You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000815_01291
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000815_01291
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Dysgonomonas capnocytophagoides | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Dysgonomonadaceae; Dysgonomonas; Dysgonomonas capnocytophagoides | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000815_01291 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM35 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 237432; End: 239777 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd14791 | GH36 | 4.44e-09 | 287 | 566 | 3 | 278 | glycosyl hydrolase family 36 (GH36). GH36 enzymes occur in prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and archaea with a wide range of hydrolytic activities, including alpha-galactosidase, alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase, stachyose synthase, and raffinose synthase. All GH36 enzymes cleave a terminal carbohydrate moiety from a substrate that varies considerably in size, depending on the enzyme, and may be either a starch or a glycoprotein. GH36 members are retaining enzymes that cleave their substrates via an acid/base-catalyzed, double-displacement mechanism involving a covalent glycosyl-enzyme intermediate. Two aspartic acid residues have been identified as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, respectively. |
| pfam18962 | Por_Secre_tail | 2.39e-05 | 715 | 780 | 6 | 71 | Secretion system C-terminal sorting domain. Species that include Porphyromonas gingivalis, Fibrobacter succinogenes, Flavobacterium johnsoniae, Cytophaga hutchinsonii, Gramella forsetii, Prevotella intermedia, and Salinibacter ruber have on average twenty or more copies of this C-terminal domain, associated with sorting to the outer membrane and covalent modification. This domain targets proteins to type IX secretion systems and is secreted then cleaved off by a C-terminal signal peptidease. Based on similarity to other families it is likely that this domain adopts an immunoglobulin like fold. |
| cd14792 | GH27 | 2.84e-04 | 287 | 530 | 2 | 214 | glycosyl hydrolase family 27 (GH27). GH27 enzymes occur in eukaryotes, prokaryotes, and archaea with a wide range of hydrolytic activities, including alpha-glucosidase (glucoamylase and sucrase-isomaltase), alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase, and 3-alpha-isomalto-dextranase. All GH27 enzymes cleave a terminal carbohydrate moiety from a substrate that varies considerably in size, depending on the enzyme, and may be either a starch or a glycoprotein. GH27 members are retaining enzymes that cleave their substrates via an acid/base-catalyzed, double-displacement mechanism involving a covalent glycosyl-enzyme intermediate. Two aspartic acid residues have been identified as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, respectively. |
| TIGR04183 | Por_Secre_tail | 0.002 | 718 | 780 | 11 | 70 | Por secretion system C-terminal sorting domain. Species that include Porphyromonas gingivalis, Fibrobacter succinogenes, Flavobacterium johnsoniae, Cytophaga hutchinsonii, Gramella forsetii, Prevotella intermedia, and Salinibacter ruber average twenty or more copies of a C-terminal domain, represented by this model, associated with sorting to the outer membrane and covalent modification. |
| pfam17801 | Melibiase_C | 0.010 | 629 | 689 | 17 | 73 | Alpha galactosidase C-terminal beta sandwich domain. This domain is found at the C-terminus of alpha galactosidase enzymes. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EIY66649.1 | 8.07e-206 | 2 | 692 | 59 | 748 |
| QUT74114.1 | 3.65e-204 | 2 | 692 | 59 | 748 |
| BCI61924.1 | 1.12e-201 | 6 | 689 | 9 | 687 |
| QQY38591.1 | 2.27e-191 | 23 | 692 | 34 | 675 |
| ABR38452.1 | 2.27e-191 | 23 | 692 | 34 | 675 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
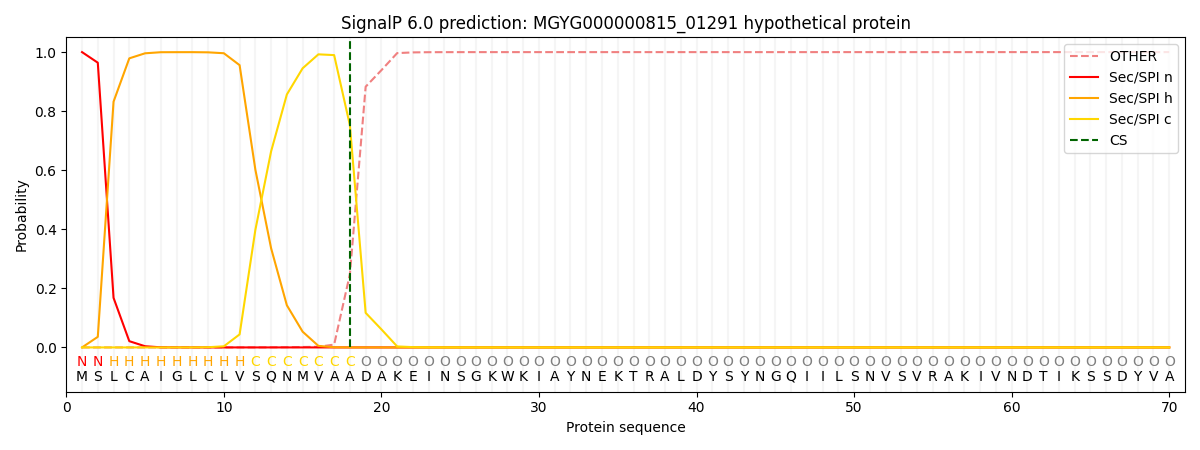
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000383 | 0.998960 | 0.000178 | 0.000165 | 0.000147 | 0.000140 |
