You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001292_01881
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001292_01881
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Bifidobacterium infantis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Actinobacteriota; Actinomycetia; Actinomycetales; Bifidobacteriaceae; Bifidobacterium; Bifidobacterium infantis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001292_01881 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT2 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 1942551; End: 1945598 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COG1216 | GT2 | 5.90e-10 | 16 | 306 | 5 | 275 | Glycosyltransferase, GT2 family [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| pfam09721 | Exosortase_EpsH | 1.10e-04 | 466 | 646 | 31 | 219 | Transmembrane exosortase (Exosortase_EpsH). Members of this family are designated exosortase, analogous to sortase in cell wall sorting mediated by LPXTG domains in Gram-positive bacteria. The phylogenetic distribution of the proteins in this entry is nearly perfectly correlated with the distribution of the proteins having the PEP-CTERM anchor motif, IPR013424. Members of this entry are integral membrane proteins with eight predicted transmembrane helices in common. Some members of this family have long trailing sequences past the region described by this model. This model does not include the region of the first predicted transmembrane region. The best characterized member is EpsH of Methylobacillus sp. 12S, where it is part of a locus associated with biosynthesis of the exopolysaccharide methanol-an. |
| cd04186 | GT_2_like_c | 6.69e-04 | 218 | 247 | 137 | 166 | Subfamily of Glycosyltransferase Family GT2 of unknown function. GT-2 includes diverse families of glycosyltransferases with a common GT-A type structural fold, which has two tightly associated beta/alpha/beta domains that tend to form a continuous central sheet of at least eight beta-strands. These are enzymes that catalyze the transfer of sugar moieties from activated donor molecules to specific acceptor molecules, forming glycosidic bonds. Glycosyltransferases have been classified into more than 90 distinct sequence based families. |
| pfam09594 | GT87 | 0.001 | 475 | 727 | 11 | 236 | Glycosyltransferase family 87. The enzymes in this family are glycosyltransferases. PimE is involved in phosphatidylinositol mannoside (PIM) synthesis, a major class of glycolipids in all mycobacteria. PimE is a polyprenol-phosphate-mannose-dependent mannosyltransferase that transfers the fifth mannose of PIM. The family also includes alpha(1-->3) arabinofuranosyltransferase, invloved in the synthesis of of mycobacterial arabinogalactan. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAJ69407.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 1015 | 17 | 1031 |
| VEG43156.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 1015 | 1 | 1015 |
| ALE10272.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 1015 | 17 | 1031 |
| QSP97359.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 1015 | 17 | 1031 |
| QTB92913.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 1015 | 17 | 1031 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000064 | 0.000001 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
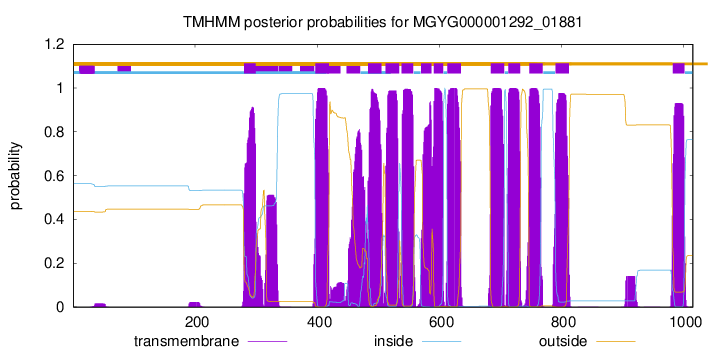
| start | end |
|---|---|
| 280 | 299 |
| 397 | 419 |
| 483 | 505 |
| 512 | 534 |
| 538 | 557 |
| 570 | 587 |
| 591 | 606 |
| 613 | 635 |
| 684 | 706 |
| 713 | 732 |
| 747 | 769 |
| 790 | 812 |
| 982 | 1001 |
