You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004469_01204
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004469_01204
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
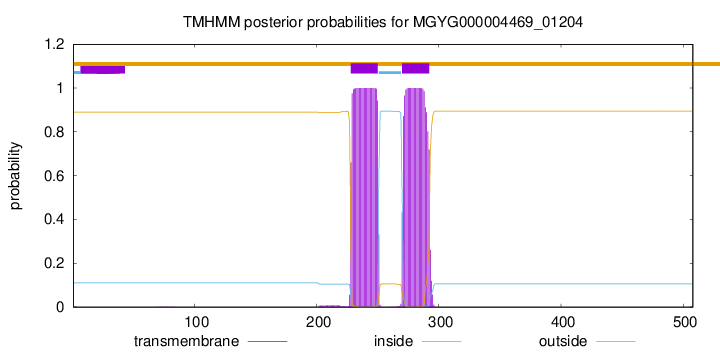
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Alistipes_A sp900545315 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Rikenellaceae; Alistipes_A; Alistipes_A sp900545315 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004469_01204 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT2 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Undecaprenyl-phosphate 4-deoxy-4-formamido-L-arabinose transferase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 33051; End: 34577 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT2 | 2 | 160 | 1.5e-32 | 0.9588235294117647 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd04187 | DPM1_like_bac | 2.22e-86 | 2 | 182 | 2 | 181 | Bacterial DPM1_like enzymes are related to eukaryotic DPM1. A family of bacterial enzymes related to eukaryotic DPM1; Although the mechanism of eukaryotic enzyme is well studied, the mechanism of the bacterial enzymes is not well understood. The eukaryotic DPM1 is the catalytic subunit of eukaryotic Dolichol-phosphate mannose (DPM) synthase. DPM synthase is required for synthesis of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor, N-glycan precursor, protein O-mannose, and C-mannose. The enzyme has three subunits, DPM1, DPM2 and DPM3. DPM is synthesized from dolichol phosphate and GDP-Man on the cytosolic surface of the ER membrane by DPM synthase and then is flipped onto the luminal side and used as a donor substrate. This protein family belongs to Glycosyltransferase 2 superfamily. |
| cd04179 | DPM_DPG-synthase_like | 4.66e-70 | 2 | 182 | 2 | 185 | DPM_DPG-synthase_like is a member of the Glycosyltransferase 2 superfamily. DPM1 is the catalytic subunit of eukaryotic dolichol-phosphate mannose (DPM) synthase. DPM synthase is required for synthesis of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor, N-glycan precursor, protein O-mannose, and C-mannose. In higher eukaryotes,the enzyme has three subunits, DPM1, DPM2 and DPM3. DPM is synthesized from dolichol phosphate and GDP-Man on the cytosolic surface of the ER membrane by DPM synthase and then is flipped onto the luminal side and used as a donor substrate. In lower eukaryotes, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Trypanosoma brucei, DPM synthase consists of a single component (Dpm1p and TbDpm1, respectively) that possesses one predicted transmembrane region near the C terminus for anchoring to the ER membrane. In contrast, the Dpm1 homologues of higher eukaryotes, namely fission yeast, fungi, and animals, have no transmembrane region, suggesting the existence of adapter molecules for membrane anchoring. This family also includes bacteria and archaea DPM1_like enzymes. However, the enzyme structure and mechanism of function are not well understood. The UDP-glucose:dolichyl-phosphate glucosyltransferase (DPG_synthase) is a transmembrane-bound enzyme of the endoplasmic reticulum involved in protein N-linked glycosylation. This enzyme catalyzes the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to dolichyl phosphate. This protein family belongs to Glycosyltransferase 2 superfamily. |
| PRK10714 | PRK10714 | 1.25e-48 | 1 | 319 | 10 | 320 | undecaprenyl phosphate 4-deoxy-4-formamido-L-arabinose transferase; Provisional |
| cd06442 | DPM1_like | 7.30e-40 | 1 | 212 | 1 | 218 | DPM1_like represents putative enzymes similar to eukaryotic DPM1. Proteins similar to eukaryotic DPM1, including enzymes from bacteria and archaea; DPM1 is the catalytic subunit of eukaryotic dolichol-phosphate mannose (DPM) synthase. DPM synthase is required for synthesis of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor, N-glycan precursor, protein O-mannose, and C-mannose. In higher eukaryotes,the enzyme has three subunits, DPM1, DPM2 and DPM3. DPM is synthesized from dolichol phosphate and GDP-Man on the cytosolic surface of the ER membrane by DPM synthase and then is flipped onto the luminal side and used as a donor substrate. In lower eukaryotes, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Trypanosoma brucei, DPM synthase consists of a single component (Dpm1p and TbDpm1, respectively) that possesses one predicted transmembrane region near the C terminus for anchoring to the ER membrane. In contrast, the Dpm1 homologues of higher eukaryotes, namely fission yeast, fungi, and animals, have no transmembrane region, suggesting the existence of adapter molecules for membrane anchoring. This family also includes bacteria and archaea DPM1_like enzymes. However, the enzyme structure and mechanism of function are not well understood. This protein family belongs to Glycosyltransferase 2 superfamily. |
| pfam00535 | Glycos_transf_2 | 3.63e-33 | 2 | 160 | 3 | 164 | Glycosyl transferase family 2. Diverse family, transferring sugar from UDP-glucose, UDP-N-acetyl- galactosamine, GDP-mannose or CDP-abequose, to a range of substrates including cellulose, dolichol phosphate and teichoic acids. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCG54484.1 | 1.78e-206 | 1 | 344 | 10 | 350 |
| QGA24118.1 | 4.22e-187 | 1 | 312 | 10 | 321 |
| BBL05620.1 | 1.50e-168 | 1 | 312 | 8 | 319 |
| AFL79003.1 | 4.75e-167 | 1 | 311 | 8 | 318 |
| CBK65006.1 | 1.92e-166 | 1 | 311 | 8 | 318 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5EKE_A | 6.14e-24 | 1 | 309 | 30 | 328 | Structureof the polyisoprenyl-phosphate glycosyltransferase GtrB (F215A mutant) [Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 substr. Kazusa],5EKE_B Structure of the polyisoprenyl-phosphate glycosyltransferase GtrB (F215A mutant) [Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 substr. Kazusa],5EKE_C Structure of the polyisoprenyl-phosphate glycosyltransferase GtrB (F215A mutant) [Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 substr. Kazusa],5EKE_D Structure of the polyisoprenyl-phosphate glycosyltransferase GtrB (F215A mutant) [Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 substr. Kazusa] |
| 5EKP_A | 1.54e-23 | 1 | 309 | 30 | 328 | Structureof the polyisoprenyl-phosphate glycosyltransferase GtrB (WT) [Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 substr. Kazusa],5EKP_B Structure of the polyisoprenyl-phosphate glycosyltransferase GtrB (WT) [Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 substr. Kazusa],5EKP_C Structure of the polyisoprenyl-phosphate glycosyltransferase GtrB (WT) [Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 substr. Kazusa],5EKP_D Structure of the polyisoprenyl-phosphate glycosyltransferase GtrB (WT) [Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 substr. Kazusa] |
| 5MLZ_A | 9.88e-16 | 1 | 165 | 27 | 194 | Dolichylphosphate mannose synthase in complex with GDP and Mg2+ [Pyrococcus furiosus DSM 3638],5MM0_A Dolichyl phosphate mannose synthase in complex with GDP-mannose and Mn2+ (donor complex) [Pyrococcus furiosus DSM 3638],5MM1_A Dolichyl phosphate mannose synthase in complex with GDP and dolichyl phosphate mannose [Pyrococcus furiosus DSM 3638] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1MJ95 | 8.88e-56 | 1 | 297 | 22 | 315 | Dodecaprenyl-phosphate galacturonate synthase OS=Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae (strain 3841) OX=216596 GN=rgtE PE=1 SV=1 |
| C3KAD3 | 1.72e-49 | 1 | 325 | 11 | 322 | Undecaprenyl-phosphate 4-deoxy-4-formamido-L-arabinose transferase OS=Pseudomonas fluorescens (strain SBW25) OX=216595 GN=arnC PE=3 SV=1 |
| A8FRR3 | 7.05e-49 | 1 | 311 | 12 | 314 | Undecaprenyl-phosphate 4-deoxy-4-formamido-L-arabinose transferase OS=Shewanella sediminis (strain HAW-EB3) OX=425104 GN=arnC PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q4KC83 | 8.65e-49 | 1 | 325 | 11 | 322 | Undecaprenyl-phosphate 4-deoxy-4-formamido-L-arabinose transferase OS=Pseudomonas fluorescens (strain ATCC BAA-477 / NRRL B-23932 / Pf-5) OX=220664 GN=arnC PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q4ZSZ3 | 3.19e-47 | 1 | 315 | 11 | 317 | Undecaprenyl-phosphate 4-deoxy-4-formamido-L-arabinose transferase OS=Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae (strain B728a) OX=205918 GN=arnC PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
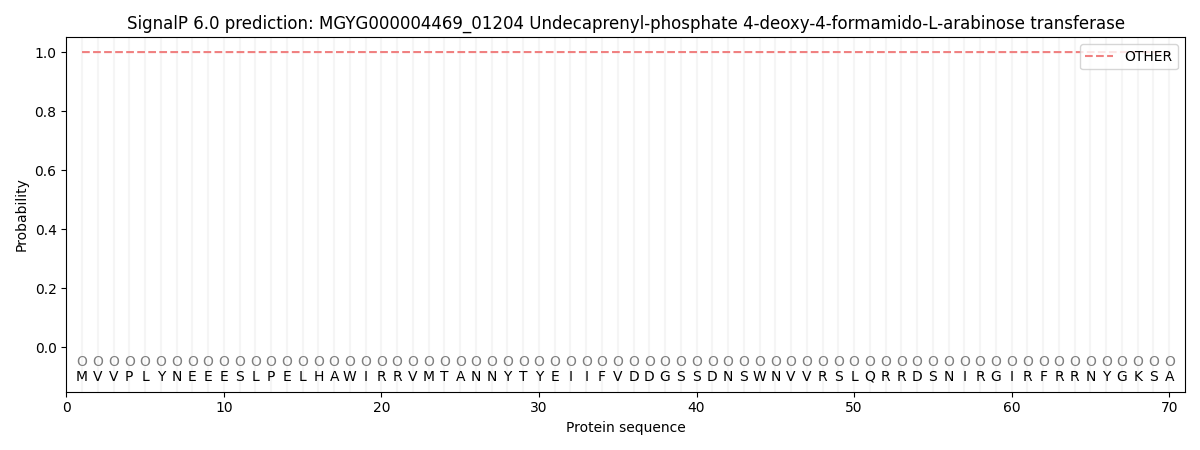
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000097 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |