You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003268_01695
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003268_01695
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Prevotella sp900762125 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; Prevotella; Prevotella sp900762125 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003268_01695 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH43 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 8044; End: 10560 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH43 | 28 | 297 | 3.3e-97 | 0.9963369963369964 |
| GH8 | 502 | 825 | 6e-67 | 0.9125 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd08990 | GH43_AXH_like | 2.50e-104 | 29 | 300 | 1 | 269 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein, includes arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase, beta-xylosidase, endo-1,4-beta-xylanase, and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase. This subgroup includes Bacillus subtilis arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (XynD;BsAXH-m23;BSU18160), Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (Xsa43E;bpr_I2319), Clostridium stercorarium alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase XylA, and metagenomic beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37) / alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55) CoXyl43. It belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) which includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62) families. The GH43_AXH-like subgroup includes enzymes that have been characterized with beta-xylosidase, alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase, endo-alpha-L-arabinanase as well as arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (AXH) activities. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. AXHs specifically hydrolyze the glycosidic bond between arabinofuranosyl substituents and xylopyranosyl backbone residues of arabinoxylan. Metagenomic beta-xylosidase/alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase CoXyl43 shows synergy with Trichoderma reesei cellulases and promotes plant biomass saccharification by degrading xylo-oligosaccharides, such as xylobiose and xylotriose, into the monosaccharide xylose. Studies show that the hydrolytic activity of CoXyl43 is stimulated in the presence of calcium. Several of these enzymes also contain carbohydrate binding modules (CBMs) that bind cellulose or xylan. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd18619 | GH43_CoXyl43_like | 7.14e-79 | 21 | 299 | 1 | 312 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as metagenomic beta-xylosidase/alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase CoXyl43. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup belongs to the GH43_AXH-like subgroup which includes enzymes that have been characterized with beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37), alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55), alpha-1,2-L-arabinofuranosidase 43A (arabinan-specific; EC 3.2.1.-), endo-alpha-L-arabinanase as well as arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (AXH) activities. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. Included in this subfamily is the metagenomic beta-xylosidase/alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase CoXyl43, which shows synergy with Trichoderma reesei cellulases and promotes plant biomass saccharification by degrading xylo-oligosaccharides, such as xylobiose and xylotriose, into the monosaccharide xylose. Studies show that the hydrolytic activity of CoXyl43 is stimulated in the presence of calcium. Several of these enzymes also contain carbohydrate binding modules (CBMs) that bind cellulose or xylan. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd18618 | GH43_Xsa43E-like | 2.12e-75 | 27 | 300 | 1 | 275 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43, including Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus arabinofuranosidase Xsa43E. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup belongs to the GH43_AXH-like subgroup which includes enzymes that have been characterized with beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37), alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55), alpha-1,2-L-arabinofuranosidase 43A (arabinan-specific; EC 3.2.1.-), endo-alpha-L-arabinanase as well as arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (AXH) activities. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. AXHs specifically hydrolyze the glycosidic bond between arabinofuranosyl substituents and xylopyranosyl backbone residues of arabinoxylan. This subgroup includes Cellvibrio japonicus arabinan-specific alpha-1,2-arabinofuranosidase, CjAbf43A, which confers its specificity by a surface cleft that is complementary to the helical backbone of the polysaccharide, and Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus GH43 enzyme Xsa43E, also an arabinofuranosidase, which has been shown to cleave arabinose side chains from short segments of xylan. Several of these enzymes also contain carbohydrate binding modules (CBMs) that bind cellulose or xylan. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd18620 | GH43_XylA-like | 7.45e-67 | 29 | 298 | 1 | 272 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43-like protein such as Clostridium stercorarium alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase XylA. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup belongs to the GH43_AXH-like subgroup which includes enzymes that have been characterized with beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37), alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55), alpha-1,2-L-arabinofuranosidase 43A (arabinan-specific; EC 3.2.1.-), endo-alpha-L-arabinanase as well as arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (AXH) activities. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. The GH43_XylA-like subgroup includes Clostridium stercorarium alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase XylA, and enzymes that have been annotated as having beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37), alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55), endo-alpha-L-arabinanase (EC 3.2.1.-) as well as arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (AXH) activities. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. AXHs specifically hydrolyze the glycosidic bond between arabinofuranosyl substituents and xylopyranosyl backbone residues of arabinoxylan. |
| cd09004 | GH43_bXyl-like | 9.81e-60 | 29 | 301 | 1 | 266 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 alpha-L-arabinofuranosidases (BT3675;BT_3675) and (BT3662;BT_3662); includes mostly xylanases. This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes enzymes that have been annotated as xylan-digesting beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37) and xylanase (endo-alpha-L-arabinanase, EC 3.2.1.8) activities, as well the Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 alpha-L-arabinofuranosidases (EC 3.2.1.55) (BT3675;BT_3675) and (BT3662;BT_3662). It belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) which includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62) families. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVM57873.1 | 0.0 | 2 | 834 | 4 | 833 |
| AVM52698.1 | 0.0 | 18 | 834 | 22 | 833 |
| QUU00913.1 | 0.0 | 11 | 834 | 15 | 832 |
| QNT67600.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 834 | 1 | 832 |
| QCD34665.1 | 0.0 | 16 | 834 | 21 | 834 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6SUD_A | 2.48e-88 | 449 | 834 | 7 | 377 | Structureof L320A mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis complexed with xylose. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis],6SUD_B Structure of L320A mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis complexed with xylose. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis] |
| 6SRD_A | 3.47e-88 | 449 | 834 | 7 | 377 | Structureof Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis complexed with xylose. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis],6SRD_B Structure of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis complexed with xylose. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis] |
| 6TPP_A | 2.59e-87 | 449 | 834 | 7 | 377 | Structureof E70A mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis],6TPP_B Structure of E70A mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis] |
| 6TO0_A | 2.84e-87 | 449 | 834 | 7 | 377 | Structureof E70A mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis complexed with 2(3)-alpha-L-arabinofuranosyl-xylotriose. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis],6TO0_B Structure of E70A mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis complexed with 2(3)-alpha-L-arabinofuranosyl-xylotriose. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis],6TOW_A Structure of E70A mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis complexed with xylotetraose. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis],6TOW_B Structure of E70A mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis complexed with xylotetraose. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis],6TRH_A Structure of E70A mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis complexed with 3(3)-alpha-L-arabinofuranosyl-xylotetraose. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis],6TRH_B Structure of E70A mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis complexed with 3(3)-alpha-L-arabinofuranosyl-xylotetraose. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis],6TRH_C Structure of E70A mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis complexed with 3(3)-alpha-L-arabinofuranosyl-xylotetraose. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis],6TRH_D Structure of E70A mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis complexed with 3(3)-alpha-L-arabinofuranosyl-xylotetraose. [Paenibacillus barcinonensis] |
| 6SHY_A | 5.06e-87 | 449 | 834 | 7 | 377 | Structureof L320A/H321S double mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis [Paenibacillus barcinonensis],6SHY_B Structure of L320A/H321S double mutant of Rex8A from Paenibacillus barcinonensis [Paenibacillus barcinonensis] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0A0S2UQQ5 | 1.79e-87 | 449 | 834 | 7 | 377 | Reducing-end xylose-releasing exo-oligoxylanase Rex8A OS=Paenibacillus barcinonensis OX=198119 GN=rex8A PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q9KB30 | 6.02e-77 | 443 | 834 | 1 | 376 | Reducing end xylose-releasing exo-oligoxylanase OS=Alkalihalobacillus halodurans (strain ATCC BAA-125 / DSM 18197 / FERM 7344 / JCM 9153 / C-125) OX=272558 GN=BH2105 PE=1 SV=1 |
| A1A048 | 2.49e-68 | 460 | 837 | 16 | 379 | Reducing end xylose-releasing exo-oligoxylanase OS=Bifidobacterium adolescentis (strain ATCC 15703 / DSM 20083 / NCTC 11814 / E194a) OX=367928 GN=xylA PE=1 SV=1 |
| P49943 | 2.69e-45 | 22 | 298 | 8 | 317 | Xylosidase/arabinosidase OS=Bacteroides ovatus OX=28116 GN=xsa PE=2 SV=1 |
| P48791 | 8.64e-43 | 22 | 301 | 6 | 318 | Beta-xylosidase OS=Prevotella ruminicola OX=839 GN=xynB PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
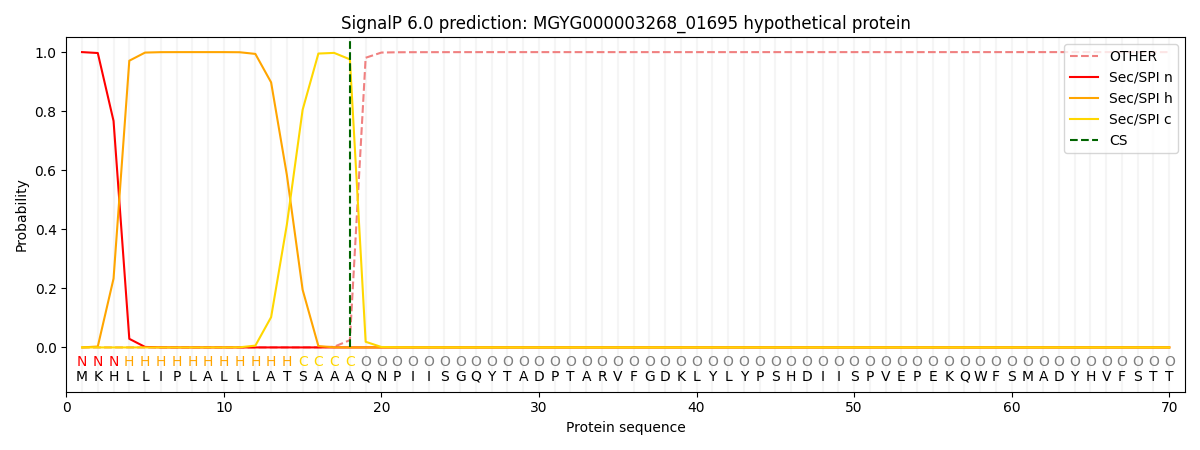
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000344 | 0.998893 | 0.000189 | 0.000203 | 0.000185 | 0.000164 |
