You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000287_01702
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000287_01702
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
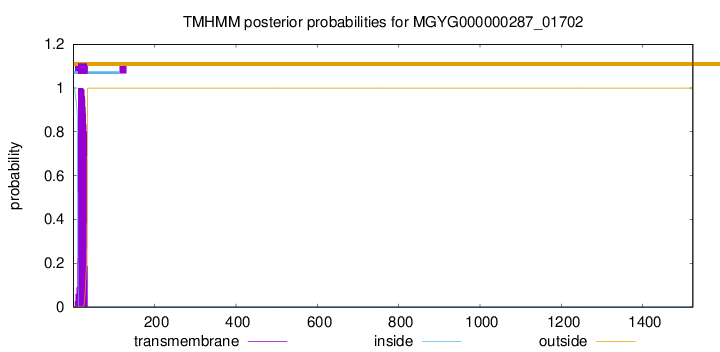
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Robinsoniella sp900539655 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; Lachnospiraceae; Robinsoniella; Robinsoniella sp900539655 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000287_01702 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH30 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 37044; End: 41615 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH30 | 690 | 1055 | 1.8e-18 | 0.709832134292566 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd14488 | CBM6-CBM35-CBM36_like_2 | 9.85e-31 | 186 | 311 | 1 | 129 | uncharacterized members of the carbohydrate binding module 6 (CBM6) and CBM35_like superfamily. Carbohydrate binding module family 6 (CBM6, family 6 CBM), also known as cellulose binding domain family VI (CBD VI), and related CBMs (CBM35 and CBM36). These are non-catalytic carbohydrate binding domains found in a range of enzymes that display activities against a diverse range of carbohydrate targets, including mannan, xylan, beta-glucans, cellulose, agarose, and arabinans. These domains facilitate the strong binding of the appended catalytic modules to their dedicated, insoluble substrates. Many of these CBMs are associated with glycoside hydrolase (GH) domains. CBM6 is an unusual CBM as it represents a chimera of two distinct binding sites with different modes of binding: binding site I within the loop regions and binding site II on the concave face of the beta-sandwich fold. CBM36s are calcium-dependent xylan binding domains. CBM35s display conserved specificity through extensive sequence similarity, but divergent function through their appended catalytic modules. |
| cd14488 | CBM6-CBM35-CBM36_like_2 | 2.49e-19 | 40 | 176 | 3 | 131 | uncharacterized members of the carbohydrate binding module 6 (CBM6) and CBM35_like superfamily. Carbohydrate binding module family 6 (CBM6, family 6 CBM), also known as cellulose binding domain family VI (CBD VI), and related CBMs (CBM35 and CBM36). These are non-catalytic carbohydrate binding domains found in a range of enzymes that display activities against a diverse range of carbohydrate targets, including mannan, xylan, beta-glucans, cellulose, agarose, and arabinans. These domains facilitate the strong binding of the appended catalytic modules to their dedicated, insoluble substrates. Many of these CBMs are associated with glycoside hydrolase (GH) domains. CBM6 is an unusual CBM as it represents a chimera of two distinct binding sites with different modes of binding: binding site I within the loop regions and binding site II on the concave face of the beta-sandwich fold. CBM36s are calcium-dependent xylan binding domains. CBM35s display conserved specificity through extensive sequence similarity, but divergent function through their appended catalytic modules. |
| COG5492 | YjdB | 1.34e-11 | 1073 | 1169 | 166 | 263 | Uncharacterized conserved protein YjdB, contains Ig-like domain [General function prediction only]. |
| pfam02368 | Big_2 | 2.13e-10 | 1090 | 1165 | 2 | 77 | Bacterial Ig-like domain (group 2). This family consists of bacterial domains with an Ig-like fold. Members of this family are found in bacterial and phage surface proteins such as intimins. |
| cd14256 | Dockerin_I | 2.05e-09 | 1458 | 1512 | 1 | 55 | Type I dockerin repeat domain. Bacterial cohesin domains bind to a complementary protein domain named dockerin, and this interaction is required for the formation of the cellulosome, a cellulose-degrading complex. The cellulosome consists of scaffoldin, a noncatalytic scaffolding polypeptide, that comprises repeating cohesion modules and a single carbohydrate-binding module (CBM). Specific calcium-dependent interactions between cohesins and dockerins appear to be essential for cellulosome assembly. This subfamily represents type I dockerins, which are responsible for anchoring a variety of enzymatic domains to the complex. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QKW09945.1 | 5.33e-133 | 610 | 1080 | 41 | 488 |
| ALN90629.1 | 7.58e-131 | 612 | 1080 | 30 | 480 |
| QWB27211.1 | 1.62e-121 | 607 | 1078 | 39 | 495 |
| AQQ08375.1 | 1.72e-117 | 610 | 1080 | 1471 | 1918 |
| AQQ08380.1 | 1.54e-116 | 610 | 1080 | 480 | 927 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6F2P_A | 5.82e-17 | 142 | 311 | 861 | 1034 | Structureof Paenibacillus xanthan lyase to 2.6 A resolution [Paenibacillus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9AQS0 | 1.78e-12 | 182 | 313 | 788 | 926 | Xanthan lyase OS=Bacillus sp. (strain GL1) OX=84635 GN=xly PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
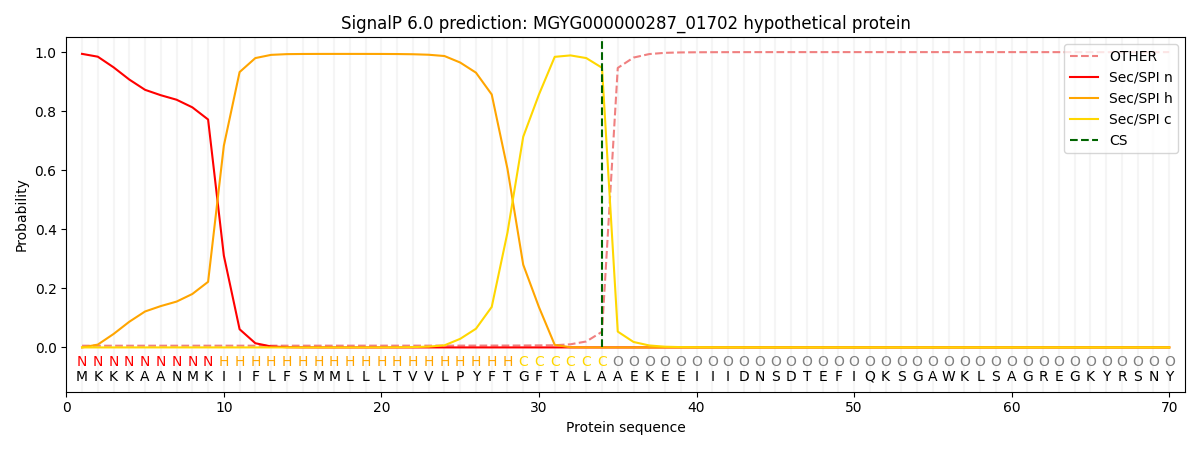
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.007371 | 0.991174 | 0.000567 | 0.000407 | 0.000235 | 0.000218 |