You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004443_00601
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004443_00601
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Coprobacteraceae; ; | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004443_00601 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH125 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 32747; End: 34171 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH125 | 67 | 466 | 3.9e-182 | 0.9975124378109452 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COG3538 | COG3538 | 0.0 | 47 | 473 | 3 | 427 | Meiotically up-regulated gene 157 (Mug157) protein (function unknown) [Function unknown]. |
| pfam06824 | Glyco_hydro_125 | 0.0 | 67 | 466 | 1 | 416 | Metal-independent alpha-mannosidase (GH125). This family, which contains bacterial and fungal glycoside hydrolases, is also known as GH125. They function as metal-independent alpha-mannosidases, with specificity for alpha-1,6-linked non-reducing terminal mannose residues. Structurally this family is part of the 6 hairpin glycosidase superfamily. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUT49828.1 | 3.38e-267 | 1 | 471 | 1 | 479 |
| QKH96733.1 | 1.17e-265 | 1 | 474 | 1 | 485 |
| QCY55535.1 | 1.17e-265 | 1 | 474 | 1 | 485 |
| ABR42144.1 | 1.17e-265 | 1 | 474 | 1 | 485 |
| QUT53395.1 | 1.17e-265 | 1 | 474 | 1 | 485 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3ON6_A | 3.89e-211 | 25 | 471 | 7 | 451 | Crystalstructure of an exo-alpha-1,6-mannosidase (bacova_03626) from bacteroides ovatus at 1.70 a resolution [Bacteroides ovatus ATCC 8483],3ON6_B Crystal structure of an exo-alpha-1,6-mannosidase (bacova_03626) from bacteroides ovatus at 1.70 a resolution [Bacteroides ovatus ATCC 8483] |
| 3P2C_A | 1.69e-210 | 41 | 471 | 21 | 453 | Crystalstructure of an exo-alpha-1,6-mannosidase (bacova_03347) from bacteroides ovatus at 1.60 a resolution [Bacteroides ovatus ATCC 8483],3P2C_B Crystal structure of an exo-alpha-1,6-mannosidase (bacova_03347) from bacteroides ovatus at 1.60 a resolution [Bacteroides ovatus ATCC 8483] |
| 2P0V_A | 2.85e-208 | 25 | 471 | 27 | 471 | Crystalstructure of BT3781 protein from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Northeast Structural Genomics Target BtR58 [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482],2P0V_B Crystal structure of BT3781 protein from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Northeast Structural Genomics Target BtR58 [Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482] |
| 6RQK_A | 6.25e-134 | 52 | 473 | 10 | 428 | Crystalstructure of GH125 1,6-alpha-mannosidase from Clostridium perfringens in complex with mannoimidazole [Clostridium perfringens str. 13],6RQK_B Crystal structure of GH125 1,6-alpha-mannosidase from Clostridium perfringens in complex with mannoimidazole [Clostridium perfringens str. 13] |
| 3QT3_A | 1.36e-133 | 52 | 472 | 10 | 427 | Analysisof a New Family of Widely Distributed Metal-independent alpha-Mannosidases Provides Unique Insight into the Processing of N-linked Glycans, Clostridium perfringens CPE0426 apo-structure [Clostridium perfringens],3QT9_A Analysis of a new family of widely distributed metal-independent alpha mannosidases provides unique insight into the processing of N-linked glycans, Clostridium perfringens CPE0426 complexed with alpha-1,6-linked 1-thio-alpha-mannobiose [Clostridium perfringens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q10449 | 3.30e-116 | 33 | 472 | 43 | 500 | Meiotically up-regulated gene 157 protein OS=Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) OX=284812 GN=mug157 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as TAT
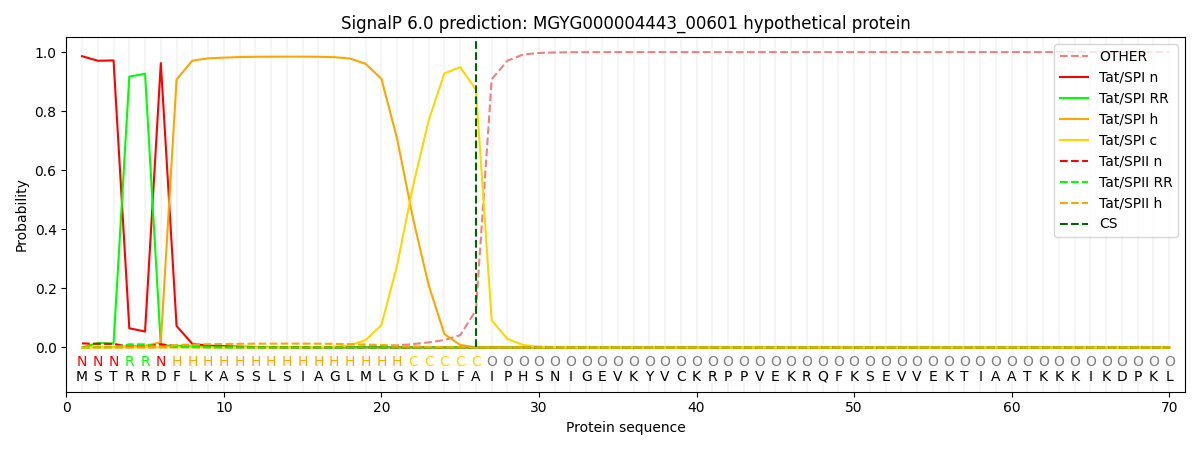
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000129 | 0.000100 | 0.000035 | 0.986094 | 0.013616 | 0.000001 |
