You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: AMAG_09783-t26_1-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: AMAG_09783-t26_1-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Allomyces macrogynus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Blastocladiomycota; Blastocladiomycetes; ; Blastocladiaceae; Allomyces; Allomyces macrogynus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | AMAG_09783-t26_1-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH63 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | ||||||||||||
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 2.4.1.16:11 |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT2 | 1158 | 1671 | 1.3e-235 | 0.9924098671726755 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 367353 | Chitin_synth_2 | 0.0 | 1158 | 1671 | 4 | 527 | Chitin synthase. Members of this family are fungal chitin synthase EC:2.4.1.16 enzymes. They catalyze chitin synthesis as follows: UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine + {(1,4)-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)}(N) <=> UDP + {(1,4)-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)}(N+1). |
| 276845 | MYSc_Myo17 | 7.31e-141 | 77 | 738 | 14 | 646 | class XVII myosin, motor domain. This fungal myosin which is also known as chitin synthase uses its motor domain to tether its vesicular cargo to peripheral actin. It works in opposition to dynein, contributing to the retention of Mcs1 vesicles at the site of cell growth and increasing vesicle fusion necessary for polarized growth. Class 17 myosins consist of a N-terminal myosin motor domain with Cyt-b5, chitin synthase 2, and a DEK_C domains at it C-terminus. The chitin synthase region contains several transmembrane domains by which myosin 17 is thought to bind secretory vesicles. The catalytic (head) domain has ATPase activity and belongs to the larger group of P-loop NTPases. Myosins are actin-dependent molecular motors that play important roles in muscle contraction, cell motility, and organelle transport. The head domain is a molecular motor, which utilizes ATP hydrolysis to generate directed movement toward the plus end along actin filaments. A cyclical interaction between myosin and actin provides the driving force. Rates of ATP hydrolysis and consequently the speed of movement along actin filaments vary widely, from about 0.04 micrometer per second for myosin I to 4.5 micrometer per second for myosin II in skeletal muscle. Myosin II moves in discrete steps about 5-10 nm long and generates 1-5 piconewtons of force. Upon ATP binding, the myosin head dissociates from an actin filament. ATP hydrolysis causes the head to pivot and associate with a new actin subunit. The release of Pi causes the head to pivot and move the filament (power stroke). Release of ADP completes the cycle. CyMoBase classifications were used to confirm and identify the myosins in this hierarchy. |
| 214580 | MYSc | 3.71e-99 | 77 | 742 | 30 | 677 | Myosin. Large ATPases. ATPase; molecular motor. Muscle contraction consists of a cyclical interaction between myosin and actin. The core of the myosin structure is similar in fold to that of kinesin. |
| 276950 | MYSc | 5.21e-97 | 77 | 730 | 11 | 633 | Myosin motor domain superfamily. Myosin motor domain. The catalytic (head) domain has ATPase activity and belongs to the larger group of P-loop NTPases. Myosins are actin-dependent molecular motors that play important roles in muscle contraction, cell motility, and organelle transport. The head domain is a molecular motor, which utilizes ATP hydrolysis to generate directed movement toward the plus end along actin filaments. A cyclical interaction between myosin and actin provides the driving force. Rates of ATP hydrolysis and consequently the speed of movement along actin filaments vary widely, from about 0.04 micrometer per second for myosin I to 4.5 micrometer per second for myosin II in skeletal muscle. Myosin II moves in discrete steps about 5-10 nm long and generates 1-5 piconewtons of force. Upon ATP binding, the myosin head dissociates from an actin filament. ATP hydrolysis causes the head to pivot and associate with a new actin subunit. The release of Pi causes the head to pivot and move the filament (power stroke). Release of ADP completes the cycle. CyMoBase classifications were used to confirm and identify the myosins in this hierarchy. |
| 395017 | Myosin_head | 3.47e-77 | 77 | 458 | 23 | 373 | Myosin head (motor domain). |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 151 | 1674 | 83 | 1714 | |
| 0.0 | 68 | 1673 | 24 | 1690 | |
| 0.0 | 81 | 1680 | 41 | 1750 | |
| 0.0 | 81 | 1680 | 41 | 1750 | |
| 0.0 | 77 | 1680 | 30 | 1755 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.18e-50 | 151 | 516 | 151 | 513 | Insights into the Importance of Hydrogen Bonding in the Gamma-Phosphate Binding Pocket of Myosin: Structural and Functional Studies of Ser236 [Dictyostelium discoideum],3MYK_X Insights into the Importance of Hydrogen Bonding in the Gamma-Phosphate Binding Pocket of Myosin: Structural and Functional Studies of Ser236 [Dictyostelium discoideum],3MYL_X Insights into the Importance of Hydrogen Bonding in the Gamma-Phosphate Binding Pocket of Myosin: Structural and Functional Studies of Ser236 [Dictyostelium discoideum] |
|
| 6.12e-50 | 151 | 516 | 151 | 513 | Dictyostelium discoideum Myosin II motor domain S456E with bound MgADP-BeFx [Dictyostelium discoideum] |
|
| 7.41e-50 | 151 | 516 | 150 | 512 | Crystal structure of myosin-2 dictyostelium discoideum motor domain S456Y mutant in complex with adp-orthovanadate [Dictyostelium discoideum] |
|
| 7.46e-50 | 151 | 516 | 151 | 513 | X-Ray Structures Of The Mgadp, Mgatpgammas, And Mgamppnp Complexes Of The Dictyostelium Discoideum Myosin Motor Domain [Dictyostelium discoideum] |
|
| 9.53e-50 | 151 | 516 | 150 | 512 | Structural basis for the allosteric interference of myosin function by mutants G680A and G680V of Dictyostelium myosin-2 [Dictyostelium discoideum],2Y8I_X Structural basis for the allosteric interference of myosin function by mutants G680A and G680V of Dictyostelium myosin-2 [Dictyostelium discoideum] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 149 | 1674 | 78 | 1752 | Chitin synthase 8 OS=Ustilago maydis (strain 521 / FGSC 9021) OX=237631 GN=CHS8 PE=3 SV=1 |
|
| 0.0 | 153 | 1676 | 96 | 1742 | Chitin synthase 5 OS=Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii serotype A (strain H99 / ATCC 208821 / CBS 10515 / FGSC 9487) OX=235443 GN=CHS5 PE=2 SV=1 |
|
| 1.52e-288 | 845 | 1705 | 57 | 927 | Chitin synthase 6 OS=Ustilago maydis (strain 521 / FGSC 9021) OX=237631 GN=CHS6 PE=3 SV=2 |
|
| 6.47e-272 | 851 | 1684 | 155 | 1004 | Chitin synthase 4 OS=Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii serotype A (strain H99 / ATCC 208821 / CBS 10515 / FGSC 9487) OX=235443 GN=CHS4 PE=2 SV=2 |
|
| 7.26e-145 | 1172 | 1701 | 679 | 1201 | Chitin synthase 4 OS=Magnaporthe oryzae (strain 70-15 / ATCC MYA-4617 / FGSC 8958) OX=242507 GN=CHS4 PE=3 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
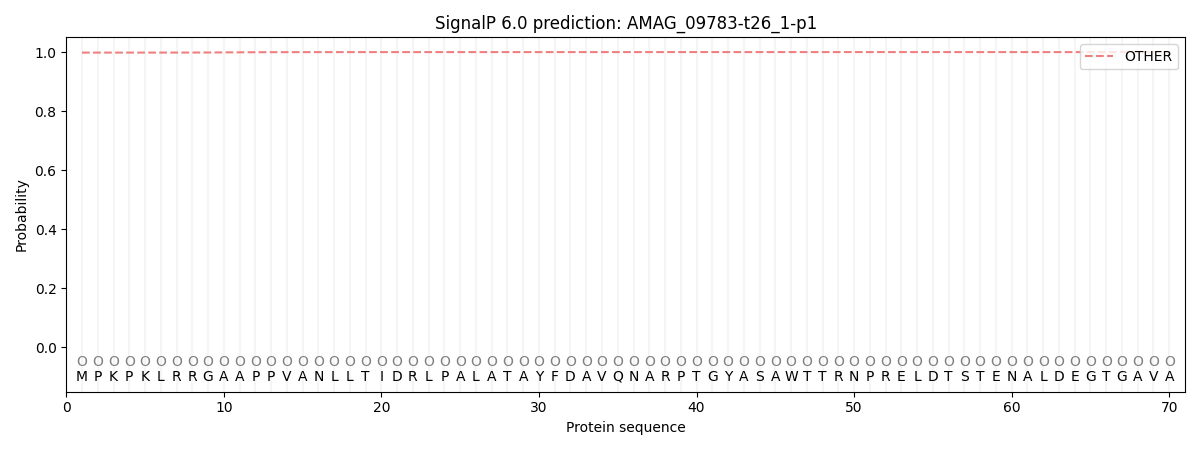
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.998490 | 0.001557 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
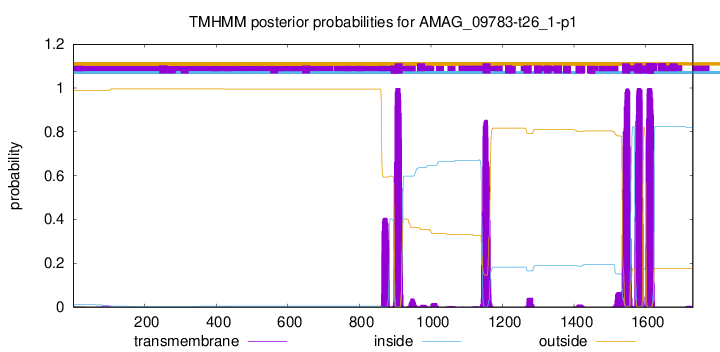
| Start | End |
|---|---|
| 899 | 921 |
| 1144 | 1166 |
| 1534 | 1556 |
| 1569 | 1591 |
| 1601 | 1623 |
