You are browsing environment: FUNGIDB
CAZyme Information: AGR57_226T0-p1
You are here: Home > Sequence: AGR57_226T0-p1
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Phanerochaete chrysosporium | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Basidiomycota; Agaricomycetes; ; Phanerochaetaceae; Phanerochaete; Phanerochaete chrysosporium | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | AGR57_226T0-p1 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH16 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Iron reductase domain / Carbohydrate-Binding Module Family 1 protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 460462; End:461623 Strand: - | |||||||||||
Full Sequence Download help
| MAFTKSLLTI LTAAGLALAQ SSTQFCDSSS GICFQGYTDP DFDVTVGFVL PPISTPPSDE | 60 |
| FIVQLVAPVS NGYTGISVGG TMADSLLFTL WPYNNELILG PRWTSGYVLP TAYAGPQITL | 120 |
| LPSSSINSTH IKATFRCQNC TIWEGGSLGS GDLTSFQVVA YVVATTTKPS DPADVDSVIQ | 180 |
| EHDDFNFFGL DLSMAHSDSY SSYIGGSVTT SAPASTTTHP TSTSHSSTVI STTSSAPSAT | 240 |
| QTEWGQCGGT GFTGPTVCAS GLTCVAVSPP YYYQCQV | 277 |
Enzyme Prediction help
| EC | 1.1.99.18:3 | - |
|---|
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA8 | 25 | 203 | 3.9e-49 | 0.9945054945054945 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 406418 | CDH-cyt | 1.54e-64 | 25 | 199 | 1 | 177 | Cytochrome domain of cellobiose dehydrogenase. CDH-cyt is the cytochrome domain, at the N-terminus, of cellobiose dehydrogenase. CDH-cyt folds as a beta sandwich with the topology of the antibody Fab V(H) domain and binds iron. The haem iron is ligated by Met83 and His181 in UniProtKB:Q01738. |
| 187688 | CDH_like_cytochrome | 1.66e-51 | 24 | 192 | 1 | 168 | Heme-binding cytochrome domain of fungal cellobiose dehydrogenases. Cellobiose dehydrogenase (CellobioseDH or CDH) is an extracellular fungal oxidoreductase that degrades both lignin and cellulose. Specifically, CDHs oxidize cellobiose, cellodextrins, and lactose to corresponding lactones, utilizing a variety of electron acceptors. Class-II CDHs are monomeric hemoflavoenzymes that are comprised of a b-type cytochrome domain linked to a large flavodehydrogenase domain. The cytochrome domain of CDH and related enzymes, which this model describes, folds as a beta sandwich and complexes a heme molecule. It is found at the N-terminus of this family of enzymes, and belongs to the DOMON domain superfamily, a ligand-interacting motif found in all three kingdoms of life. |
| 395595 | CBM_1 | 4.66e-11 | 244 | 271 | 2 | 29 | Fungal cellulose binding domain. |
| 197593 | fCBD | 1.78e-10 | 242 | 276 | 1 | 34 | Fungal-type cellulose-binding domain. Small four-cysteine cellulose-binding domain of fungi |
| 320158 | 7tmF_SMO_homolog | 0.003 | 6 | 53 | 147 | 189 | class F smoothened family membrane region, a homolog of frizzled receptors. This group represents smoothened (SMO), a transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor that acts as the transducer of the hedgehog (HH) signaling pathway. SMO is activated by the hedgehog (HH) family of proteins acting on the 12-transmembrane domain receptor patched (PTCH), which constitutively inhibits SMO. Thus, in the absence of HH proteins, PTCH inhibits SMO signaling. On the other hand, binding of HH to the PTCH receptor activates its internalization and degradation, thereby releasing the PTCH inhibition of SMO. This allows SMO to trigger intracellular signaling and the subsequent activation of the Gli family of zinc finger transcriptional factors and induction of HH target gene expression (PTCH, Gli1, cyclin, Bcl-2, etc). SMO is closely related to the frizzled (FZD) family of seven transmembrane-spanning proteins, which constitute a novel and separate family of G-protein coupled receptors. The FZDs are activated by the wingless/int-1 (WNT) family of secreted lipoglycoproteins and preferentially couple to stimulatory G proteins of the Gs family, which activate adenylate cyclase, but can also couple to G proteins of the Gi/Gq families. In the WNT/beta-catenin signaling pathway, the WNT ligand binds to FZD and a lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) co-receptor. This leads to the stabilization and translocation of beta-catenin to the nucleus, where it induces the activation of TCF/LEF family transcription factors. The WNT and HH signaling pathways play critical roles in many developmental processes, such as cell-fate determination, cell proliferation, neural patterning, stem cell renewal, tissue homeostasis and repair, and tumorigenesis, among many others. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAU12274.1|AA8|CBM1 | 1.20e-197 | 1 | 277 | 1 | 277 |
| BAD95668.1|AA8|CBM1 | 7.34e-183 | 1 | 276 | 1 | 276 |
| VWO94841.1|AA8|CBM1 | 3.03e-92 | 44 | 272 | 1 | 220 |
| AAC49277.1|AA3_1|AA8 | 2.97e-52 | 5 | 228 | 4 | 225 |
| AAO32063.1|AA3_1|AA8 | 6.43e-49 | 1 | 220 | 1 | 214 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1D7C_A | 4.21e-52 | 21 | 206 | 2 | 187 | Chain A, CELLOBIOSE DEHYDROGENASE [Phanerodontia chrysosporium],1D7C_B Chain B, CELLOBIOSE DEHYDROGENASE [Phanerodontia chrysosporium] |
| 1D7B_A | 2.97e-51 | 21 | 204 | 2 | 185 | Chain A, CELLOBIOSE DEHYDROGENASE [Phanerodontia chrysosporium],1D7B_B Chain B, CELLOBIOSE DEHYDROGENASE [Phanerodontia chrysosporium],1D7D_A Chain A, CELLOBIOSE DEHYDROGENASE [Phanerodontia chrysosporium],1D7D_B Chain B, CELLOBIOSE DEHYDROGENASE [Phanerodontia chrysosporium] |
| 1PL3_A | 3.36e-50 | 21 | 204 | 2 | 185 | Chain A, Cellobiose dehydrogenase [Phanerodontia chrysosporium],1PL3_B Chain B, Cellobiose dehydrogenase [Phanerodontia chrysosporium] |
| 6JT6_A | 1.13e-30 | 21 | 204 | 3 | 186 | Chain A, Extracellular PQQ-dependent sugar dehydrogenase [Coprinopsis cinerea] |
| 4QI3_A | 2.27e-21 | 25 | 203 | 8 | 199 | Chain A, Cellobiose dehydrogenase [Thermothelomyces myriococcoides],4QI3_B Chain B, Cellobiose dehydrogenase [Thermothelomyces myriococcoides] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sp|Q01738|CDH_PHACH | 5.28e-53 | 5 | 228 | 4 | 225 | Cellobiose dehydrogenase OS=Phanerodontia chrysosporium OX=2822231 GN=CDH-1 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|Q9P8P3|GUX1_TRIHA | 5.18e-09 | 235 | 275 | 465 | 504 | Exoglucanase 1 OS=Trichoderma harzianum OX=5544 GN=cbh1 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|P19355|GUX1_HYPRU | 1.69e-08 | 235 | 275 | 474 | 513 | Exoglucanase 1 OS=Hypocrea rufa OX=5547 GN=cbh1 PE=3 SV=2 |
| sp|Q99034|AXE1_HYPJE | 1.93e-08 | 205 | 275 | 247 | 301 | Acetylxylan esterase OS=Hypocrea jecorina OX=51453 GN=axe1 PE=1 SV=1 |
| sp|P62695|GUX1_TRIKO | 2.26e-08 | 206 | 275 | 460 | 512 | Exoglucanase 1 OS=Trichoderma koningii OX=97093 GN=cbh1 PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
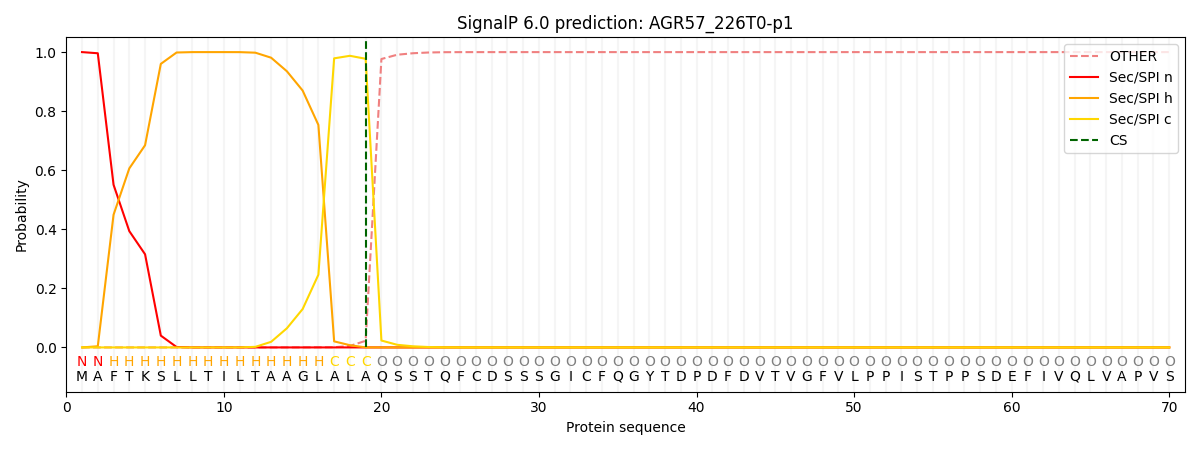
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | CS Position |
|---|---|---|
| 0.000216 | 0.999761 | CS pos: 19-20. Pr: 0.9774 |
