You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001507_02687
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001507_02687
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Paenibacillus ihuae | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Paenibacillales; Paenibacillaceae; Paenibacillus; Paenibacillus ihuae | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001507_02687 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM50 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Cell wall-binding protein YocH | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 2833660; End: 2834331 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd14667 | 3D_containing_proteins | 2.33e-22 | 136 | 222 | 14 | 90 | Non-mltA associated 3D domain containing proteins, named for 3 conserved aspartate residues. This family contains the 3D domain, named for its 3 conserved aspartates, including similar uncharacterized proteins. These proteins contain the critical active site aspartate of mltA-like lytic transglycosylases where the 3D domain forms a larger domain with the N-terminal region. This domain is also found in conjunction with numerous other domains such as the Escherichia coli MltA, a membrane-bound lytic transglycosylase comprised of 2 domains separated by a large groove, where the peptidoglycan strand binds. Domain A is made up of an N-terminal and a C-terminal portion, corresponding to the 3D domain and Domain B is inserted within the linear sequence of domain A. MltA is distinct from other bacterial LTs, which are similar to each other. Escherichia coli peptidoglycan lytic transglycosylase (LT) initiates cell wall recycling in response to damage, during bacterial fission, and cleaves peptidoglycan (PG) to create functional spaces in its wall. PG chains (also known as murein), the major components of the bacterial cell wall, are comprised of alternating beta-1-4-linked N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), and lytic transglycosylases cleave this beta-1-4 bond. |
| pfam06725 | 3D | 2.32e-13 | 153 | 223 | 2 | 72 | 3D domain. This short presumed domain contains three conserved aspartate residues, hence the name 3D. It has been shown to be part of the catalytic double psi beta barrel domain of MltA. |
| COG3584 | 3D | 2.40e-13 | 153 | 221 | 51 | 109 | 3D (Asp-Asp-Asp) domain [Function unknown]. |
| cd14486 | 3D_domain | 2.59e-13 | 147 | 222 | 33 | 104 | 3D domain, named for 3 conserved aspartate residues, is found in mltA-like lytic transglycosylases and numerous other contexts. This family contains the 3D domain, named for its 3 conserved aspartates. It is found in conjunction with numerous other domains such as MltA (membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase A). These aspartates are critical active site residues of mltA-like lytic transglycosylases. Escherichia coli peptidoglycan lytic transglycosylase (LT) initiates cell wall recycling in response to damage, during bacterial fission, and cleaves peptidoglycan (PG) to create functional spaces in its wall. MltA has 2 domains, separated by a large groove, where the peptidoglycan strand binds. The C-terminus has a double-psi beta barrel fold within the 3D domain, which forms the larger A domain along with the N-terminal region of Mlts, but is also found in various other domain architectures. Peptigoglycan (also known as murein) chains, the primary structural component of bacterial cells walls, are comprised of alternating beta-1-4-linked N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc); lytic transglycosylases (LTs) cleave this beta-1-4 bond. Typically, LTs are exolytic, releasing Metabolite 1 (GlcNAc-anhMurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu-m-Dap-D-Ala-D-Ala) from the ends of the PG strands. In contrast, membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase E (MltE) is endolytic , cleaving in the middle of PG strands, with further processing to Metabolite 1 accomplished by other LTs. In E. coli, there are six membrane- bound LTs: MltA-MltF and soluble Slt70. Slt35 is a soluble fragment cleaved from MltB. Bacterial LTs are classified in 4 families: Family 1 includes slt70 MltC-MltF, Family 2 includes MltA, Family 3 includes MltB, and family 4 of bacteriophage origin. While most LTs are related members of the lysozyme-like lytic transglycosylase family, MltA represents a distinct fold and sequence conservation. |
| cd14485 | mltA_like_LT_A | 5.66e-09 | 144 | 201 | 72 | 136 | Domain A of MltA and related lytic transglycosylase; domain A is interrupted by domain B. Escherichia coli MltA is a membrane-bound lytic transglycosylase comprised of two domains separated by a large groove, where the peptidoglycan strand binds. Domain A is made up of an N-terminal and a C-terminal portion, which correspond to the 3D domain, named for 3 conserved aspartate residues. Domain B is inserted within the linear sequence of domain A. MltA is distinct from other bacterial lytic transglycosylases (LTs), which are similar to each other. Escherichia coli peptidoglycan lytic transglycosylase (LT) initiates cell wall recycling in response to damage, during bacterial fission, and cleaves peptidoglycan (PG) to create functional spaces in its wall. PG chains (also known as murein), the major components of the bacterial cell wall, are comprised of alternating beta-1-4-linked N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), and lytic transglycosylases cleave this beta-1-4 bond. Typically, peptidoglycan lytic transglycosylases (LT) are exolytic, releasing Metabolite 1 (GlcNAc-anhMurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu-m-Dap-D-Ala-D-Ala) from the ends of the PG strands. In contrast, MltE is endolytic , cleaving in the middle of PG strands, with further processing to Metabolite 1 accomplished by other LTs. In E. coli, there are six membrane-bound LTs: MltA-MltF and soluble Slt70. Slt35 is a soluble fragment cleaved from MltB. Bacterial LTs are classified in 4 families: Family 1 includes slt70 MltC-MltF, Family 2 includes MltA, Family 3 includes MltB, and Family 4 of bacteriophage origin. While most of the LT family members are similar in structure and sequence with a lysozyme-like fold, Family 2 (including mltA) is distinct. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QSF42584.1 | 1.96e-148 | 1 | 223 | 1 | 223 |
| AIQ53037.1 | 1.23e-119 | 1 | 223 | 6 | 233 |
| AIQ47560.1 | 4.20e-119 | 1 | 223 | 1 | 228 |
| QQZ59982.1 | 2.66e-116 | 1 | 223 | 1 | 222 |
| CQR56193.1 | 1.54e-115 | 1 | 223 | 1 | 222 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4WLK_A | 1.53e-08 | 101 | 223 | 12 | 135 | StationaryPhase Survival Protein YuiC from B.subtilis complexed with reaction product [Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168],4WLK_B Stationary Phase Survival Protein YuiC from B.subtilis complexed with reaction product [Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168] |
| 4WJT_A | 1.55e-08 | 101 | 223 | 12 | 135 | StationaryPhase Survival Protein YuiC from B.subtilis complexed with NAG [Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168],4WJT_B Stationary Phase Survival Protein YuiC from B.subtilis complexed with NAG [Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168] |
| 4WLI_A | 7.47e-08 | 116 | 223 | 6 | 114 | StationaryPhase Survival Protein YuiC from B.subtilis [Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O34669 | 4.63e-11 | 120 | 222 | 193 | 286 | Cell wall-binding protein YocH OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=yocH PE=1 SV=1 |
| P37546 | 2.47e-10 | 81 | 222 | 278 | 406 | Putative cell wall shaping protein YabE OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=yabE PE=2 SV=2 |
| O32108 | 1.59e-07 | 101 | 223 | 63 | 186 | Uncharacterized protein YuiC OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=yuiC PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
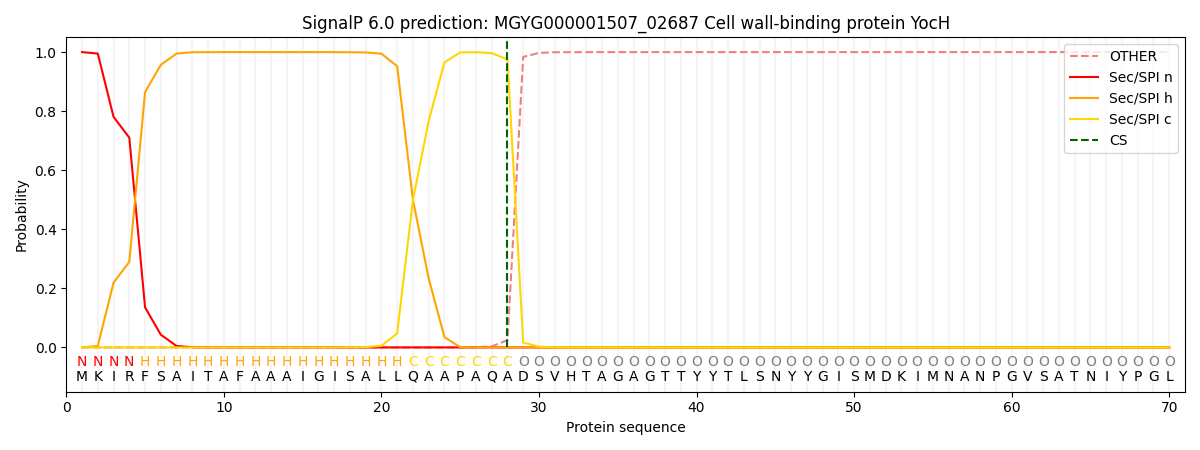
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000298 | 0.998891 | 0.000191 | 0.000229 | 0.000195 | 0.000171 |
