You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002478_00032
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002478_00032
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Phocaeicola dorei | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; Phocaeicola; Phocaeicola dorei | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002478_00032 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH67 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Extracellular xylan exo-alpha-(1->2)-glucuronosidase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 35544; End: 37589 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH67 | 65 | 650 | 3.8e-266 | 0.9028400597907325 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COG3661 | AguA2 | 0.0 | 91 | 647 | 92 | 674 | Alpha-glucuronidase [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| pfam07488 | Glyco_hydro_67M | 0.0 | 124 | 424 | 1 | 324 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 67 middle domain. Alpha-glucuronidases, components of an ensemble of enzymes central to the recycling of photosynthetic biomass, remove the alpha-1,2 linked 4-O-methyl glucuronic acid from xylans. This family represents the central catalytic domain of alpha-glucuronidase. |
| pfam07477 | Glyco_hydro_67C | 1.70e-135 | 426 | 653 | 1 | 223 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 67 C-terminus. Alpha-glucuronidases, components of an ensemble of enzymes central to the recycling of photosynthetic biomass, remove the alpha-1,2 linked 4-O-methyl glucuronic acid from xylans. This family represents the C terminal region of alpha-glucuronidase which is mainly alpha-helical. It wraps around the catalytic domain (pfam07488), making additional interactions both with the N-terminal domain (pfam03648) of its parent monomer and also forming the majority of the dimer-surface with the equivalent C-terminal domain of the other monomer of the dimer. |
| pfam03648 | Glyco_hydro_67N | 2.14e-04 | 41 | 121 | 1 | 120 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 67 N-terminus. Alpha-glucuronidases, components of an ensemble of enzymes central to the recycling of photosynthetic biomass, remove the alpha-1,2 linked 4-O-methyl glucuronic acid from xylans. This family represents the N-terminal region of alpha-glucuronidase. The N-terminal domain forms a two-layer sandwich, each layer being formed by a beta sheet of five strands. A further two helices form part of the interface with the central, catalytic, module (pfam07488). |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALA72078.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 681 | 1 | 681 |
| QJR54275.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 681 | 1 | 681 |
| QJR60927.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 681 | 1 | 681 |
| AII66219.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 681 | 1 | 681 |
| QJR73691.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 681 | 1 | 681 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1GQI_A | 2.81e-237 | 36 | 663 | 1 | 686 | Structureof Pseudomonas cellulosa alpha-D-glucuronidase [Cellvibrio japonicus],1GQI_B Structure of Pseudomonas cellulosa alpha-D-glucuronidase [Cellvibrio japonicus],1GQJ_A Structure of Pseudomonas cellulosa alpha-D-glucuronidase complexed with xylobiose [Cellvibrio japonicus],1GQJ_B Structure of Pseudomonas cellulosa alpha-D-glucuronidase complexed with xylobiose [Cellvibrio japonicus],1GQK_A Structure of Pseudomonas cellulosa alpha-D-glucuronidase complexed with glucuronic acid [Cellvibrio japonicus],1GQK_B Structure of Pseudomonas cellulosa alpha-D-glucuronidase complexed with glucuronic acid [Cellvibrio japonicus],1GQL_A Structure of Pseudomonas cellulosa alpha-D-glucuronidase complexed with glucuronic acid and xylotriose [Cellvibrio japonicus],1GQL_B Structure of Pseudomonas cellulosa alpha-D-glucuronidase complexed with glucuronic acid and xylotriose [Cellvibrio japonicus] |
| 1H41_A | 2.27e-236 | 36 | 663 | 1 | 686 | Pseudomonascellulosa E292A alpha-D-glucuronidase mutant complexed with aldotriuronic acid [Cellvibrio japonicus],1H41_B Pseudomonas cellulosa E292A alpha-D-glucuronidase mutant complexed with aldotriuronic acid [Cellvibrio japonicus] |
| 1K9D_A | 1.27e-171 | 48 | 646 | 33 | 669 | The1.7 A crystal structure of alpha-D-glucuronidase, a family-67 glycoside hydrolase from Bacillus stearothermophilus T-1 [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],1L8N_A The 1.5A crystal structure of alpha-D-glucuronidase from Bacillus stearothermophilus T-1, complexed with 4-O-methyl-glucuronic acid and xylotriose [Geobacillus stearothermophilus],1MQQ_A THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ALPHA-D-GLUCURONIDASE FROM BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS T-1 COMPLEXED WITH GLUCURONIC ACID [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
| 1MQP_A | 1.80e-171 | 48 | 646 | 33 | 669 | TheCrystal Structure Of Alpha-D-Glucuronidase From Bacillus Stearothermophilus T-6 [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
| 1MQR_A | 5.08e-171 | 48 | 646 | 33 | 669 | ChainA, ALPHA-D-GLUCURONIDASE [Geobacillus stearothermophilus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B3PC73 | 3.47e-236 | 36 | 663 | 25 | 710 | Extracellular xylan exo-alpha-(1->2)-glucuronosidase OS=Cellvibrio japonicus (strain Ueda107) OX=498211 GN=gla67A PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q09LY5 | 9.86e-171 | 48 | 646 | 33 | 669 | Xylan alpha-(1->2)-glucuronosidase OS=Geobacillus stearothermophilus OX=1422 GN=aguA PE=1 SV=1 |
| P96105 | 1.36e-163 | 106 | 651 | 103 | 669 | Xylan alpha-(1->2)-glucuronosidase OS=Thermotoga maritima (strain ATCC 43589 / DSM 3109 / JCM 10099 / NBRC 100826 / MSB8) OX=243274 GN=aguA PE=1 SV=2 |
| A1CC12 | 3.30e-145 | 93 | 663 | 113 | 706 | Probable alpha-glucuronidase A OS=Aspergillus clavatus (strain ATCC 1007 / CBS 513.65 / DSM 816 / NCTC 3887 / NRRL 1 / QM 1276 / 107) OX=344612 GN=aguA PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q4WW45 | 5.59e-143 | 93 | 646 | 113 | 686 | Probable alpha-glucuronidase A OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain ATCC MYA-4609 / Af293 / CBS 101355 / FGSC A1100) OX=330879 GN=aguA PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
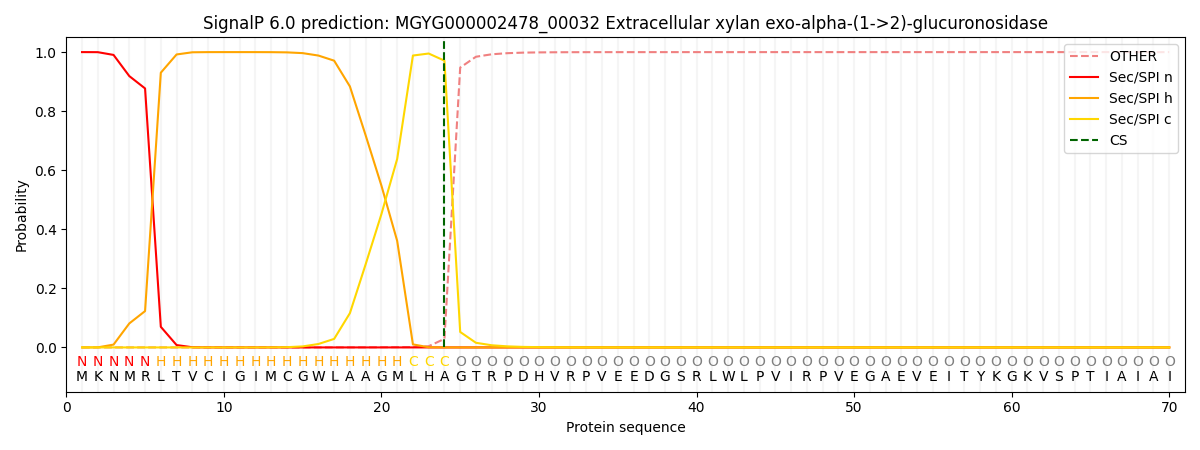
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000471 | 0.998590 | 0.000336 | 0.000213 | 0.000194 | 0.000173 |
