You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004823_01727
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004823_01727
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | CAG-462 sp900765575 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; CAG-462; CAG-462 sp900765575 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004823_01727 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH33 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Hercynine oxygenase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 5677; End: 7869 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH33 | 301 | 606 | 1.2e-22 | 0.8421052631578947 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam03781 | FGE-sulfatase | 3.87e-48 | 29 | 249 | 5 | 258 | Sulfatase-modifying factor enzyme 1. This domain is found in eukaryotic proteins required for post-translational sulfatase modification (SUMF1). These proteins are associated with the rare disorder multiple sulfatase deficiency (MSD). The protein product of the SUMF1 gene is FGE, formylglycine (FGly),-generating enzyme, which is a sulfatase. Sulfatases are enzymes essential for degradation and remodelling of sulfate esters, and formylglycine (FGly), the key catalytic in the active site, is unique to sulfatases. FGE is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and interacts with and modifies the unfolded form of newly synthesized sulfatases. FGE is a single-domain monomer with a surprising paucity of secondary structure that adopts a unique fold which is stabilized by two Ca2+ ions. The effect of all mutations found in MSD patients is explained by the FGE structure, providing a molecular basis for MSD. A redox-active disulfide bond is present in the active site of FGE. An oxidized cysteine residue, possibly cysteine sulfenic acid, has been detected that may allow formulation of a structure-based mechanism for FGly formation from cysteine residues in all sulfatases. In Mycobacteria and Treponema denticola this enzyme functions as an iron(II)-dependent oxidoreductase. |
| COG1262 | YfmG | 1.21e-47 | 14 | 249 | 41 | 310 | Formylglycine-generating enzyme, required for sulfatase activity, contains SUMF1/FGE domain [Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones]. |
| cd15482 | Sialidase_non-viral | 4.41e-33 | 304 | 646 | 11 | 321 | Non-viral sialidases. Sialidases or neuraminidases function to bind and hydrolyze terminal sialic acid residues from various glycoconjugates, they play vital roles in pathogenesis, bacterial nutrition and cellular interactions. They have a six-bladed, beta-propeller fold with the non-viral sialidases containing 2-5 Asp-box motifs (most commonly Ser/Thr-X-Asp-[X]-Gly-X-Thr- Trp/Phe). This CD includes eubacterial and eukaryotic sialidases. |
| pfam13088 | BNR_2 | 1.63e-23 | 318 | 606 | 1 | 260 | BNR repeat-like domain. This family of proteins contains BNR-like repeats suggesting these proteins may act as sialidases. |
| PRK00635 | PRK00635 | 0.006 | 631 | 691 | 893 | 961 | excinuclease ABC subunit A; Provisional |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AII65153.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 660 | 1 | 660 |
| QEW38154.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 660 | 1 | 660 |
| ALK82864.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 674 | 120 | 792 |
| QUT59623.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 661 | 1 | 661 |
| ABR39477.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 661 | 1 | 661 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5HHA_A | 1.06e-27 | 17 | 250 | 30 | 284 | Structureof PvdO from Pseudomonas aeruginosa [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1],5HHA_B Structure of PvdO from Pseudomonas aeruginosa [Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1] |
| 2AFT_X | 5.57e-18 | 29 | 247 | 6 | 279 | ChainX, Sulfatase modifying factor 1 [Homo sapiens],2AIJ_X Chain X, Sulfatase modifying factor 1 [Homo sapiens],2AIK_X Chain X, Sulfatase modifying factor 1 [Homo sapiens],2HI8_X Chain X, Sulfatase-modifying factor 1 [Homo sapiens],2HIB_X Chain X, Sulfatase-modifying factor 1 [Homo sapiens] |
| 6MUJ_A | 6.79e-18 | 30 | 257 | 32 | 316 | Formylglycinegenerating enzyme bound to copper [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)],6MUJ_B Formylglycine generating enzyme bound to copper [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)],6MUJ_C Formylglycine generating enzyme bound to copper [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)],6MUJ_D Formylglycine generating enzyme bound to copper [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)],6MUJ_E Formylglycine generating enzyme bound to copper [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)] |
| 2Q17_A | 9.63e-18 | 30 | 257 | 59 | 343 | FormylglycineGenerating Enzyme from Streptomyces coelicolor [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)],2Q17_B Formylglycine Generating Enzyme from Streptomyces coelicolor [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)],2Q17_C Formylglycine Generating Enzyme from Streptomyces coelicolor [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)],2Q17_D Formylglycine Generating Enzyme from Streptomyces coelicolor [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)],2Q17_E Formylglycine Generating Enzyme from Streptomyces coelicolor [Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)] |
| 2AFY_X | 1.02e-17 | 29 | 247 | 6 | 279 | ChainX, Sulfatase modifying factor 1 [Homo sapiens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q7AJA5 | 2.20e-18 | 21 | 247 | 377 | 613 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase pkn1 OS=Chlamydia pneumoniae OX=83558 GN=pkn1 PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q0P5L5 | 3.00e-17 | 17 | 247 | 82 | 364 | Formylglycine-generating enzyme OS=Bos taurus OX=9913 GN=SUMF1 PE=2 SV=1 |
| Q9F3C7 | 3.47e-17 | 30 | 257 | 27 | 311 | Formylglycine-generating enzyme OS=Streptomyces coelicolor (strain ATCC BAA-471 / A3(2) / M145) OX=100226 GN=SCO7548 PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q8R0F3 | 3.93e-17 | 14 | 247 | 77 | 362 | Formylglycine-generating enzyme OS=Mus musculus OX=10090 GN=Sumf1 PE=1 SV=2 |
| Q8NBK3 | 1.73e-16 | 29 | 247 | 91 | 364 | Formylglycine-generating enzyme OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=SUMF1 PE=1 SV=3 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
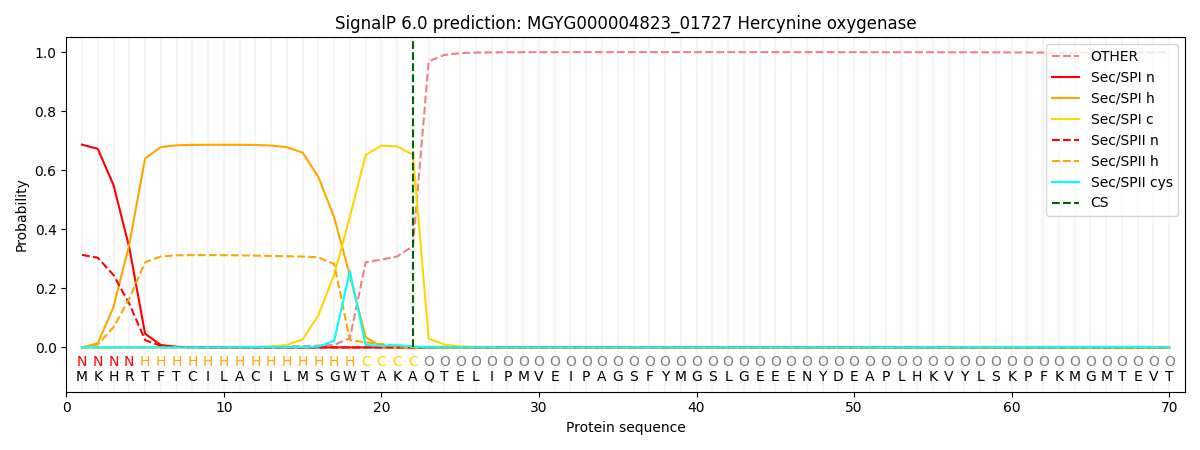
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000728 | 0.676579 | 0.321840 | 0.000335 | 0.000279 | 0.000215 |
