You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003317_01250
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003317_01250
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Lentilactobacillus buchneri | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Lactobacillales; Lactobacillaceae; Lentilactobacillus; Lentilactobacillus buchneri | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003317_01250 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH20 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 23339; End: 24484 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH20 | 40 | 379 | 3.6e-45 | 0.9376854599406528 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd06564 | GH20_DspB_LnbB-like | 7.60e-57 | 40 | 374 | 2 | 319 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 20 (GH20) catalytic domain of dispersin B (DspB), lacto-N-biosidase (LnbB) and related proteins. Dispersin B is a soluble beta-N-acetylglucosamidase found in bacteria that hydrolyzes the beta-1,6-linkages of PGA (poly-beta-(1,6)-N-acetylglucosamine), a major component of the extracellular polysaccharide matrix. Lacto-N-biosidase hydrolyzes lacto-N-biose (LNB) type I oligosaccharides at the nonreducing terminus to produce lacto-N-biose as part of the GNB/LNB (galacto-N-biose/lacto-N-biose I) degradation pathway. The lacto-N-biosidase from Bifidobacterium bifidum has this GH20 domain, a carbohydrate binding module 32, and a bacterial immunoglobulin-like domain 2, as well as a YSIRK signal peptide and a G5 membrane anchor at the N and C termini, respectively. The GH20 hexosaminidases are thought to act via a catalytic mechanism in which the catalytic nucleophile is not provided by solvent or the enzyme, but by the substrate itself. |
| cd02742 | GH20_hexosaminidase | 3.07e-41 | 40 | 357 | 1 | 282 | Beta-N-acetylhexosaminidases of glycosyl hydrolase family 20 (GH20) catalyze the removal of beta-1,4-linked N-acetyl-D-hexosamine residues from the non-reducing ends of N-acetyl-beta-D-hexosaminides including N-acetylglucosides and N-acetylgalactosides. These enzymes are broadly distributed in microorganisms, plants and animals, and play roles in various key physiological and pathological processes. These processes include cell structural integrity, energy storage, cellular signaling, fertilization, pathogen defense, viral penetration, the development of carcinomas, inflammatory events and lysosomal storage disorders. The GH20 enzymes include the eukaryotic beta-N-acetylhexosaminidases A and B, the bacterial chitobiases, dispersin B, and lacto-N-biosidase. The GH20 hexosaminidases are thought to act via a catalytic mechanism in which the catalytic nucleophile is not provided by the solvent or the enzyme, but by the substrate itself. |
| pfam00728 | Glyco_hydro_20 | 1.03e-24 | 40 | 352 | 3 | 318 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 20, catalytic domain. This domain has a TIM barrel fold. |
| cd06568 | GH20_SpHex_like | 6.78e-18 | 40 | 276 | 3 | 227 | A subgroup of the Glycosyl hydrolase family 20 (GH20) catalytic domain found in proteins similar to the N-acetylhexosaminidase from Streptomyces plicatus (SpHex). SpHex catalyzes the hydrolysis of N-acetyl-beta-hexosaminides. An Asp residue within the active site plays a critical role in substrate-assisted catalysis by orienting the 2-acetamido group and stabilizing the transition state. The GH20 hexosaminidases are thought to act via a catalytic mechanism in which the catalytic nucleophile is not provided by solvent or the enzyme, but by the substrate itself. Proteins belonging to this subgroup lack the C-terminal PKD (polycystic kidney disease I)-like domain found in the chitobiases. |
| cd06569 | GH20_Sm-chitobiase-like | 2.09e-17 | 40 | 351 | 7 | 389 | The chitobiase of Serratia marcescens is a beta-N-1,4-acetylhexosaminidase with a glycosyl hydrolase family 20 (GH20) domain that hydrolyzes the beta-1,4-glycosidic linkages in oligomers derived from chitin. Chitin is degraded by a two step process: i) a chitinase hydrolyzes the chitin to oligosaccharides and disaccharides such as di-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and chitobiose, ii) chitobiase then further degrades these oligomers into monomers. The GH20 hexosaminidases are thought to act via a catalytic mechanism in which the catalytic nucleophile is not provided by solvent or the enzyme, but by the substrate itself. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFR99311.1 | 4.31e-279 | 1 | 381 | 1 | 381 |
| QUX06558.1 | 4.31e-279 | 1 | 381 | 1 | 381 |
| APR07016.1 | 1.36e-215 | 1 | 381 | 1 | 379 |
| QOP51663.1 | 7.29e-211 | 9 | 381 | 1 | 370 |
| QOJ86140.1 | 7.29e-211 | 9 | 381 | 1 | 370 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1YHT_A | 2.23e-56 | 39 | 375 | 17 | 354 | Crystalstructure analysis of Dispersin B [Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans] |
| 6EZR_A | 1.30e-13 | 39 | 253 | 264 | 479 | Crystalstructure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi [Vibrio harveyi],6EZR_B Crystal structure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi [Vibrio harveyi],6EZS_A Crystal structure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi in complex with N-acetylglucosamine [Vibrio harveyi],6EZS_B Crystal structure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi in complex with N-acetylglucosamine [Vibrio harveyi],6K35_A Crystal structure of GH20 exo beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi in complex with NAG-thiazoline [Vibrio harveyi],6K35_B Crystal structure of GH20 exo beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Vibrio harveyi in complex with NAG-thiazoline [Vibrio harveyi] |
| 7PUL_A | 6.59e-13 | 45 | 314 | 15 | 303 | ChainA, Beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase [Enterococcus faecalis] |
| 6EZT_A | 1.29e-12 | 39 | 253 | 261 | 476 | Crystalstructure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase D437A inactive mutant from Vibrio harveyi [Vibrio harveyi],6EZT_B Crystal structure of GH20 Exo beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase D437A inactive mutant from Vibrio harveyi [Vibrio harveyi] |
| 4AZI_A | 1.67e-12 | 35 | 353 | 5 | 331 | Differentialinhibition of the tandem GH20 catalytic modules in the pneumococcal exo-beta-D-N-acetylglucosaminidase, StrH [Streptococcus pneumoniae TIGR4],4AZI_B Differential inhibition of the tandem GH20 catalytic modules in the pneumococcal exo-beta-D-N-acetylglucosaminidase, StrH [Streptococcus pneumoniae TIGR4] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B2UPR7 | 1.02e-11 | 42 | 300 | 236 | 490 | Beta-hexosaminidase Amuc_2136 OS=Akkermansia muciniphila (strain ATCC BAA-835 / DSM 22959 / JCM 33894 / BCRC 81048 / CCUG 64013 / CIP 107961 / Muc) OX=349741 GN=Amuc_2136 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P49610 | 5.02e-11 | 30 | 354 | 177 | 520 | Beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase OS=Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 4 (strain ATCC BAA-334 / TIGR4) OX=170187 GN=strH PE=1 SV=2 |
| Q86M34 | 7.85e-08 | 42 | 261 | 191 | 418 | Beta-hexosaminidase subunit beta OS=Entamoeba histolytica OX=5759 GN=HEXB PE=1 SV=1 |
| P49010 | 5.83e-07 | 40 | 240 | 213 | 403 | Chitooligosaccharidolytic beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase OS=Bombyx mori OX=7091 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P43077 | 3.08e-06 | 39 | 261 | 167 | 389 | Beta-hexosaminidase OS=Candida albicans OX=5476 GN=HEX1 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
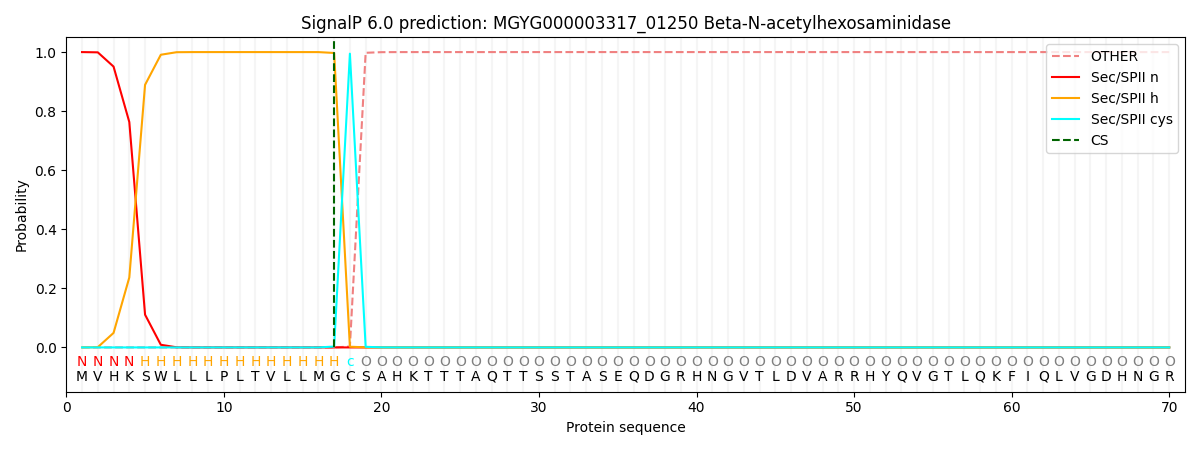
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000057 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
