You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000217_02192
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000217_02192
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
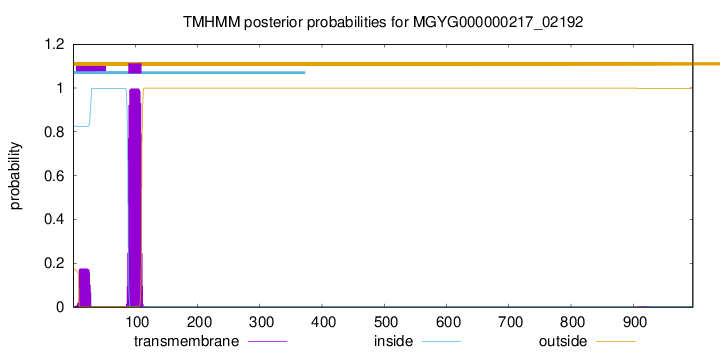
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Acetatifactor sp900066565 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; Lachnospiraceae; Acetatifactor; Acetatifactor sp900066565 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000217_02192 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT4 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | D-inositol-3-phosphate glycosyltransferase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 6430; End: 9420 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd03808 | GT4_CapM-like | 7.05e-82 | 615 | 982 | 2 | 351 | capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis glycosyltransferase CapM and similar proteins. This family is most closely related to the GT4 family of glycosyltransferases. CapM in Staphylococcus aureus is required for the synthesis of type 1 capsular polysaccharides. |
| pfam02397 | Bac_transf | 7.64e-76 | 84 | 261 | 1 | 179 | Bacterial sugar transferase. This Pfam family represents a conserved region from a number of different bacterial sugar transferases, involved in diverse biosynthesis pathways. |
| COG2148 | WcaJ | 2.93e-75 | 73 | 261 | 30 | 219 | Sugar transferase involved in LPS biosynthesis (colanic, teichoic acid) [Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis]. |
| TIGR03025 | EPS_sugtrans | 1.65e-63 | 80 | 261 | 254 | 438 | exopolysaccharide biosynthesis polyprenyl glycosylphosphotransferase. Members of this family are generally found near other genes involved in the biosynthesis of a variety of exopolysaccharides. These proteins consist of two fused domains, an N-terminal hydrophobic domain of generally low conservation and a highly conserved C-terminal sugar transferase domain (pfam02397). Characterized and partially characterized members of this subfamily include Salmonella WbaP (originally RfbP), E. coli WcaJ, Methylobacillus EpsB, Xanthomonas GumD, Vibrio CpsA, Erwinia AmsG, Group B Streptococcus CpsE (originally CpsD), and Streptococcus suis Cps2E. Each of these is believed to act in transferring the sugar from, for instance, UDP-glucose or UDP-galactose, to a lipid carrier such as undecaprenyl phosphate as the first (priming) step in the synthesis of an oligosaccharide "block". This function is encoded in the C-terminal domain. The liposaccharide is believed to be subsequently transferred through a "flippase" function from the cytoplasmic to the periplasmic face of the inner membrane by the N-terminal domain. Certain closely related transferase enzymes, such as Sinorhizobium ExoY and Lactococcus EpsD, lack the N-terminal domain and are not found by this model. |
| cd05232 | UDP_G4E_4_SDR_e | 5.55e-58 | 309 | 577 | 1 | 276 | UDP-glucose 4 epimerase, subgroup 4, extended (e) SDRs. UDP-glucose 4 epimerase (aka UDP-galactose-4-epimerase), is a homodimeric extended SDR. It catalyzes the NAD-dependent conversion of UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose, the final step in Leloir galactose synthesis. This subgroup is comprised of bacterial proteins, and includes the Staphylococcus aureus capsular polysaccharide Cap5N, which may have a role in the synthesis of UDP-N-acetyl-d-fucosamine. This subgroup has the characteristic active site tetrad and NAD-binding motif of the extended SDRs. Extended SDRs are distinct from classical SDRs. In addition to the Rossmann fold (alpha/beta folding pattern with a central beta-sheet) core region typical of all SDRs, extended SDRs have a less conserved C-terminal extension of approximately 100 amino acids. Extended SDRs are a diverse collection of proteins, and include isomerases, epimerases, oxidoreductases, and lyases; they typically have a TGXXGXXG cofactor binding motif. SDRs are a functionally diverse family of oxidoreductases that have a single domain with a structurally conserved Rossmann fold, an NAD(P)(H)-binding region, and a structurally diverse C-terminal region. Sequence identity between different SDR enzymes is typically in the 15-30% range; they catalyze a wide range of activities including the metabolism of steroids, cofactors, carbohydrates, lipids, aromatic compounds, and amino acids, and act in redox sensing. Classical SDRs have an TGXXX[AG]XG cofactor binding motif and a YXXXK active site motif, with the Tyr residue of the active site motif serving as a critical catalytic residue (Tyr-151, human 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase numbering). In addition to the Tyr and Lys, there is often an upstream Ser and/or an Asn, contributing to the active site; while substrate binding is in the C-terminal region, which determines specificity. The standard reaction mechanism is a 4-pro-S hydride transfer and proton relay involving the conserved Tyr and Lys, a water molecule stabilized by Asn, and nicotinamide. Atypical SDRs generally lack the catalytic residues characteristic of the SDRs, and their glycine-rich NAD(P)-binding motif is often different from the forms normally seen in classical or extended SDRs. Complex (multidomain) SDRs such as ketoreductase domains of fatty acid synthase have a GGXGXXG NAD(P)-binding motif and an altered active site motif (YXXXN). Fungal type ketoacyl reductases have a TGXXXGX(1-2)G NAD(P)-binding motif. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUO31262.1 | 0.0 | 2 | 996 | 5 | 1013 |
| VCV20929.1 | 1.58e-193 | 307 | 992 | 1 | 684 |
| QMW80818.1 | 3.90e-168 | 54 | 615 | 3 | 635 |
| QIB56408.1 | 3.90e-168 | 54 | 615 | 3 | 635 |
| QFJ56086.1 | 2.54e-122 | 612 | 992 | 2 | 375 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5W7L_A | 2.49e-33 | 79 | 261 | 6 | 184 | Structureof Campylobacter concisus PglC I57M/Q175M variant [Campylobacter concisus 13826],5W7L_B Structure of Campylobacter concisus PglC I57M/Q175M variant [Campylobacter concisus 13826] |
| 3C4Q_A | 2.38e-14 | 701 | 993 | 99 | 403 | Structureof the retaining glycosyltransferase MshA : The first step in mycothiol biosynthesis. Organism : Corynebacterium glutamicum- Complex with UDP [Corynebacterium glutamicum],3C4Q_B Structure of the retaining glycosyltransferase MshA : The first step in mycothiol biosynthesis. Organism : Corynebacterium glutamicum- Complex with UDP [Corynebacterium glutamicum],3C4V_A Structure of the retaining glycosyltransferase MshA:The first step in mycothiol biosynthesis. Organism: Corynebacterium glutamicum : Complex with UDP and 1L-INS-1-P. [Corynebacterium glutamicum],3C4V_B Structure of the retaining glycosyltransferase MshA:The first step in mycothiol biosynthesis. Organism: Corynebacterium glutamicum : Complex with UDP and 1L-INS-1-P. [Corynebacterium glutamicum] |
| 7EC2_A | 2.52e-14 | 688 | 980 | 203 | 478 | ChainA, Glycosyl transferase, group 1 family protein [Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus USA300],7EC2_B Chain B, Glycosyl transferase, group 1 family protein [Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus USA300] |
| 3C48_A | 2.54e-14 | 701 | 993 | 119 | 423 | Structureof the retaining glycosyltransferase MshA: The first step in mycothiol biosynthesis. Organism: Corynebacterium glutamicum- APO (OPEN) structure. [Corynebacterium glutamicum],3C48_B Structure of the retaining glycosyltransferase MshA: The first step in mycothiol biosynthesis. Organism: Corynebacterium glutamicum- APO (OPEN) structure. [Corynebacterium glutamicum] |
| 2IW1_A | 5.19e-14 | 803 | 957 | 177 | 333 | CrystalStructure of WaaG, a glycosyltransferase involved in lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis [Escherichia coli str. K-12 substr. W3110] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P71053 | 3.13e-60 | 613 | 996 | 3 | 372 | Putative glycosyltransferase EpsD OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=epsD PE=2 SV=1 |
| Q0P9D0 | 6.23e-35 | 79 | 261 | 2 | 179 | Undecaprenyl phosphate N,N'-diacetylbacillosamine 1-phosphate transferase OS=Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni serotype O:2 (strain ATCC 700819 / NCTC 11168) OX=192222 GN=pglC PE=1 SV=1 |
| P71062 | 2.32e-32 | 83 | 261 | 3 | 177 | Uncharacterized sugar transferase EpsL OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=epsL PE=2 SV=1 |
| P71241 | 3.06e-31 | 66 | 260 | 250 | 456 | UDP-glucose:undecaprenyl-phosphate glucose-1-phosphate transferase OS=Escherichia coli (strain K12) OX=83333 GN=wcaJ PE=1 SV=2 |
| Q56770 | 4.45e-29 | 79 | 261 | 288 | 477 | UDP-glucose:undecaprenyl-phosphate glucose-1-phosphate transferase OS=Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris OX=340 GN=gumD PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
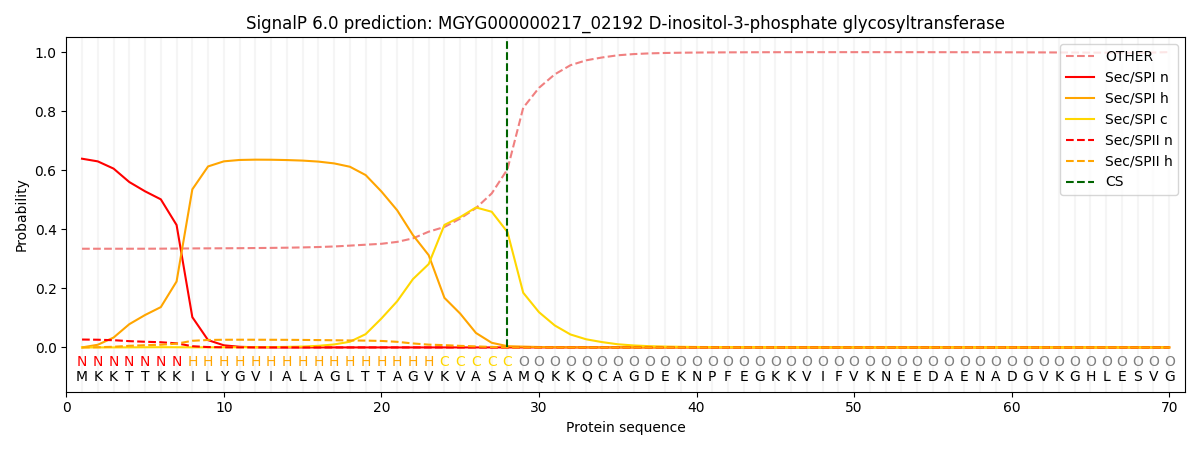
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.347369 | 0.622662 | 0.028445 | 0.000689 | 0.000357 | 0.000449 |