You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000053_00971
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000053_00971
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Alistipes sp002358415 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Rikenellaceae; Alistipes; Alistipes sp002358415 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000053_00971 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH38 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 254690; End: 258145 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH38 | 302 | 575 | 2.2e-17 | 0.9628252788104089 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd10791 | GH38N_AMII_like_1 | 6.95e-83 | 302 | 546 | 1 | 254 | N-terminal catalytic domain of mainly uncharacterized eukaryotic proteins similar to alpha-mannosidases; glycoside hydrolase family 38 (GH38). The subfamily of mainly uncharacterized eukaryotic proteins shows sequence homology with class II alpha-mannosidases (AlphaAMIIs). AlphaAMIIs possess a-1,3, a-1,6, and a-1,2 hydrolytic activity, and catalyze the degradation of N-linked oligosaccharides. The N-terminal catalytic domain of alphaMII adopts a structure consisting of parallel 7-stranded beta/alpha barrel. This subfamily belongs to the GH38 family of retaining glycosyl hydrolases, which employ a two-step mechanism involving the formation of a covalent glycosyl enzyme complex; two carboxylic acids positioned within the active site act in concert: one as a catalytic nucleophile and the other as a general acid/base catalyst. |
| pfam01074 | Glyco_hydro_38 | 7.81e-35 | 302 | 577 | 1 | 271 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 38 N-terminal domain. Glycosyl hydrolases are key enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism. |
| pfam14683 | CBM-like | 1.55e-17 | 29 | 192 | 1 | 157 | Polysaccharide lyase family 4, domain III. CBM-like is domain III of rhamnogalacturonan lyase (RG-lyase). The full-length protein specifically recognizes and cleaves alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds between l-rhamnose and d-galacturonic acids in the backbone of rhamnogalacturonan-I, a major component of the plant cell wall polysaccharide, pectin. This domain possesses a jelly roll beta-sandwich fold structurally homologous to carbohydrate binding modules (CBMs), and it carries two sulfate ions and a hexa-coordinated calcium ion. |
| cd10317 | RGL4_C | 7.37e-17 | 31 | 192 | 1 | 160 | C-terminal domain of rhamnogalacturonan lyase, a family 4 polysaccharide lyase. The rhamnogalacturonan lyase of the polysaccharide lyase family 4 (RGL4) is involved in the degradation of RG (rhamnogalacturonan) type-I, an important pectic plant cell wall polysaccharide, by cleaving the alpha-1,4 glycoside bond between L-rhamnose and D-galacturonic acids in the backbone of RG type-I through a beta-elimination reaction. RGL4 consists of three domains, an N-terminal catalytic domain, a middle domain with a FNIII type fold and a C-terminal domain with a jelly roll fold. Both the middle and the C-terminal domain are putative carbohydrate binding modules. There are two types of RG lyases, which both cleave the alpha-1,4 bonds of the RG-I main chain (RG chain) through the beta-elimination reaction, but belong to two structurally unrelated polysaccharide lyase (PL) families, 4 and 11. |
| cd10786 | GH38N_AMII_like | 2.93e-11 | 302 | 482 | 1 | 179 | N-terminal catalytic domain of class II alpha-mannosidases and similar proteins; glycoside hydrolase family 38 (GH38). Alpha-mannosidases (EC 3.2.1.24) are extensively found in eukaryotes and play important roles in the processing of newly formed N-glycans and in degradation of mature glycoproteins. A deficiency of this enzyme causes the lysosomal storage disease alpha-mannosidosis. Many bacterial and archaeal species also possess putative alpha-mannosidases, but their activity and specificity is largely unknown. Based on different functional characteristics and sequence homology, alpha-mannosidases have been organized into two classes (class I, belonging to glycoside hydrolase family 47, and class II, belonging to glycoside hydrolase family 38). Members of this family corresponds to class II alpha-mannosidases (alphaMII), which contain intermediate Golgi alpha-mannosidases II, acidic lysosomal alpha-mannosidases, animal sperm and epididymal alpha -mannosidases, neutral ER/cytosolic alpha-mannosidases, and some putative prokaryotic alpha-mannosidases. AlphaMII possess a-1,3, a-1,6, and a-1,2 hydrolytic activity, and catalyzes the degradation of N-linked oligosaccharides. The N-terminal catalytic domain of alphaMII adopts a structure consisting of parallel 7-stranded beta/alpha barrel. Members in this family are retaining glycosyl hydrolases of family GH38 that employs a two-step mechanism involving the formation of a covalent glycosyl enzyme complex. Two carboxylic acids positioned within the active site act in concert: one as a catalytic nucleophile and the other as a general acid/base catalyst. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBL07455.1 | 0.0 | 2 | 1148 | 3 | 1148 |
| BBL10048.1 | 0.0 | 8 | 1147 | 7 | 1146 |
| BBL12841.1 | 0.0 | 8 | 1147 | 7 | 1146 |
| BBL02110.1 | 0.0 | 8 | 1147 | 7 | 1146 |
| ALJ40506.1 | 0.0 | 30 | 1147 | 27 | 1138 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
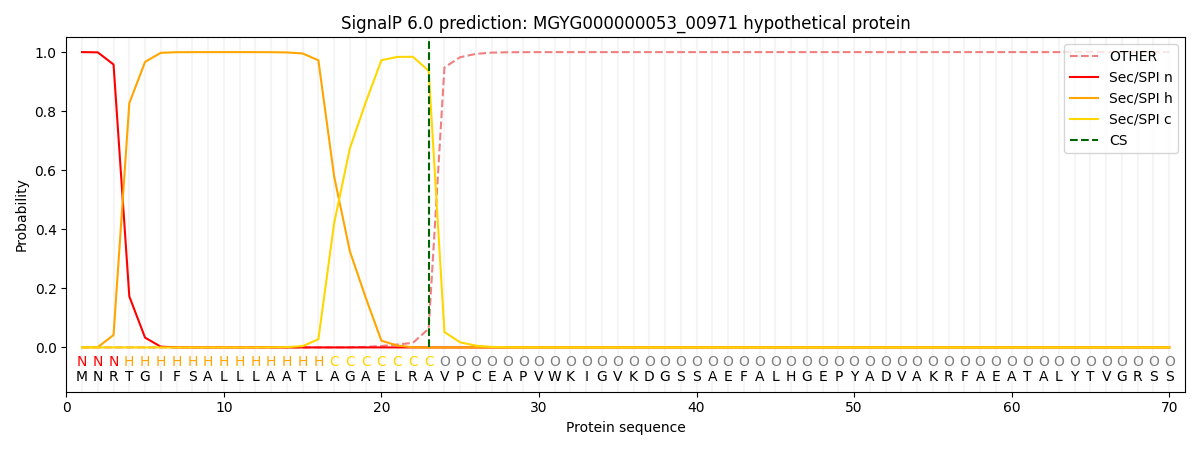
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000321 | 0.998886 | 0.000282 | 0.000184 | 0.000155 | 0.000143 |
