You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004547_00062
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004547_00062
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
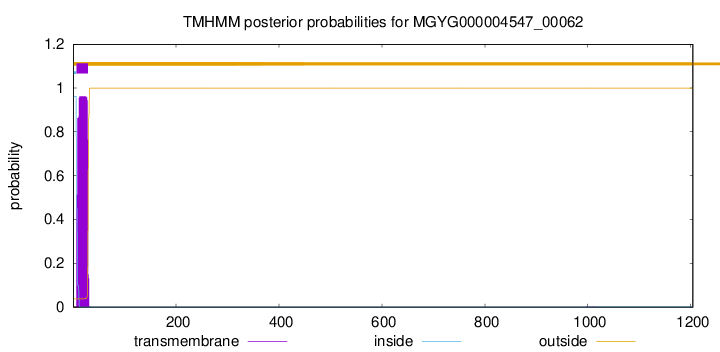
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; CAG-274; ; | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004547_00062 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE12 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 14784; End: 18398 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE12 | 237 | 465 | 3.2e-37 | 0.9952380952380953 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd01821 | Rhamnogalacturan_acetylesterase_like | 6.75e-28 | 236 | 465 | 1 | 198 | Rhamnogalacturan_acetylesterase_like subgroup of SGNH-hydrolases. Rhamnogalacturan acetylesterase removes acetyl esters from rhamnogalacturonan substrates, and renders them susceptible to degradation by rhamnogalacturonases. Rhamnogalacturonans are highly branched regions in pectic polysaccharides, consisting of repeating -(1,2)-L-Rha-(1,4)-D-GalUA disaccharide units, with many rhamnose residues substituted by neutral oligosaccharides such as arabinans, galactans and arabinogalactans. Extracellular enzymes participating in the degradation of plant cell wall polymers, such as Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase, would typically be found in saprophytic and plant pathogenic fungi and bacteria. |
| cd14256 | Dockerin_I | 9.58e-11 | 1138 | 1195 | 1 | 57 | Type I dockerin repeat domain. Bacterial cohesin domains bind to a complementary protein domain named dockerin, and this interaction is required for the formation of the cellulosome, a cellulose-degrading complex. The cellulosome consists of scaffoldin, a noncatalytic scaffolding polypeptide, that comprises repeating cohesion modules and a single carbohydrate-binding module (CBM). Specific calcium-dependent interactions between cohesins and dockerins appear to be essential for cellulosome assembly. This subfamily represents type I dockerins, which are responsible for anchoring a variety of enzymatic domains to the complex. |
| pfam00404 | Dockerin_1 | 3.99e-07 | 1139 | 1195 | 1 | 56 | Dockerin type I repeat. The dockerin repeat is the binding partner of the cohesin domain pfam00963. The cohesin-dockerin interaction is the crucial interaction for complex formation in the cellulosome. The dockerin repeats, each bearing homology to the EF-hand calcium-binding loop bind calcium. |
| pfam18998 | Flg_new_2 | 7.95e-07 | 1036 | 1100 | 16 | 74 | Divergent InlB B-repeat domain. This family of domains are found in bacterial cell surface proteins. They are often found in tandem array. This domain is closely related to pfam09479. |
| cd14255 | Dockerin_III | 1.49e-06 | 1139 | 1193 | 1 | 59 | Type III dockerin repeat domain. Bacterial cohesin domains bind to a complementary protein domain named dockerin, and this interaction is required for the formation of the cellulosome, a cellulose-degrading complex. Two specific calcium-dependent interactions between cohesin and dockerin appear to be essential for cellulosome assembly, type I and type II. This subfamily represents the atypical type III dockerins and related domains. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUO20403.1 | 9.65e-297 | 13 | 1099 | 15 | 1093 |
| QYR20260.1 | 1.34e-172 | 62 | 727 | 67 | 701 |
| QYR22257.1 | 1.55e-171 | 10 | 727 | 9 | 703 |
| AFH63140.2 | 4.65e-166 | 4 | 727 | 12 | 715 |
| AFC30818.1 | 6.11e-166 | 47 | 727 | 49 | 702 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O31528 | 4.70e-13 | 238 | 465 | 5 | 202 | Probable rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase YesY OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=yesY PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
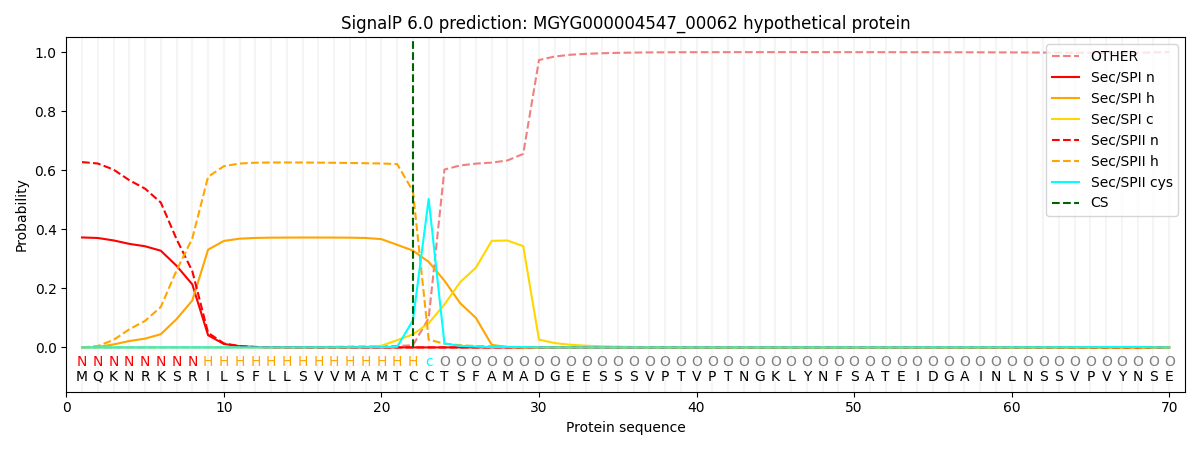
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000599 | 0.364327 | 0.634292 | 0.000328 | 0.000255 | 0.000186 |