You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002233_00659
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002233_00659
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
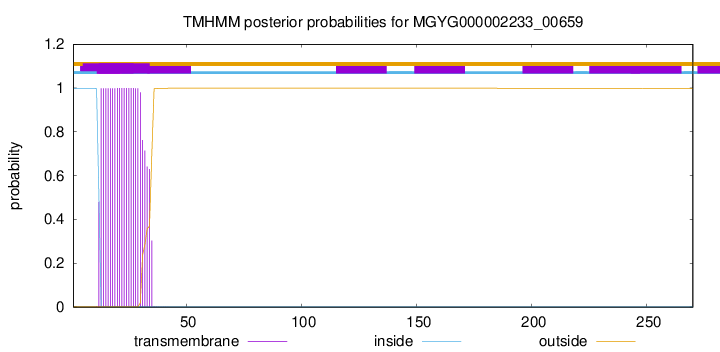
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Acutalibacter sp900543555 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Oscillospirales; Acutalibacteraceae; Acutalibacter; Acutalibacter sp900543555 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002233_00659 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE4 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylmuramic acid deacetylase PdaA | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 62677; End: 63489 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE4 | 75 | 201 | 2.1e-33 | 0.9384615384615385 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIGR02884 | spore_pdaA | 3.02e-103 | 46 | 269 | 1 | 224 | delta-lactam-biosynthetic de-N-acetylase. Muramic delta-lactam is an unusual constituent of peptidoglycan, found only in bacterial spores in the peptidoglycan wall, or spore cortex. The proteins in this family are PdaA (yfjS), a member of a larger family of polysaccharide deacetylases, and are specificially involved in delta-lactam biosynthesis. PdaA acts immediately after CwlD, an N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase and performs a de-N-acetylation. PdaA may also perform the following transpeptidation for lactam ring formation, as heterologous expression in E. coli of CwlD and PdaA together is sufficient for delta-lactam production. [Cell envelope, Biosynthesis and degradation of murein sacculus and peptidoglycan, Cellular processes, Sporulation and germination] |
| cd10948 | CE4_BsPdaA_like | 1.34e-101 | 46 | 265 | 4 | 223 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of Bacillus subtilis polysaccharide deacetylase PdaA, and its bacterial homologs. The Bacillus subtilis genome contains six polysaccharide deacetylase gene homologs: pdaA, pdaB (previously known as ybaN), yheN, yjeA, yxkH and ylxY. This family is represented by Bacillus subtilis pdaA gene encoding polysaccharide deacetylase BsPdaA, which is a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. BsPdaA deacetylates peptidoglycan N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) residues to facilitate the formation of muramic delta-lactam, which is required for recognition of germination lytic enzymes. BsPdaA deficiency leads to the absence of muramic delta-lactam residues in the spore cortex. Like other CE4 esterases, BsPdaA consists of a single catalytic NodB homology domain that appears to adopt a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold with a putative substrate binding groove harboring the majority of the conserved residues. It utilizes a general acid/base catalytic mechanism involving a tetrahedral transition intermediate, where a water molecule functions as the nucleophile tightly associated to the zinc cofactor. |
| cd10917 | CE4_NodB_like_6s_7s | 2.27e-59 | 81 | 254 | 1 | 169 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of rhizobial NodB-like proteins. This family belongs to the large and functionally diverse carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily, whose members show strong sequence similarity with some variability due to their distinct carbohydrate substrates. It includes many rhizobial NodB chitooligosaccharide N-deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.-)-like proteins, mainly from bacteria and eukaryotes, such as chitin deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.41), bacterial peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.-), and acetylxylan esterases (EC 3.1.1.72), which catalyze the N- or O-deacetylation of substrates such as acetylated chitin, peptidoglycan, and acetylated xylan. All members of this family contain a catalytic NodB homology domain with the same overall topology and a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold with 6- or 7 strands. Their catalytic activity is dependent on the presence of a divalent cation, preferably cobalt or zinc, and they employ a conserved His-His-Asp zinc-binding triad closely associated with the conserved catalytic base (aspartic acid) and acid (histidine) to carry out acid/base catalysis. Several family members show diversity both in metal ion specificities and in the residues that coordinate the metal. |
| TIGR02764 | spore_ybaN_pdaB | 2.01e-52 | 76 | 268 | 1 | 190 | polysaccharide deacetylase family sporulation protein PdaB. This model describes the YbaN protein family, also called PdaB and SpoVIE, of Gram-positive bacteria. Although ybaN null mutants have only a mild sporulation defect, ybaN/ytrI double mutants show drastically reducted sporulation efficiencies. This synthetic defect suggests the role of this sigmaE-controlled gene in sporulation had been masked by functional redundancy. Members of this family are homologous to a characterized polysaccharide deacetylase; the exact function this protein family is unknown. [Cellular processes, Sporulation and germination] |
| cd10950 | CE4_BsYlxY_like | 6.48e-49 | 98 | 268 | 23 | 187 | Putative catalytic NodB homology domain of uncharacterized protein YlxY from Bacillus subtilis and its bacterial homologs. The Bacillus subtilis genome contains six polysaccharide deacetylase gene homologs: pdaA, pdaB (previously known as ybaN), yheN, yjeA, yxkH and ylxY. This family is represented by Bacillus subtilis putative polysaccharide deacetylase BsYlxY, encoded by the ylxY gene, which is a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. Although its biological function still remains unknown, BsYlxY shows high sequence homology to the catalytic domain of Bacillus subtilis pdaB gene encoding a putative polysaccharide deacetylase (BsPdaB), which is essential for the maintenance of spores after the late stage of sporulation and is highly conserved in spore-forming bacteria. However, disruption of the ylxY gene in B. subtilis did not cause any sporulation defect. Moreover, the Asp residue in the classical His-His-Asp zinc-binding motif of CE4 esterases is mutated to a Val residue in this family. Other catalytically relevant residues of CE4 esterases are also not conserved, which suggest that members of this family may be inactive. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASB39592.1 | 1.03e-124 | 5 | 265 | 9 | 262 |
| ANU53732.1 | 1.03e-124 | 5 | 265 | 9 | 262 |
| QQR28884.1 | 1.03e-124 | 5 | 265 | 9 | 262 |
| BCI60049.1 | 4.28e-112 | 9 | 268 | 6 | 265 |
| QEK18529.1 | 5.88e-111 | 3 | 268 | 2 | 268 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1W17_A | 2.11e-62 | 23 | 268 | 7 | 252 | Structureof Bacillus subtilis PdaA, a family 4 Carbohydrate esterase. [Bacillus subtilis],1W17_B Structure of Bacillus subtilis PdaA, a family 4 Carbohydrate esterase. [Bacillus subtilis] |
| 1W1A_1 | 2.49e-62 | 35 | 268 | 10 | 246 | Structureof Bacillus subtilis PdaA in complex with NAG, a family 4 Carbohydrate esterase. [Bacillus subtilis],1W1A_2 Structure of Bacillus subtilis PdaA in complex with NAG, a family 4 Carbohydrate esterase. [Bacillus subtilis],1W1B_1 Structure of Bacillus subtilis PdaA with Cadmium, a family 4 Carbohydrate esterase. [Bacillus subtilis],1W1B_2 Structure of Bacillus subtilis PdaA with Cadmium, a family 4 Carbohydrate esterase. [Bacillus subtilis] |
| 1NY1_A | 1.91e-60 | 43 | 268 | 4 | 229 | CrystalStructure Of B. Subtilis Polysaccharide Deacetylase Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium Target Sr127. [Bacillus subtilis],1NY1_B Crystal Structure Of B. Subtilis Polysaccharide Deacetylase Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium Target Sr127. [Bacillus subtilis] |
| 2J13_A | 2.42e-57 | 46 | 268 | 19 | 241 | Structureof a family 4 carbohydrate esterase from Bacillus anthracis [Bacillus anthracis str. Ames] |
| 5O6Y_A | 8.38e-33 | 65 | 262 | 5 | 201 | Crystalstructure of the Bc1960 peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase in complex with 4-naphthalen-1-yl-~{N}-oxidanyl-benzamide [Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q04729 | 1.63e-67 | 41 | 268 | 22 | 253 | Uncharacterized 30.6 kDa protein in fumA 3'region OS=Geobacillus stearothermophilus OX=1422 PE=3 SV=1 |
| O34928 | 1.16e-61 | 23 | 268 | 7 | 252 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylmuramic acid deacetylase PdaA OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=pdaA PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q81EK9 | 2.00e-31 | 65 | 262 | 65 | 261 | Peptidoglycan-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase BC_1960 OS=Bacillus cereus (strain ATCC 14579 / DSM 31 / CCUG 7414 / JCM 2152 / NBRC 15305 / NCIMB 9373 / NCTC 2599 / NRRL B-3711) OX=226900 GN=BC_1960 PE=1 SV=1 |
| P02963 | 2.92e-30 | 78 | 238 | 18 | 174 | Chitooligosaccharide deacetylase OS=Rhizobium meliloti (strain 1021) OX=266834 GN=nodB PE=3 SV=3 |
| P04676 | 2.27e-28 | 76 | 238 | 15 | 172 | Chitooligosaccharide deacetylase OS=Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii OX=386 GN=nodB PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
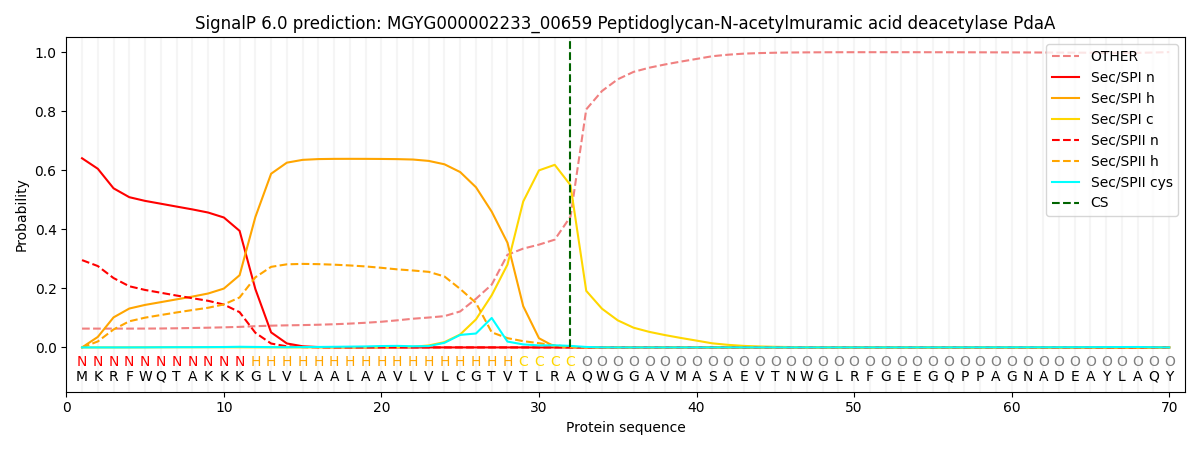
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.067812 | 0.628116 | 0.302912 | 0.000414 | 0.000324 | 0.000390 |