You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002136_02153
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002136_02153
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
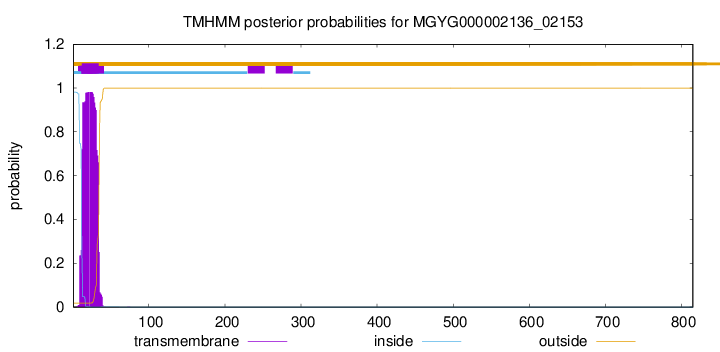
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | UC5-1-2E3 sp001304875 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; Lachnospiraceae; UC5-1-2E3; UC5-1-2E3 sp001304875 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002136_02153 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH73 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 12426; End: 14873 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd14256 | Dockerin_I | 3.36e-20 | 756 | 812 | 1 | 57 | Type I dockerin repeat domain. Bacterial cohesin domains bind to a complementary protein domain named dockerin, and this interaction is required for the formation of the cellulosome, a cellulose-degrading complex. The cellulosome consists of scaffoldin, a noncatalytic scaffolding polypeptide, that comprises repeating cohesion modules and a single carbohydrate-binding module (CBM). Specific calcium-dependent interactions between cohesins and dockerins appear to be essential for cellulosome assembly. This subfamily represents type I dockerins, which are responsible for anchoring a variety of enzymatic domains to the complex. |
| COG4193 | LytD | 3.28e-18 | 369 | 524 | 101 | 245 | Beta- N-acetylglucosaminidase [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| pfam00404 | Dockerin_1 | 4.26e-14 | 757 | 812 | 1 | 56 | Dockerin type I repeat. The dockerin repeat is the binding partner of the cohesin domain pfam00963. The cohesin-dockerin interaction is the crucial interaction for complex formation in the cellulosome. The dockerin repeats, each bearing homology to the EF-hand calcium-binding loop bind calcium. |
| pfam12733 | Cadherin-like | 6.41e-10 | 544 | 624 | 1 | 88 | Cadherin-like beta sandwich domain. This domain is found in several bacterial, metazoan and chlorophyte algal proteins. A profile-profile comparison recovered the cadherin domain and a comparison of the predicted structure of this domain with the crystal structure of the cadherin showed a congruent seven stranded secondary structure. The domain is widespread in bacteria and seen in the firmicutes, actinobacteria, certain proteobacteria, bacteroides and chlamydiae with an expansion in Clostridium. In contrast, it is limited in its distribution in eukaryotes suggesting that it was derived through lateral transfer from bacteria. In prokaryotes, this domain is widely fused to other domains such as FNIII (Fibronectin Type III), TIG, SLH (S-layer homology), discoidin, cell-wall-binding repeat domain and alpha-amylase-like glycohydrolases. These associations are suggestive of a carbohydrate-binding function for this cadherin-like domain. In animal proteins it is associated with an ATP-grasp domain. |
| cd14254 | Dockerin_II | 2.45e-09 | 757 | 812 | 1 | 54 | Type II dockerin repeat domain. Bacterial cohesin domains bind to a complementary protein domain named dockerin, and this interaction is required for the formation of the cellulosome, a cellulose-degrading complex. The cellulosome consists of scaffoldin, a noncatalytic scaffolding polypeptide, that comprises repeating cohesion modules and a single carbohydrate-binding module (CBM). Specific calcium-dependent interactions between cohesins and dockerins appear to be essential for cellulosome assembly. This subfamily represents type II dockerins, which are responsible for mediating attachment of the cellulosome complex to the bacterial cell wall. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QRV21758.1 | 4.15e-234 | 1 | 636 | 1 | 619 |
| ADL03932.1 | 4.15e-234 | 1 | 636 | 1 | 619 |
| QJU23484.1 | 1.18e-224 | 1 | 634 | 1 | 693 |
| ASN95383.1 | 1.29e-223 | 1 | 634 | 1 | 693 |
| QRP39925.1 | 1.29e-223 | 1 | 634 | 1 | 693 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6FXO_A | 1.70e-09 | 412 | 523 | 143 | 243 | ChainA, Bifunctional autolysin [Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus Mu50] |
| 4PI7_A | 8.89e-08 | 372 | 507 | 88 | 212 | ChainA, Autolysin E [Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus Mu50],4PI9_A Chain A, Autolysin E [Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus Mu50],4PIA_A Chain A, Autolysin E [Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus Mu50] |
| 4PI8_A | 5.27e-07 | 372 | 507 | 88 | 212 | ChainA, Autolysin E [Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus Mu50] |
| 2KRS_A | 7.10e-06 | 49 | 110 | 8 | 59 | SolutionNMR structure of SH3 domain from CPF_0587 (fragment 415-479) from Clostridium perfringens. Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium (NESG) Target CpR74A. [Clostridium perfringens] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q8CPQ1 | 1.01e-09 | 370 | 523 | 1185 | 1334 | Bifunctional autolysin OS=Staphylococcus epidermidis (strain ATCC 12228 / FDA PCI 1200) OX=176280 GN=atl PE=3 SV=1 |
| O33635 | 2.29e-09 | 370 | 523 | 1185 | 1334 | Bifunctional autolysin OS=Staphylococcus epidermidis OX=1282 GN=atl PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q5HQB9 | 2.29e-09 | 370 | 523 | 1185 | 1334 | Bifunctional autolysin OS=Staphylococcus epidermidis (strain ATCC 35984 / RP62A) OX=176279 GN=atl PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q931U5 | 5.90e-08 | 412 | 523 | 1147 | 1247 | Bifunctional autolysin OS=Staphylococcus aureus (strain Mu50 / ATCC 700699) OX=158878 GN=atl PE=1 SV=2 |
| Q99V41 | 5.90e-08 | 412 | 523 | 1147 | 1247 | Bifunctional autolysin OS=Staphylococcus aureus (strain N315) OX=158879 GN=atl PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
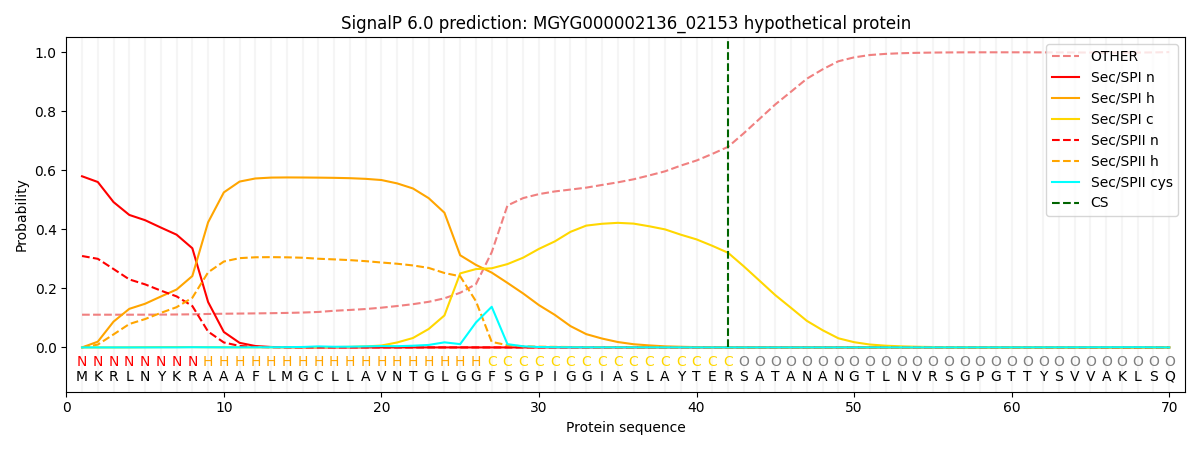
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.115448 | 0.570337 | 0.313003 | 0.000522 | 0.000319 | 0.000347 |