You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000162_00358
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000162_00358
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
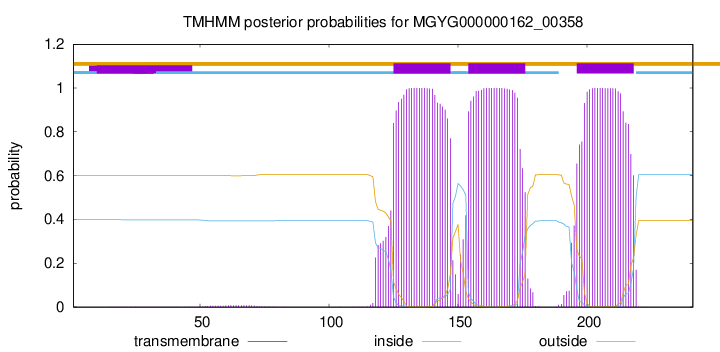
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Enterococcus_B durans | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Lactobacillales; Enterococcaceae; Enterococcus_B; Enterococcus_B durans | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000162_00358 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT2 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 47262; End: 47987 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COG1215 | BcsA | 3.45e-07 | 45 | 222 | 236 | 411 | Glycosyltransferase, catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase and poly-beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine synthase [Cell motility]. |
| cd06436 | GlcNAc-1-P_transferase | 3.05e-06 | 2 | 49 | 140 | 191 | N-acetyl-glucosamine transferase is involved in the synthesis of Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-acetyl-glucosamine transferase is responsible for the synthesis of bacteria Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (PGA). Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine is a homopolymer that serves as an adhesion for the maintenance of biofilm structural stability in diverse eubacteria. N-acetyl-glucosamine transferase is the product of gene pgaC. Genetic analysis indicated that all four genes of the pgaABCD locus were required for the PGA production, pgaC being a glycosyltransferase. |
| pfam13632 | Glyco_trans_2_3 | 2.79e-05 | 41 | 147 | 89 | 192 | Glycosyl transferase family group 2. Members of this family of prokaryotic proteins include putative glucosyltransferases, which are involved in bacterial capsule biosynthesis. |
| PRK11204 | PRK11204 | 8.55e-04 | 82 | 171 | 268 | 359 | N-glycosyltransferase; Provisional |
| cd06435 | CESA_NdvC_like | 0.004 | 12 | 95 | 145 | 230 | NdvC_like proteins in this family are putative bacterial beta-(1,6)-glucosyltransferase. NdvC_like proteins in this family are putative bacterial beta-(1,6)-glucosyltransferase. Bradyrhizobium japonicum synthesizes periplasmic cyclic beta-(1,3),beta-(1,6)-D-glucans during growth under hypoosmotic conditions. Two genes (ndvB, ndvC) are involved in the beta-(1, 3), beta-(1,6)-glucan synthesis. The ndvC mutant strain resulted in synthesis of altered cyclic beta-glucans composed almost entirely of beta-(1, 3)-glycosyl linkages. The periplasmic cyclic beta-(1,3),beta-(1,6)-D-glucans function for osmoregulation. The ndvC mutation also affects the ability of the bacteria to establish a successful symbiotic interaction with host plant. Thus, the beta-glucans may function as suppressors of a host defense response. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASV94770.1 | 2.23e-164 | 1 | 241 | 193 | 433 |
| AKZ47445.1 | 3.66e-163 | 1 | 241 | 193 | 433 |
| QCJ63063.1 | 3.66e-163 | 1 | 241 | 193 | 433 |
| AKX86070.1 | 3.66e-163 | 1 | 241 | 193 | 433 |
| QPQ27061.1 | 3.66e-163 | 1 | 241 | 193 | 433 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
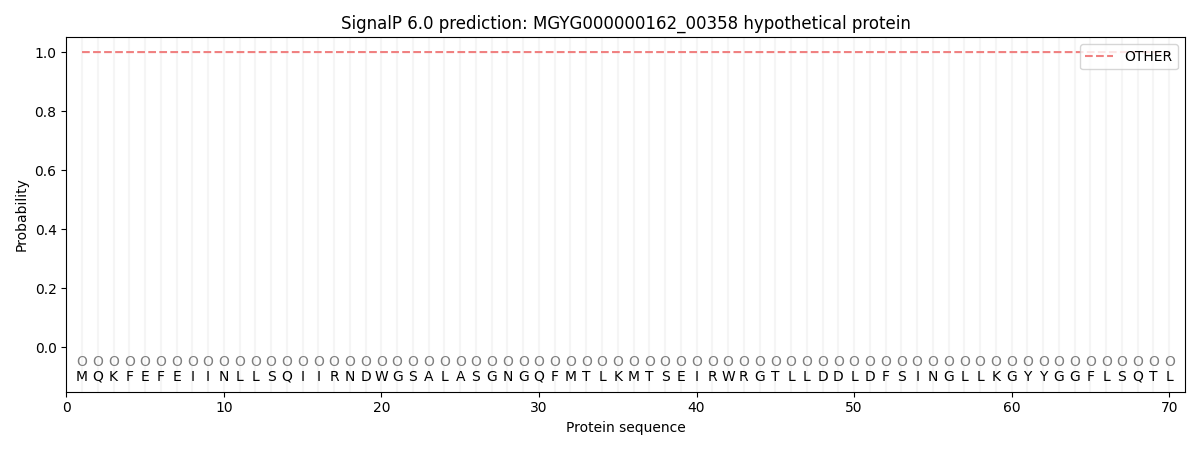
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000086 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |