You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001100_01485
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001100_01485
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
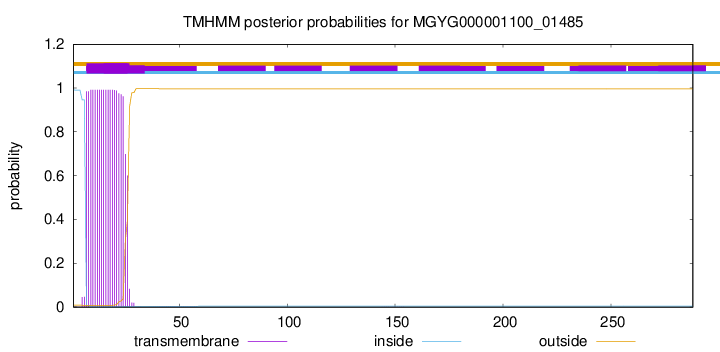
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Weissella viridescens | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Lactobacillales; Lactobacillaceae; Weissella; Weissella viridescens | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001100_01485 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE4 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine N-deacetylase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 1960; End: 2826 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE4 | 116 | 251 | 1.7e-22 | 0.8923076923076924 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd10965 | CE4_IcaB_5s | 4.43e-55 | 117 | 287 | 2 | 172 | Putative catalytic polysaccharide deacetylase domain of bacterial intercellular adhesion protein IcaB and similar proteins. The family is represented by the surface-attached protein intercellular adhesion protein IcaB (Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine N-deacetylase, EC 3.5.1.-), encoded by Staphylococcus epidermidis icaB gene from the icaABC gene cluster that is involved in the synthesis of polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA), which is located mainly on the cell surface. IcaB is a secreted, cell wall-associated protein that plays a crucial role in exopolysaccharide modification in bacterial biofilm formation. It catalyzes the N-deacetylation of poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (PNAG, also referred to as PIA), a biofilm adhesin polysaccharide. IcaB shows high homology to the N-terminal NodB homology domain of Escherichia coli PgaB. At this point, they are classified in the same family. |
| cd10918 | CE4_NodB_like_5s_6s | 1.92e-32 | 119 | 276 | 1 | 155 | Putative catalytic NodB homology domain of PgaB, IcaB, and similar proteins which consist of a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold with 5- or 6-strands. This family belongs to the large and functionally diverse carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily, whose members show strong sequence similarity with some variability due to their distinct carbohydrate substrates. It includes bacterial poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine N-deacetylase PgaB, hemin storage system HmsF protein in gram-negative species, intercellular adhesion proteins IcaB, and many uncharacterized prokaryotic polysaccharide deacetylases. It also includes a putative polysaccharide deacetylase YxkH encoded by the Bacillus subtilis yxkH gene, which is one of six polysaccharide deacetylase gene homologs present in the Bacillus subtilis genome. Sequence comparison shows all family members contain a conserved domain similar to the catalytic NodB homology domain of rhizobial NodB-like proteins, which consists of a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold with 6 or 7 strands. However, in this family, most proteins have 5 strands and some have 6 strands. Moreover, long insertions are found in many family members, whose function remains unknown. |
| cd10964 | CE4_PgaB_5s | 2.10e-25 | 118 | 275 | 4 | 190 | N-terminal putative catalytic polysaccharide deacetylase domain of bacterial poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine N-deacetylase PgaB, and similar proteins. This family is represented by an outer membrane lipoprotein, poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine N-deacetylase (PgaB, EC 3.5.1.-), encoded by Escherichia coli pgaB gene from the pgaABCD (formerly ycdSRQP) operon, which affects biofilm development by promoting abiotic surface binding and intercellular adhesion. PgaB catalyzes the N-deacetylation of poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (PGA), a biofilm adhesin polysaccharide that stabilizes biofilms of E. coli and other bacteria. PgaB contains an N-terminal NodB homology domain with a 5-stranded beta/alpha barrel, and a C-terminal carbohydrate binding domain required for PGA N-deacetylation, which may be involved in binding to unmodified poly-beta-1,6-GlcNAc and assisting catalysis by the deacetylase domain. This family also includes several orthologs of PgaB, such as the hemin storage system HmsF protein, encoded by Yersinia pestis hmsF gene from the hmsHFRS operon, which is essential for Y. pestis biofilm formation. Like PgaB, HmsF is an outer membrane protein with an N-terminal NodB homology domain, which is likely involved in the modification of the exopolysaccharide (EPS) component of the biofilm. HmsF also has a conserved but uncharacterized C-terminal domain that is present in other HmsF-like proteins in Gram-negative bacteria. This alignment model corresponds to the N-terminal NodB homology domain. |
| cd10973 | CE4_DAC_u4_5s | 5.93e-24 | 118 | 278 | 1 | 156 | Putative catalytic NodB homology domain of uncharacterized bacterial polysaccharide deacetylases which consist of a 5-stranded beta/alpha barrel. This family contains many uncharacterized bacterial polysaccharide deacetylases. Although their biological functions remain unknown, all members of the family are predicted to contain a conserved domain with a 5-stranded beta/alpha barrel, which is similar to the catalytic NodB homology domain of rhizobial NodB-like proteins, belonging to the larger carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. |
| pfam01522 | Polysacc_deac_1 | 3.33e-23 | 112 | 250 | 1 | 121 | Polysaccharide deacetylase. This domain is found in polysaccharide deacetylase. This family of polysaccharide deacetylases includes NodB (nodulation protein B from Rhizobium) which is a chitooligosaccharide deacetylase. It also includes chitin deacetylase from yeast, and endoxylanases which hydrolyzes glucosidic bonds in xylan. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QOD85501.1 | 2.64e-208 | 1 | 288 | 1 | 288 |
| QNN75287.1 | 1.72e-87 | 38 | 288 | 40 | 288 |
| ARE15354.1 | 1.98e-66 | 37 | 287 | 43 | 291 |
| ARE12944.1 | 1.98e-66 | 37 | 287 | 43 | 291 |
| ARE20276.1 | 1.98e-66 | 37 | 287 | 43 | 291 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4WCJ_A | 8.36e-33 | 31 | 286 | 19 | 259 | Structureof IcaB from Ammonifex degensii [Ammonifex degensii KC4] |
| 3VUS_A | 4.70e-08 | 80 | 285 | 27 | 262 | Escherichiacoli PgaB N-terminal domain [Escherichia coli K-12],3VUS_B Escherichia coli PgaB N-terminal domain [Escherichia coli K-12] |
| 4F9D_A | 9.26e-08 | 80 | 285 | 31 | 266 | Structureof Escherichia coli PgaB 42-655 in complex with nickel [Escherichia coli K-12],4F9D_B Structure of Escherichia coli PgaB 42-655 in complex with nickel [Escherichia coli K-12] |
| 4F9J_A | 9.26e-08 | 80 | 285 | 31 | 266 | Structureof Escherichia coli PgaB 42-655 in complex with iron [Escherichia coli K-12],4F9J_B Structure of Escherichia coli PgaB 42-655 in complex with iron [Escherichia coli K-12] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q6G606 | 9.66e-27 | 43 | 285 | 39 | 281 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine N-deacetylase OS=Staphylococcus aureus (strain MSSA476) OX=282459 GN=icaB PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q7A349 | 9.66e-27 | 43 | 285 | 39 | 281 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine N-deacetylase OS=Staphylococcus aureus (strain N315) OX=158879 GN=icaB PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q8NUI6 | 9.66e-27 | 43 | 285 | 39 | 281 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine N-deacetylase OS=Staphylococcus aureus (strain MW2) OX=196620 GN=icaB PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q9RQP7 | 9.66e-27 | 43 | 285 | 39 | 281 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine N-deacetylase OS=Staphylococcus aureus (strain NCTC 8325 / PS 47) OX=93061 GN=icaB PE=3 SV=2 |
| Q99QX2 | 9.66e-27 | 43 | 285 | 39 | 281 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine N-deacetylase OS=Staphylococcus aureus (strain Mu50 / ATCC 700699) OX=158878 GN=icaB PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.050622 | 0.944434 | 0.004017 | 0.000288 | 0.000279 | 0.000334 |