a family GH25 lysozyme from Aspergillus fumigatus [Aspergillus fumigatus Af293],2X8R_B The structure of a family GH25 lysozyme from Aspergillus fumigatus [Aspergillus fumigatus Af293],2X8R_C The structure of a family GH25 lysozyme from Aspergillus fumigatus [Aspergillus fumigatus Af293],2X8R_D The structure of a family GH25 lysozyme from Aspergillus fumigatus [Aspergillus fumigatus Af293],2X8R_E The structure of a family GH25 lysozyme from Aspergillus fumigatus [Aspergillus fumigatus Af293],2X8R_F The structure of a family GH25 lysozyme from Aspergillus fumigatus [Aspergillus fumigatus Af293] |
|
| 1.55e-61 | 15 | 215 | 3 | 214 | Crystal structure of the bacterial lysozyme from Streptomyces coelicolor at 1.65 A resolution [Streptomyces coelicolor] |
|
| 3.27e-12 | 21 | 200 | 26 | 193 | Crystal structure of the CTP1L endolysin reveals how its activity is regulated by a secondary translation product [Clostridium phage phiCTP1] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.22e-94 | 16 | 216 | 29 | 234 | N,O-diacetylmuramidase OS=Arthroderma benhamiae (strain ATCC MYA-4681 / CBS 112371) OX=663331 GN=ARB_05911 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 1.69e-90 | 17 | 216 | 2 | 211 | N,O-diacetylmuramidase OS=Chalaropsis sp. OX=36534 PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 8.04e-60 | 15 | 215 | 80 | 291 | Lysozyme M1 OS=Streptomyces globisporus OX=1908 GN=acm PE=1 SV=1 |
|
| 2.06e-16 | 17 | 212 | 9 | 203 | Probable autolytic lysozyme OS=Clostridium perfringens (strain 13 / Type A) OX=195102 GN=lyc PE=3 SV=2 |
|
| 5.08e-11 | 17 | 200 | 1 | 172 | Autolytic lysozyme OS=Clostridium acetobutylicum (strain ATCC 824 / DSM 792 / JCM 1419 / LMG 5710 / VKM B-1787) OX=272562 GN=lyc PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
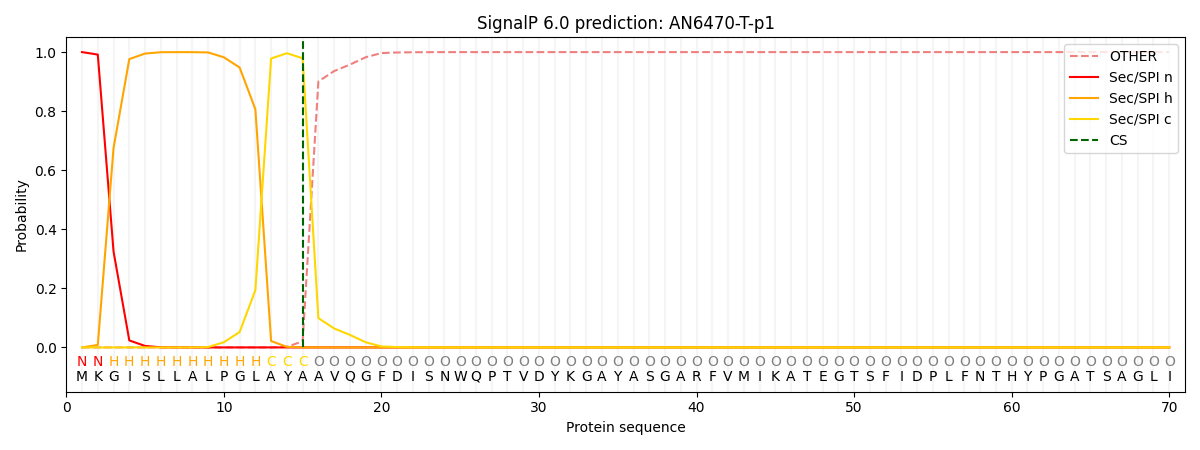
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000392 | 0.999609 | CS pos: 15-16. Pr: 0.9792 |
