You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002310_07050
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002310_07050
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
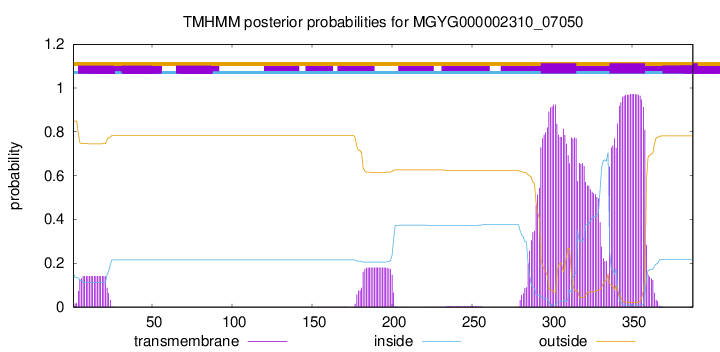
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Microvirga massiliensis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Alphaproteobacteria; Rhizobiales; Beijerinckiaceae; Microvirga; Microvirga massiliensis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002310_07050 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT2 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 170312; End: 171478 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT2 | 45 | 222 | 1e-21 | 0.9647058823529412 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIGR03469 | HpnB | 6.56e-158 | 5 | 380 | 7 | 384 | hopene-associated glycosyltransferase HpnB. This family of genes include a glycosyl transferase, group 2 domain (pfam00535) which are responsible, generally for the transfer of nucleotide-diphosphate sugars to substrates such as polysaccharides and lipids. The genes of this family are often found in the same genetic locus with squalene-hopene cyclase genes, and are never associated with genes for the metabolism of phytoene. Indeed, the members of this family appear to never be found in a genome lacking squalene-hopene cyclase (SHC), although not all genomes encoding SHC have this glycosyl transferase. In the organism Zymomonas mobilis the linkage of this gene to hopanoid biosynthesis has been noted and the gene named HpnB. Hopanoids are known to feature polar glycosyl head groups in many organisms. |
| pfam00535 | Glycos_transf_2 | 4.20e-19 | 42 | 222 | 1 | 164 | Glycosyl transferase family 2. Diverse family, transferring sugar from UDP-glucose, UDP-N-acetyl- galactosamine, GDP-mannose or CDP-abequose, to a range of substrates including cellulose, dolichol phosphate and teichoic acids. |
| cd06423 | CESA_like | 4.61e-19 | 46 | 238 | 2 | 180 | CESA_like is the cellulose synthase superfamily. The cellulose synthase (CESA) superfamily includes a wide variety of glycosyltransferase family 2 enzymes that share the common characteristic of catalyzing the elongation of polysaccharide chains. The members include cellulose synthase catalytic subunit, chitin synthase, glucan biosynthesis protein and other families of CESA-like proteins. Cellulose synthase catalyzes the polymerization reaction of cellulose, an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues in plants, most algae, some bacteria and fungi, and even some animals. In bacteria, algae and lower eukaryotes, there is a second unrelated type of cellulose synthase (Type II), which produces acylated cellulose, a derivative of cellulose. Chitin synthase catalyzes the incorporation of GlcNAc from substrate UDP-GlcNAc into chitin, which is a linear homopolymer of beta-(1,4)-linked GlcNAc residues and Glucan Biosynthesis protein catalyzes the elongation of beta-1,2 polyglucose chains of Glucan. |
| cd06438 | EpsO_like | 6.69e-18 | 46 | 166 | 2 | 113 | EpsO protein participates in the methanolan synthesis. The Methylobacillus sp EpsO protein is predicted to participate in the methanolan synthesis. Methanolan is an exopolysaccharide (EPS), composed of glucose, mannose and galactose. A 21 genes cluster was predicted to participate in the methanolan synthesis. Gene disruption analysis revealed that EpsO is one of the glycosyltransferase enzymes involved in the synthesis of repeating sugar units onto the lipid carrier. |
| cd04192 | GT_2_like_e | 8.98e-18 | 46 | 158 | 2 | 106 | Subfamily of Glycosyltransferase Family GT2 of unknown function. GT-2 includes diverse families of glycosyltransferases with a common GT-A type structural fold, which has two tightly associated beta/alpha/beta domains that tend to form a continuous central sheet of at least eight beta-strands. These are enzymes that catalyze the transfer of sugar moieties from activated donor molecules to specific acceptor molecules, forming glycosidic bonds. Glycosyltransferases have been classified into more than 90 distinct sequence based families. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARQ02741.1 | 4.20e-135 | 3 | 379 | 7 | 377 |
| BCJ91988.1 | 9.03e-135 | 5 | 385 | 9 | 390 |
| BAP89644.1 | 7.48e-134 | 1 | 379 | 8 | 381 |
| CCB66985.1 | 8.74e-132 | 3 | 383 | 8 | 386 |
| AMN40767.1 | 1.37e-131 | 3 | 379 | 7 | 385 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
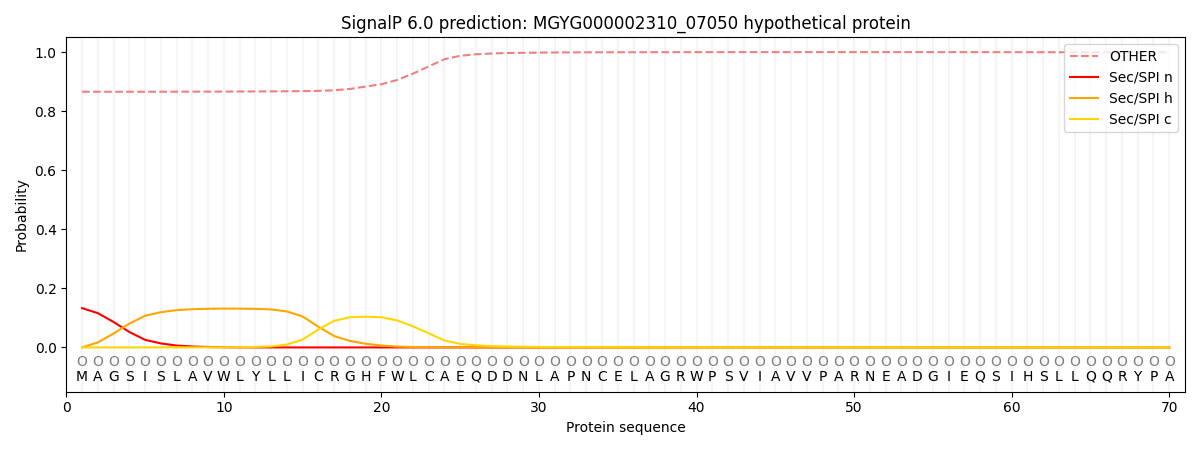
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.875648 | 0.122133 | 0.001528 | 0.000192 | 0.000172 | 0.000320 |