You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001389_00001
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001389_00001
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Cloacibacillus evryensis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Synergistota; Synergistia; Synergistales; Synergistaceae; Cloacibacillus; Cloacibacillus evryensis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001389_00001 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH23 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase C | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 686; End: 1549 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH23 | 179 | 281 | 2.9e-17 | 0.8148148148148148 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam01464 | SLT | 2.56e-19 | 169 | 276 | 3 | 108 | Transglycosylase SLT domain. This family is distantly related to pfam00062. Members are found in phages, type II, type III and type IV secretion systems. |
| cd00254 | LT-like | 4.11e-16 | 179 | 262 | 2 | 81 | lytic transglycosylase(LT)-like domain. Members include the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria and LTs in bacteriophage lambda. LTs catalyze the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. |
| cd13400 | LT_IagB-like | 6.11e-16 | 174 | 274 | 1 | 106 | Escherichia coli invasion protein IagB and similar proteins. Lytic transglycosylase-like protein, similar to Escherichia coli invasion protein IagB. IagB is encoded within a pathogenicity island in Salmonella enterica and has been shown to degrade polymeric peptidoglycan. IagB-like invasion proteins are implicated in the invasion of eukaryotic host cells by bacteria. Lytic transglycosylase (LT) catalyzes the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. Members of this family resemble the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria and the LTs in bacteriophage lambda. |
| cd16896 | LT_Slt70-like | 1.92e-15 | 170 | 274 | 11 | 143 | uncharacterized lytic transglycosylase subfamily with similarity to Slt70. Uncharacterized lytic transglycosylase (LT) with a conserved sequence pattern suggesting similarity to the Slt70, a 70kda soluble lytic transglycosylase which also has an N-terminal U-shaped U-domain and a linker L-domain. LTs catalyze the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. |
| cd16893 | LT_MltC_MltE | 6.48e-15 | 170 | 264 | 6 | 105 | membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylases MltC and MltE, and similar proteins. MltC and MltE are periplasmic, outer membrane attached lytic transglycosylases (LTs), which cleave beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds joining N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetylglucosamine in the cell wall peptidoglycan, yielding 1,6-anhydromuropeptides. Proteins similar to this family include the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria and the LTs in bacteriophage lambda |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANZ46429.1 | 2.40e-147 | 66 | 287 | 1 | 222 |
| ACZ18328.1 | 5.00e-58 | 82 | 279 | 60 | 256 |
| AFM20682.1 | 1.91e-53 | 90 | 279 | 42 | 230 |
| QTX32309.1 | 2.27e-42 | 97 | 281 | 80 | 263 |
| QVL36175.1 | 2.27e-42 | 97 | 281 | 80 | 263 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4C5F_A | 3.57e-08 | 171 | 263 | 182 | 278 | Structureof Lytic Transglycosylase MltC from Escherichia coli at 2.3 A resolution. [Escherichia coli],4C5F_B Structure of Lytic Transglycosylase MltC from Escherichia coli at 2.3 A resolution. [Escherichia coli] |
| 4CFO_A | 8.60e-08 | 171 | 263 | 182 | 278 | Structureof Lytic Transglycosylase MltC from Escherichia coli in complex with tetrasaccharide at 2.9 A resolution. [Escherichia coli],4CFO_B Structure of Lytic Transglycosylase MltC from Escherichia coli in complex with tetrasaccharide at 2.9 A resolution. [Escherichia coli],4CFP_A Crystal structure of MltC in complex with tetrasaccharide at 2.15 A resolution [Escherichia coli],4CFP_B Crystal structure of MltC in complex with tetrasaccharide at 2.15 A resolution [Escherichia coli],4CHX_A Crystal structure of MltC in complex with disaccharide pentapeptide DHl89 [Escherichia coli],4CHX_B Crystal structure of MltC in complex with disaccharide pentapeptide DHl89 [Escherichia coli] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1CEV1 | 7.07e-11 | 171 | 263 | 199 | 295 | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase C OS=Yersinia pestis bv. Antiqua (strain Nepal516) OX=377628 GN=mltC PE=3 SV=2 |
| A9R6R2 | 7.07e-11 | 171 | 263 | 199 | 295 | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase C OS=Yersinia pestis bv. Antiqua (strain Angola) OX=349746 GN=mltC PE=3 SV=1 |
| B2K0V2 | 7.07e-11 | 171 | 263 | 199 | 295 | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase C OS=Yersinia pseudotuberculosis serotype IB (strain PB1/+) OX=502801 GN=mltC PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q1CB94 | 7.07e-11 | 171 | 263 | 199 | 295 | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase C OS=Yersinia pestis bv. Antiqua (strain Antiqua) OX=360102 GN=mltC PE=3 SV=2 |
| A4TI58 | 7.07e-11 | 171 | 263 | 199 | 295 | Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase C OS=Yersinia pestis (strain Pestoides F) OX=386656 GN=mltC PE=3 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
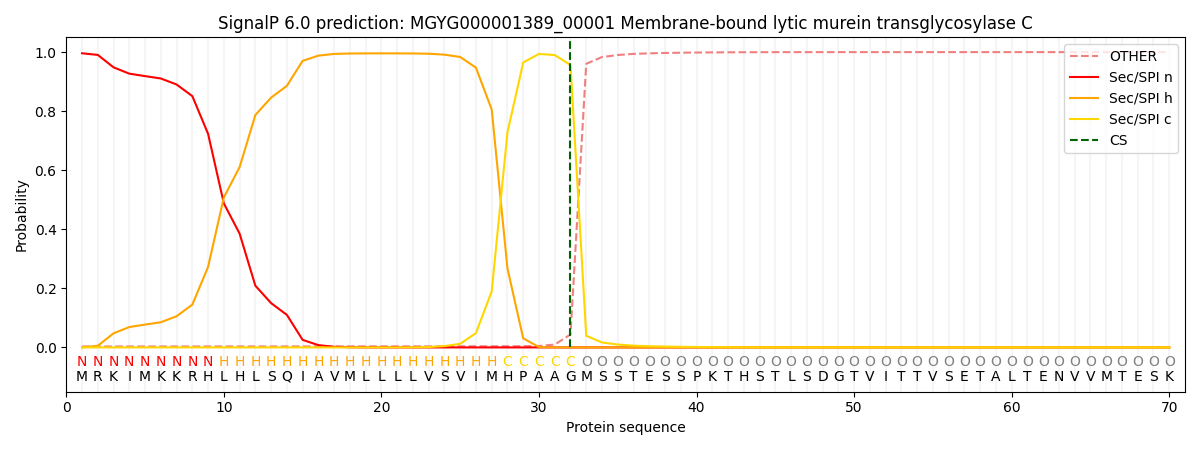
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.004450 | 0.993681 | 0.001241 | 0.000216 | 0.000184 | 0.000188 |

